EDITORIAL
This article briefly presents a perspective on the usage of the commonly accepted terms — “urethral stricture” and “urethral stricture disease”. The author offers a considered opinion on the correctness of employing these medical terms in various clinical contexts.
The May 2025 updates to the American Urological Association (AUA) and the Society for Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Microhaematuria (MH) Guideline 2020 have been published. The updates are based on the latest publications of the last five years and mainly address diagnostic programmes for bladder, upper urinary tract and renal parenchyma cancers. The importance of urinary markers, endoscopy, ultrasound and MRI to improve the diagnostic capabilities of tumour diseases is evaluated.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. COVID-19 has been associated with both acute and chronic extrapulmonary complications, including renal dysfunction. Understanding the long-term effects of COVID-19 on renal function is essential for managing recovery in affected individuals.
Objective. This study aimed to evaluate the long-term renal outcomes in patients who recovered from COVID-19, focusing on changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine levels in Iran.
Materials & methods. A retrospective cohort study was conducted using data from the Mashhad University of Medical Sciences cohort. The study included patients who had confirmed COVID-19 and a minimum follow-up period of six months post-recovery. Renal function was assessed by measuring the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine levels both at baseline (when COVID-19 was initially diagnosed) and at follow-up. Statistical analysis was performed to explore the associations between renal outcomes and various factors, including gender, the severity of COVID-19, and blood pressure status.
Results. In the study, 55.3% were male, and the mean age of 51.38 ± 13.41. Among the patients, 55.3% were male and 44.7% were female. The difference in mean creatinine level between baseline and follow-up was significant (p < 0.001). The difference in mean GFR between baseline and follow-up was significant (p < 0.001). In men, the mean blood urea nitrogen at the first visit and at the follow-up difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.241). In women, the mean blood urea nitrogen was a statistically significant decrease (p = 0.003). Other parameters, including creatinine and GFR, did not differ significantly in both male and female groups at the time of hospitalization and follow-up.
Conclusion. Overall, the results of this study suggest that COVID-19 can affect kidney function, especially in association with underlying factors such as hypertension and diabetes, and female gender, which may be risk factors for more severe renal complications in patients with COVID-19. The decrease in GFR in patients with hypertension and diabetes highlights the importance of controlling these diseases in patients with COVID-19. Overall, this study showed that COVID-19 can have lasting effects on patients' kidney function.
Introduction. Various surgical methods for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) effectively alleviate voiding symptoms and improve urinary flow quality. However, patient satisfaction often decreases due to the persistence of storage symptoms following surgical intervention.
Objective. To determine the prevalence of persistent storage symptoms and overactive bladder (OAB), optimal approaches to the treatment of symptoms after surgical treatment of BPH in clinical practice.
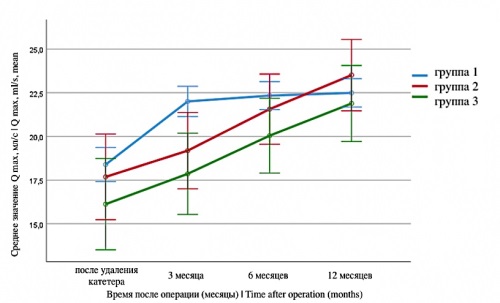
Materials & methods. The study included 94 patients aged 53 – 79 years who underwent surgery for BPH, with persistent storage symptoms in 1 – 3 months after surgery (IPSS-storage score ≥ 3). The patients underwent urodynamic examination. In the case of persistent symptoms without confirmed OAB, behavioral therapy was performed (group 1). In case of detrusor overactivity («dry» OAB), patients were prescribed medication solifenacin 5 mg daily (group 2), in case of terminal detrusor overactivity, urgent urinary incontinence («wet» OAB), combination therapy solifenacin 5 mg + mirabegron 50 mg (group 3) was prescribed.
