ORIGINAL ARTICLES
This article contains the results of research of the endothelial dysfunction arising during the modeling of thermal local asphyxia of kidney and possibilities of their correction by distant ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning. The modeling of thermal local asphyxia of kidney is characterized by the disturbance of microcirculation and expression of eNOS in the kidney tissue. The usage of distant ischemic preconditioning and phosphodiesterase inhibitors type 5 sildenafil and tadalafil leads to pronounced correction of microcirculation dysfunction and activity of eNOS. During the modeling of thermal local asphyxia of kidney against endothelium dysfunction caused by ADMA-like L-NAME induced deficiency of nitric oxide more pronounced dysfunction of microcirculation and activity of eNOS are observed. The usage of distant ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning with the help of phosphodiesterase inhibitors type 5 in this type of pathology led to pronounced correction of microcirculation dysfunction and activity of eNOS. The injection of glibenclamide blocker of ATP – dependent K+ channels during the correction of the disturbance caused by the modeling of thermal local asphyxia of kidney with the help of distant ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning leads to the decrease of its efficiency.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Introduction. The main treatment component of asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute cystitis and pyelonephritis in pregnant women is antibiotic therapy, which in many patients is prescribed empirically. For successful selection of the drug, it is necessary to know both the structure of pathogens and the current profile of their antibiotic resistance.
Purpose of research. The study of species composition and resistance to antibiotics of bacteria that cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnant women in the Moscow Region
Materials and methods. The study included 104 pregnant women with uncomplicated UTIs who were observed and treated at the Lapino Clinical Hospital between 2016 and 2017. The material for bacteriological studies was the midstream portion of urine or urine collected by a catheter.
Results. 90 patients had asymptomatic bacteriuria, 10 had acute cystitis, and 4 had acute gestational pyelonephritis. The structure of the pathogens of UTI is presented: E. coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Enterobacter cloacae. The most frequently detected pathogens were E. coli (67.3%) and E. faecalis (50%). Resistance rate of E.coli strains more than 20% was detected to ampicillin (36.4%), amoxicillin / clavulanate (23.2%), trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole (27.4%), nalidixic acid (20.7%), cephalosporins 2 and 3 generation (respectively, 25.7% and 24.3%). Resistance rate more than 20% in Enterobacteriaceae family strains was detected to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (24.4%), nalidixic acid (20.7%), cephalosporins 2 generations (21.7%). Antibiotic resistance of E.coli and other Enterobacteriaceae family taxons less than 10% was noted only with respect to carbapenems (0%) and fosfomycin (1.5% and 3.5%, respectively).
Conclusions. It is expedient to use the obtained data on the composition and sensitivity profile of uropathogens in UTIs in pregnant women when choosing starting empirical antibiotic therapy.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Introduction. Tuberculosis of the prostate is difficult for diagnosis, especially in the early stages.
Material and methods. In an open prospective cohort study 84 patients with clinical and laboratory manifestations of chronic prostatitis were included.
Purpose of the study. Тo estimate the most significant diagnostic criteria for prostate tuberculosis; role of prostate biopsy in differential diagnosis.
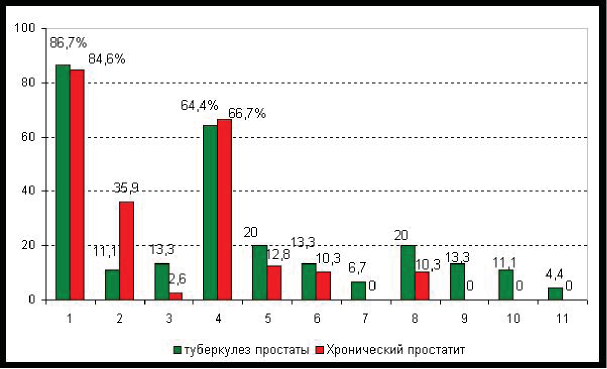
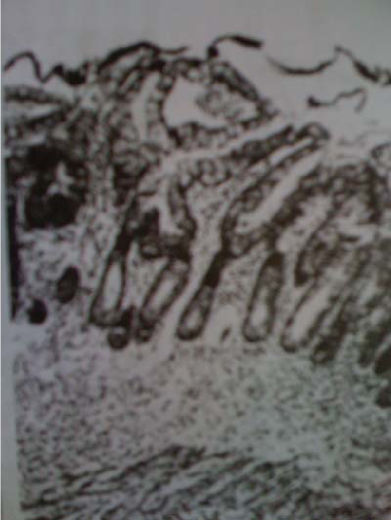
Results. In 45 patients (53.6%) prostate tuberculosis was diagnosed, and in 39 patients (46.4%) chronic bacterial prostatitis was diagnosed. The diagnosis of prostate tuberculosis was confirmed microbiologically in 33.3% of patients, radiologically - in 24.4% of patients. A prostate biopsy followed by histological, bacteriological and molecular-genetic examination of the biopsy specimen confirmed the diagnosis in 20% of patients.
Conclusion. The most informative in the differential diagnosis of tuberculosis and chronic prostatitis is the identification of M. tuberculosis; verification of diagnosis radiographically is possible only with the development of destruction of the parenchyma. The biopsy of the prostate should be examined not only pathologically, but also by molecular genetic methods.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Introduction. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections of practical interest to specialists in different areas. The most common form of UTI is acute uncomplicated cystitis (AUC). To date, there is a limited number of studies devoted to the study of this problem in the Russian Federation.