Results. Patient characteristics in the preoperative period showed no statistically significant differences between groups regarding age, urodynamic parameters, and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) as assessed by the IPSS questionnaire. At the initiation of therapy, the median storage symptom scores were 4, 8, and 9 points in groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Both the behavioral and pharmacological therapy groups demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in the severity of storage symptoms over time (p < 0.001). After 12 weeks, the median storage symptom scores were 3 points in group 1, 4 points in group 2, and 6 points in group 3. Urgent incontinence was eliminated in group 3 after treatment. By 12 months after surgical treatment and drug therapy, the irritative symptoms and the number of nocturia episodes approach equal values in all groups (p > 0.05). Patients from the drug therapy groups showed high adherence to therapy, among them there were no significant side effects requiring discontinuation of therapy.
Conclusion. The use of pharmacological therapy with M-cholinergic antagonists and/or β3-adrenoceptor agonists in the postoperative period in patients with confirmed detrusor overactivity contributes to a reduction in urgency symptoms and enhances patient treatment satisfaction. In the absence of detrusor overactivity or with an IPSS storage score ≤ 6, behavioral therapy represents a viable alternative to pharmacological treatment.
Introduction. Autoimmune reactions against spermatozoa represent a recognized cause of male infertility. The presence of antisperm antibodies (ASAs) can lead to reduced sperm motility, impaired capacitation and acrosome reaction, as well as increased sperm DNA fragmentation. However, current WHO guidelines do not establish definitive diagnostic criteria for «male immune infertility.» Instead, they recommend developing regional reference ranges based on the 5th to 95th percentile values derived from fertile men populations.
Objective. To establish reference ranges for the percentage of ASAs-IgG-positive spermatozoa in fertile Russian men in order to enhance the clinical and economic effectiveness of infertility management in couples.
Materials & Methods. The study is an observational, multicenter, cross-sectional, retrospective analysis. Antisperm antibodies (ASAT) on spermatozoa were assessed using the mixed antiglobulin reaction (“MAR-IgG”) method recommended by the WHO (“FertiPro”, Beernem, Belgium). A cohort of fertile men (n = 358) was selected based on the following criteria: 1) their partners achieved pregnancy (hCG > 100 mIU/ml and/or ultrasound confirmation of a gestational sac) occurring naturally within 12 months after discontinuation of contraception, with the semen analysis performed within 3 months of conception at a specialized andrology laboratory; 2) absence of any specific treatment for at least 3 months prior to the date of conception. Two subgroups were identified: subgroup 1 (n = 255), in which semen volume, concentration, motility, and morphology met the WHO 2021 reference ranges; and subgroup 2 (n = 337), in which these parameters corresponded to Russian regional reference criteria (Bozhedomov et al., 2023).
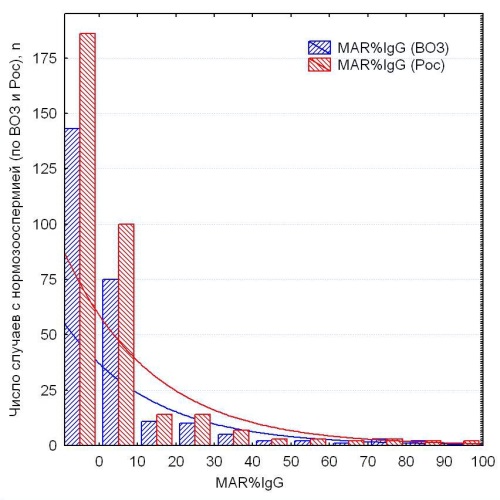
Results. In the cohort of fertile men (n = 358), MAR-IgG test results ranged from 0 to 100%, with a median of 0% and the 5th to 95th percentiles spanning 0% to 40%. MAR-IgG levels exceeding 40% were observed in 4.5% of cases (16 out of 358). Within subgroup 1, all instances of MAR-IgG > 10% were identified as statistical outliers based on the standard English “non-outlier range,” with the 95th percentile at 36%. According to the Russian reference criteria, MAR-IgG values above 12% and the 95th percentile of 40% were considered outliers. No statistically significant differences were found between subgroups 1 and 2 regarding distribution patterns and frequency of cases exceeding these thresholds (p > 0.05).
Conclusion. In Russian men, the proportion of IgG-positive progressively motile spermatozoa should not exceed 12%. When this proportion ranges from 13% to 40%, an immune-mediated contribution to infertility is considered probable. Pregnancy is statistically unlikely when more than 40% of progressively motile spermatozoa are IgG-positive, even in the presence of normozoospermia, indicating a threshold for clinically significant immune infertility.
Introduction. The importance of urethroscopy in the diagnosis of urethral stricture has been underestimated recently due to the priority in favor of urethrography. However, this method allows us to identify various aspects of urethral stricture, which can significantly affect the choice of the extent of surgical intervention.
Objective. To evaluate the diagnostic capabilities of urethroscopy and the outcomes of treatment strategies selected based on its findings in patients with urethral stricture.
Materials & methods. The study included seven men with short stricture (less than 20 mm) of the bulbous urethra, who were treated by removing fibrinous tissues of the urethra during urethroscopy. The age of the patients ranged from 19 to 73 years with a mean value of 44.6 ± 19.4 years. The length of the stricture according to retrograde urethrography ranged from 0.5 to 1.5 cm with a mean value of 1.0 ± 0.3 cm. In 4 patients (57.1%), the urethral stricture was primary, in 3 (42.9%) it was recurrent. Cystostomy drainage was present in four patients (57.1%). Ureteroscopy was performed using a standard technique using a ureteroscope 9.5 Ch, during which the nature of the changes in the mucosa and the degree of narrowing of the urethral lumen were examined. Next, the possibility of easy (without applying strong pressure) separation of fibrin adhesions from the urethral wall using a ureteroscope was assessed. The instrument was then removed and a urethral silicone catheter 18 Ch was installed for 21 days.
Results. In all patients, fibrin membranes (n = 5) or cords (n = 2) were found in the bulbar urethra during urethroscopy, which almost completely blocked the lumen of the urethra in this area. At the same time, no annular (true) narrowing of the urethra was noted in this area, which is typical for spongiofibrosis or true damage to the urethral mucosa. Fibrin membranes and cords had a thin layer and a loose structure, which made it possible to pass an endourological guidewire through them. After this, with a smooth movement of the ureteroscope, it was easy to remove fibrin adhesions along the entire perimeter of the urethral wall in all patients, since they had a loose nature of connections with the urethral mucosa. In none of the observations was cold or laser dissection of fibrin fibers or the urethral wall itself performed in this area, and during removal of fibrin tissues with an endoscope, there was no rupture of the urethral mucosa. After release from fibrin adhesions, the urethral wall had good elasticity, which allowed free passage of a Foley 18 Ch catheter. The duration of the manipulation ranged from 5 to 10 minutes and averaged 7.6 ± 1.7 minutes. The follow-up periods after treatment of patients varied from 8 to 24 months with a mean value of 13.6 ± 5.3 months. No complications during or after the manipulation, as well as recurrence of urethral stricture during the entire observation period were noted in any patient.
Conclusions. Urethroscopy examination reveals many cases of urethral stricture that can be corrected without urethroplasty or internal urethrotomy. Therefore, it is advisable to use urethroscopy examination more actively in patients with urethral stricture.
Introduction. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are diseases associated with morphological changes in prostate tissue, which have a proven hormone-dependent pathogenesis. The identification of risk factors for the development of these diseases and the development of an etiological prevention concept are important clinical objectives.
Objective. To assess male sexuality (sexual constitution) as a potential risk factor for BPH or PCa.
Materials & methods. The study included 47 men (Group 1) aged 49 – 71 years with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) caused by BPH, as well as 87 patients aged 47 – 70 years with a newly diagnosed PCa T 1c-3b N 0-1 M 0-1a. The main laboratory and instrumental parameters (PSA, testosterone, prostate volume) were studied, and an assessment and grading of male sexuality throughout life were conducted using the Rostov Questionnaire.
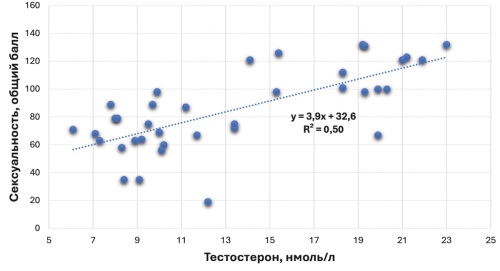
Results. Among men with BPH, individuals with hypo-, normo-, and hypersexuality are found with approximately equal frequency, while PCa patients are hyposexual in 90.8% of cases, with only 9.2% being normosexual. In the BPH patient group, there is a direct statistically significant relationship between sexuality and testosterone levels, ranging from moderate (total score at the time of diagnosis) to high (early and middle stages of sexual life), p < 0.001. In PCa patients, no relationship between testosterone and sexuality was established (p > 0.05). The identification of the relationship between male sexuality and prostate diseases allowed for the evaluation of three logistic regression models predicting the development of BPH or PCa depending on the level of male sexuality.
Conclusion. Male sexual constitution is a risk factor for the development of BPH and PCa. All three variants of male sexual constitution correlate with blood testosterone levels in BPH, while such correlation is absent in PCa. Numerical values of male sexuality, prostate volume levels, and blood PSA allow determining the likelihood of detecting BPH or PCa in a patient.
Introduction. A novel drug based on a somatostatin-containing protein is being developed for use in female and male infertility to increase the reproductive capacity, activate ovarian reserve follicles and their entry into the growth phase, accelerate the growth of resting follicles, increase the volume of ejaculate and improve the sperm quality characteristics.
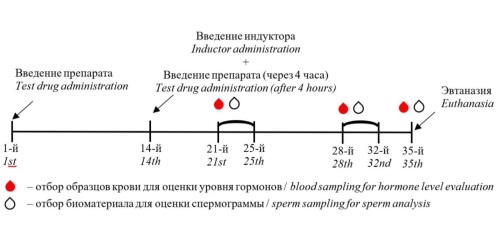
Objective. To evaluate the efficacy of a somatostatin-containing protein-based drug in a rat model of spermatogenesis disorder induced by a single injection of 600 µg/kg leuprorelin.
Materials & methods. The study evaluated several factors, including microscopic changes in testicular tissue, mass ratios of reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles), semen parameters, and serum testosterone and somatotropin levels.
Results. It was demonstrated that in the context of gonadotropin reduction and subsequent testosterone decline resulting from prolonged exposure to leuprorelin, the tested preparation, comprising a somatostatin-containing protein in a dosage range of 10 to 250 µg/kg, led to an increase in somatotropin and testosterone levels and the normalization of the spermatogenesis process. It was observed that the studied preparation resulted in a notable elevation in the concentration and proportion of motile spermatozoa.
Conclusion. The obtained results are consistent with previously published data demonstrating improved spermatogenesis parameters following administration of exogenous somatotropic hormone in animal models. This allows us to hypothesize a potential mechanism of action for the tested drug, namely the synthesis of specific autoantibodies against somatostatin and subsequent blockade of its activity, which in turn leads to increased endogenous levels of somatotropic and sex hormones in the organism.
Introduction. Bladder cancer is one of the most prevalent malignancies, characterized by high rates of recurrence and progression—even in its superficial forms, such as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Recent research has increasingly focused on the molecular and genetic profiles of these tumors, as these factors, together with tumor grade and stage, play a crucial role in determining disease prognosis.
Objective. To investigate the impact of molecular genetic subtypes in NMIBC on disease prognosis and assess the feasibility of their evaluation in routine clinical practice.
Materials & methods. We conducted a retrospective study that included 162 patients with newly diagnosed primary NMIBC treated at the University Urology Clinic between 2011 and 2021. Subsequently, an IHC study of postoperative material from patients with antibodies to GATA3, CK5/6 and FOXA1 was carried out. Subsequently, patients were monitored, and the percentage of relapses and progressions was assessed depending on the molecular genetic subtype. The median follow-up was 36 months.
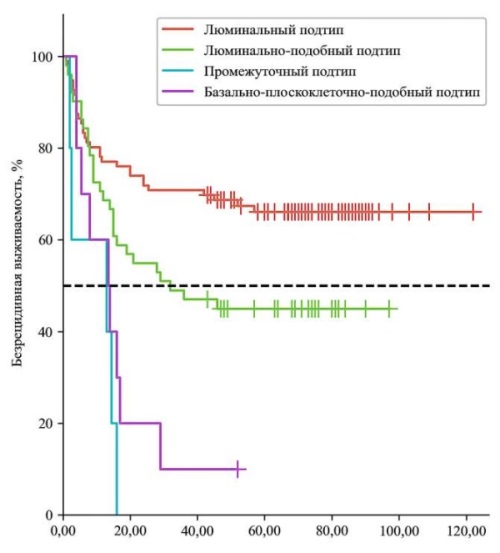
Results. Based on IHC results, tumors were classified into four subtypes: luminal (96; 59.3%), luminal-like (51; 31.5%), intermediate (5; 3.1%), and basal-squamous-like (10; 6.2%). During follow-up, recurrence and progression rates differed significantly between groups. Luminal tumors exhibited low recurrence (33.3%) and progression rates (2.1%), while luminal-like tumors showed higher recurrence (54.9%) but maintained low progression risk (5.9%). In contrast, intermediate and basal-squamous-like subtypes were associated with aggressive behavior: both demonstrated high recurrence rates (100% and 90.0%, respectively) and elevated progression risk (25.0% and 50.0%, respectively) (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. Basal-squamous-like tumors demonstrate the worst prognosis in terms of disease recurrence and progression, necessitating more aggressive treatment, whereas luminal tumors are associated with the most favorable outcomes.
Introduction. The comprehensive analysis of prognostic factors influencing survival outcomes in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and metastatic lymph node (LN) involvement represents a critical component for evidence-based decision-making in clinical practice and the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Objective. To systematically identify and evaluate prognostic factors impacting overall survival (OS) in patients diagnosed with lymph node metastases of renal cell carcinoma.
Materials & methods. A comprehensive retrospective analysis was conducted on a cohort of 332 patients with RСС metastases to LN, who received treatment at the Moscow City Oncological Hospital No. 62 and St. Petersburg City Clinical Oncological Dispensary between 2006 and 2022. The patient population was stratified into prognostic groups as follows: 110 patients (33.0%) were categorized into the intermediate prognosis group, while 160 patients (48.0%) were classified into the unfavourable prognosis group. The study systematically evaluated clinical and morphological prognostic factors that potentially influence OS indices in patients with RCC metastases to LN.
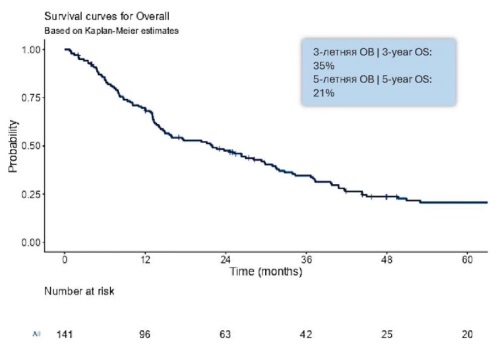
Results. The 3-year and 5-year OS rates in patients with RCC metastases to LN (n = 332) were 35% (95% CI 27 to 44) and 21% (95% CI 15 to 29), respectively, with a median OS of 21.9 months (95% CI 14.9 to 29.9). Univariate analysis revealed several factors with a statistically significant negative impact on OS in patients with RCC metastases to LN: 1) ECOG performance status (p < 0.001), tumour histological subtype (p < 0.001), tumour differentiation according to Fuhrman grading (p < 0.001), type of metastases (p < 0.001), bone metastases (p = 0.001), liver metastases (p < 0.001), IMDC prognostic score (p < 0.001), nephrectomy (p < 0.001), metastasectomy (p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis identified the following independent predictors of poor OS: tumour histological subtype (OR 1.50; 95% CI 1.01 to 2.23), tumour differentiation grade according to Fuhrman (OR 1.74; 95% CI 1.00 to 3.03), IMDC prognostic score (OR 2.60; 95% CI 1.46 to 4.62), nephrectomy (OR 2.39; 95% CI 1.51 to 3.79), metastasectomy (OR 0.61; 95% CI 0.39 to 0.95).
Conclusion. In patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) metastases to lymph nodes, several key factors have been identified as adverse predictors of survival: histological subtype of RCC, degree of tumour differentiation according to Fuhrman grading, IMDC prognostic score, nephrectomy, metastasectomy. These findings underscore the necessity for further comprehensive research to elucidate additional prognostic factors. Such investigations are essential for enhancing the efficacy of personalized treatment strategies and ultimately improving OS outcomes in patients with RCC.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of newly diagnosed cases of prostate cancer (PCa). Radical prostatectomy (RPE) remains the gold standard treatment for localized forms of the disease. With rapid technological advancements, surgical techniques have evolved from the classical RPE to robot-assisted approaches. However, despite improvements in surgical outcomes and reductions in mortality rates associated with PCa, adverse effects such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction remain significant concerns. These complications substantially impact patients' psycho-emotional well-being, leading to increased levels of anxiety and depression, and often necessitate lifestyle modifications characterized by reduced social and daily activity. This study presents a review and analysis of literature sourced from both domestic and international databases, including the Federal Electronic Medical Library, eLIBRARY, and PubMed. The research focused on current data regarding PCa worldwide, as well as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction following RPE, and their effects on the psychological health of patients.
Introduction. Distal urethral strictures account for up to 18% of anterior urethral narrowing and are frequently linked to lichen sclerosus, iatrogenic trauma, or failed hypospadias repair, causing marked voiding dysfunction and reduced quality of life. The absence of unified guidelines for selecting the optimal management strategy necessitates a critical analysis of the accumulated data. This systematic review with network meta-analysis summarises the current evidence base regarding the efficacy and safety of surgical and endoscopic approaches for strictures of the glans urethra.
Objective. To assess the efficacy and safety of various treatments for distal urethral strictures (glandular urethra, navicular fossa, and external urethral meatus) through a systematic review and meta-analysis, including a network meta-analysis.
Materials & methods. A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library following PRISMA guidelines. Studies reporting recurrence rates, patient satisfaction, complication rates, and long-term efficacy of different treatments, including meatotomy, one-stage and two-stage urethroplasty, and minimally invasive methods (dilation, urethrotomy), were included.
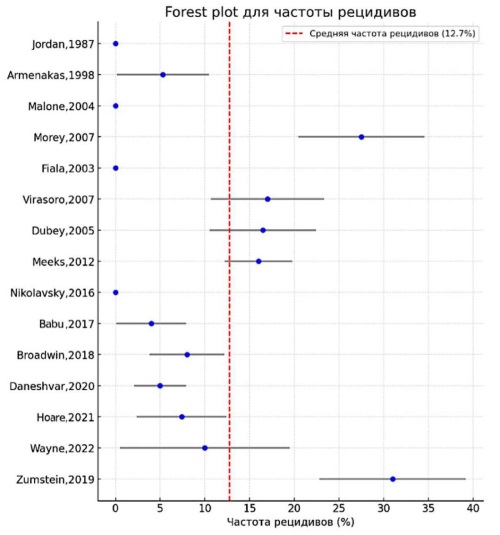
Results. The analysis included 15 studies with a total of 422 patients. The average recurrence rate after minimally invasive treatment (dilation, urethrotomy) was 60 – 80%, while after reconstructive surgery (urethroplasty), it was 10 – 15% (OR 10; 95% CI 5 – 20). Patient satisfaction exceeded 90% after urethroplasty. The network meta-analysis showed that two-stage and one-stage BMG urethroplasty were the most effective methods, with a success probability > 90%. Minimally invasive techniques had significantly lower long-term effectiveness (SUCRA ≤ 30%).
Conclusion. Surgical reconstruction is the preferred treatment method for glandular urethral strictures. Both two-stage and single-stage urethroplasty provide the best long-term outcomes, whereas meatotomy may be an option for limited strictures. Endoscopic treatment is associated with a high recurrence rate and should be reserved for select cases only.
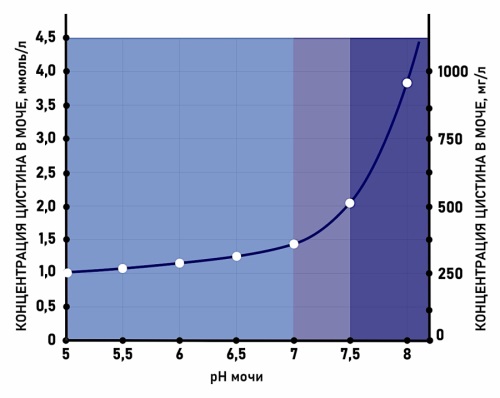
Introduction. Cystinuria is a rare genetic disorder characterised by a markedly elevated concentration of cystine in the urine. Due to the low solubility of cystine in urine, patients with cystinuria face a lifelong increased risk of urinary stone formation. The exceptionally high recurrence rate necessitates the implementation of preventive measures. Given that most practising urologists have limited experience managing patients with cystine nephrolithiasis due to the disease’s rarity, the development of clinical guidelines for recurrence prevention represents a pressing need.
Objective. To summarize the world literature on managing patients with cystine nephrolithiasis and present an algorithm for preventing the disease.
Materials & methods. A systematic review of the literature in foreign and domestic scientific databases was conducted using the keywords: “cystine”, “cystine stones”, “cystinuria”, “cystine”, “cystine nephrolithiasis”, “cystinuria”. Two hundred forty-seven sources of literature were processed, 45 of which were included in the review.
Results. Despite the currently irreversible genetic cause of cystinuria, the implementation of stone prevention strategies significantly reduces the recurrence rate of urolithiasis in affected patients. Prevention of cystine nephrolithiasis involves a multimodal, stepwise treatment approach. This includes reducing urinary cystine concentration through dietary modifications and increasing its solubility by alkalinising the urine, as well as the use of cystine-binding agents. This article presents a step-by-step algorithm for the prevention of cystine nephrolithiasis, based on the clinical course of the disease and objective parameters such as 24-hour cystine excretion and urinary pH.
Conclusion. Current algorithms for preventing cystine nephrolithiasis, which combine both non-pharmacological and pharmacological strategies, are readily applicable in clinical practice and have been shown to effectively reduce the recurrence of this condition.
One of the contemporary methods for treating kidney stones up to 2 cm in size is retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS). Advances in technology and the development of new techniques have expanded the indications for RIRS. The use of ureteral access sheaths is not mandatory; however, there are several reasons why urologists commonly employ them, including facilitating repeated and safe access to the kidney, reducing intrarenal pressure, minimizing the risk of instrument damage, and decreasing the likelihood of ureteral wall trauma during stone extraction. This literature review presents findings from studies demonstrating the safety and efficacy of ureteral access sheaths in RIRS for patients with kidney stones up to 2 cm. Parameters assessed included characteristics of the ureteral sheaths, operative time, stone-free rate, intra- and postoperative complications, as well as the impact of the sheath on the ureteral wall. The review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA protocol (http://www.prisma-statement.org) applicable to this type of study (ID-423604). Articles published in international databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus were analyzed.
CLINICAL CASES
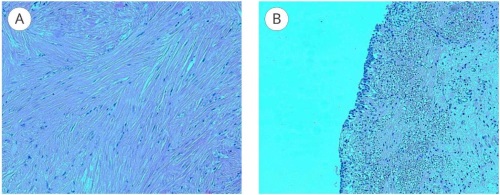
Introduction. Most bladder tumors are represented by transitional cell carcinoma, while leiomyomas account for less than 0.5% of cases. The extreme rarity of this mesenchymal tumor leads to diagnostic challenges and the absence of unified treatment protocols. The management strategy depends on the location and size of the lesion.
Objective. To describe the surgical technique and clinical features of bladder leiomyoma in a female patient.
Case presentation. We report a clinical case of a 65-year-old woman diagnosed with bladder leiomyoma. Ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, and urine cytology were performed for diagnosis. The patient underwent transurethral laser enucleoresection using a U-max thulium fiber laser. The operation lasted 35 minutes without intraoperative complications. In the early postoperative period, following the removal of the urethral catheter, the patient developed voiding difficulties, subfebrile fever, and pelvic pain syndrome, requiring repeat bladder catheterization. Histological examination confirmed the diagnosis of bladder leiomyoma.
Clinical discussion. Bladder leiomyoma is a benign mesenchymal tumor. The absence of standardized treatment guidelines necessitates an individualized therapeutic approach. Various surgical options have been described, but transurethral resection remains the primary method. Endoscopic intervention is minimally invasive, provides shorter hospital stays, and promotes rapid rehabilitation. In cases of pronounced extravesical growth, open or laparoscopic resection is preferable due to the risk of intraoperative bladder perforation.
Conclusion. The presented clinical case demonstrates that transurethral laser enucleoresection is an effective and safe method for bladder leiomyoma treatment, ensuring complete removal with minimal trauma. Early comprehensive diagnostics and individualized surgical management result in a favorable prognosis for this rare pathology.
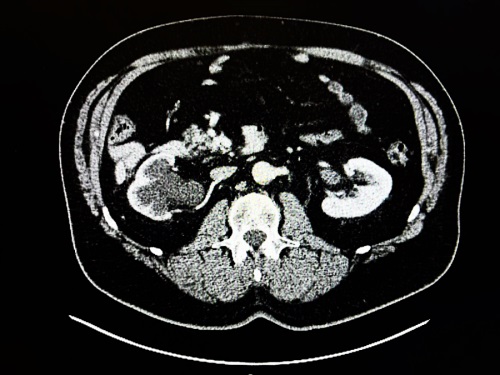
Hydronephrotic transformation can result from external compression of the uretero-pelvic junction by a tumor. Without timely intervention, this may lead to irreversible loss of renal parenchyma. Retroperitoneal liposarcoma is one potential cause of such compression. This article presents a clinical case highlighting the progression of the condition and explores surgical treatment options. Special emphasis is placed on evaluating various operative approaches. Comparative analysis indicates that laparoscopic nephrectomy combined with complete resection of the liposarcoma with negative surgical margins remains the preferred strategy, as it is associated with improved patient survival outcomes.
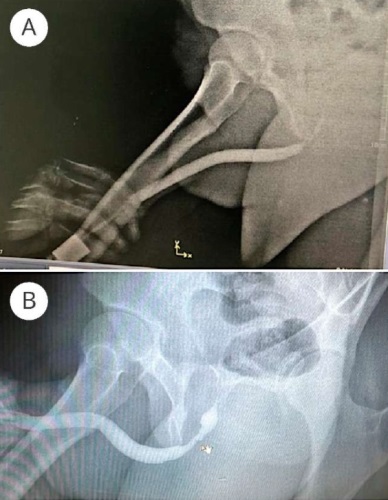
Introduction. A urethrovaginal fistula is a type of genitourinary fistula characterised by an abnormal communication between the urethra and the vagina. The principal clinical features include urinary leakage through the vagina, partial or complete stress urinary incontinence (SUI) precipitated by coughing, sneezing, or physical exertion, as well as dysuria and spraying of the urinary stream.
Objective. We present a clinical case demonstrating the possibility of addressing the patient’s primary complaint through the placement of an adjustable suburethral sling (SUS) without closure of the urethral fistula.
Case presentation. A 44-year-old female patient was diagnosed with SUI, urethrovaginal fistula, and meatal obliteration. At the time of examination, she reported significant urinary leakage during coughing, sneezing, and physical exertion, altered urinary stream direction, and urine leakage from the vagina following micturition. The symptoms first appeared in 2005 postpartum, complicated by urethral prolapse with subsequent excision of the necrotic distal segment. On examination, the external urethral meatus was obliterated. A fistulous opening was observed 15 mm proximal to the obliterated urethral meatus. The urethral length measured 25 mm. The cough stress test was positive. Quality of life questionnaire scores were as follows: POPDI-6 — 8.33, CRADI-8 — 25, UDI-6 — 50, PFDI-20 — 83.33; PISQ-12 — 23; ICIQ-SF — 10. The patient underwent implantation of an adjustable SUS. Postoperatively, sling tension was adjusted. At 12-month follow-up, the cough stress test was negative. Voiding was unobstructed with no residual urine. A significant improvement in quality of life was noted according to questionnaire scores: POPDI-6 — 5, CRADI-8 — 0, UDI-6 — 4, PISQ-12 — 38, ICIQ-SF — 2.
Conclusion. This clinical case demonstrates the successful use of an adjustable SUS to address the primary complaint of SUI in a patient with a urethrovaginal fistula.