Purpose of research. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence and clinical features of communitybased UTI in Russia.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted in two stages, the first stage was completed in 2005- 2006, the second stage – in 2017, the method of questionnaire was used. During the first stage, young women were surveyed in organized groups (Universities and Colleges) using a paper traditional questionnaire in 20 cities of the Russian Federation, the Republic of Belarus and Kazakhstan. The second stage of the research was carried out using the technology of online surveys. Information about the online questionnaire was shared at specialized events in which mainly young people of 18-25 years participated – lectures at Universities, youth events, social networks, etc. During the second stage of the study, 20 cities of the Russian Federation were covered.
Results. At the first stage of the study, 660 women were interviewed, the average age was 20.9 ± 1.6 (median - 18.0) years. At least one episode of dysuria was reported by 19.0% ± 1.5% of the respondents, with 22.9% of the respondents having recurrent cystitis. In the second stage of the study, 525 respondents were interviewed, the average age was 21.1 ± 1.8 years. The occurrence of at least one episode of dysuria during the life о21.1% ± 1.7 of the respondents, while 28.5% of ± 2.0 of the respondents reported the development of 3 or more episodes of the dysuria over the last 12 months.
The median duration of cystitis symptoms was 2 days in both the first and second stages of the study. Most often, symptoms of dysuria persisted 1-3 days (64.1%), 4-5 days (23.0%) or 5-7 days (9.5%). The most correlated with the development of cystitis were family history (OR - 2.26-2.42), sexual activity and use of spermicides (OR – 1.69 and 2.43). From 40% to 50.9% of respondents in the case of dysuria do not seek medical care. When reached a medical care, most often consulted a doctor urologist (15.8% - 22.3%), gynecologist (16.7% - 17.7%), rarely a therapist (8.8 – 11.4) or other specialties (1.3% - 14.8%). No pharmacological treatments were used and 20.1% - 23.1% of the respondents, herbal medicine – 24.0% - 23.9%. Antibiotics, spasmolytic drugs and NSAIDs were the most commonly used. Over the past 12 years, there have been significant changes in the structure of antibiotics used in cystitis – the frequency of use of ampicillin, amoxicillin, co-trimoxazole, gentamicin has clearly decreased. On the contrary, increased frequency of use of phosphomycin, norfloxacin, levofloxacin.
Conclusions. According to the survey of young women, 19.1%-21.1% of respondents report the occurrence of symptoms of AUC. 22.9% - 28.5% of women report the development of 3 or more episodes of dysuria during the year. Usually clinical symptoms persist for 2 days (median), the duration of dysuria in the range of 1-3 days reported 64.1% - 70.9% of patients. The risk of AUC correlated with the activity of sexual life, family history of UTI, spermicides using – OR – 1.69, 2.42 and 2.43, respectively. 40.3-50.9% patients with AUC did not seek medical care, the main method of treatment of cystitis in an outpatient setting is the use of antibiotics.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Introduction. The histomorphological state and mechanisms of transformation of the intestinal epithelium of the orthotopic urinary bladder are unexplored.
Purpose of research. The study the morphological adaptive and compensatory changes in the intestinal graft wall (IGW) and their relationship with homeostasis at various stages after surgical treatment. Materials and methods. The morphological state of the intestinal graft wall (IGW) was studied in 42 patient’s cystectomy undergoing with the formation of an orthotopic intestinal bladder (15-ileum, 27-sigmoid) at terms from 1 to 6.5 months and 1 year or more after the treatment.
Results. Morphological changes occurring in the IGW wall begin with the moment of urine entering the lumen, which occurs in combination with changes in the stereotyped dynamics of the organ. Expressed changes are observed in all parts of the wall of the small and large intestine. There is regeneration and restructuring of the epithelium, expressed in atrophy and a decrease in the number of suction cylindrical cells and an increase in the number of mucus-forming goblet elements, terminating by 12 months and more after the operation. This combined with a decrease in the number and size of villi and crypts, reduction of the lymphatic channel and sclerosis of the blood vessels and stroma blocks suction. An increase in the number of mucus-forming goblet cells provides a barrier that protects the IGW mucosa from the effects of urine.
Conclusion. Morphological changes occurring in the IGW wall under the influence of urine contribute to the preservation of homeostasis and are identical in the thick and thin-intestinal variant of plastic of the bladder.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest
Introduction. Chronic prostatitis is the most common and difficult to diagnose androurologic disease. However, the etiology, pathogenesis and pathophysiology of chronic abacterial prostatitis are not well understood.
Objective. Analysis of the role of the body’s proteolytic systems in inflammatory processes in the prostate, detection of markers of inflammation in the blood, prostate secretion in various forms of chronic abacterial prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CAP/CPPS).
Materials and methods. The study included 52 patients with inflammatory (CAP/CPPS IIIA) and 46 patients with non - inflammatory (CAP/CPPS IIIB) forms of chronic abacterial prostatitis. We determined the activity of kallikrein, level of prekallikrein, inhibitory activity α1-proteinase inhibitor and α2- macroglobulin, total arginine-esterase activity, activity of leukocyte elastase and elastase-like activity in the blood serum and the prostate secret.
Results. Disturbance of metabolic processes of inflammation development in chronic abacterial prostatitis occurs against the background of imbalance of the proteinase inhibitors system, uncontrolled enhancement of proteolytic processes in the prostate in conditions of weakening of natural resistance of the organism is the most significant factor in the development of CAP/CPPS.
Conclusions. The analysis of the activity of proteolytic processes in the blood and prostate secretion can serve as an additional diagnostic criterion for chronic abacterial prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Disclosure: TInformation about sponsorship. The publication was prepared within the framework of the implementation of the State Task of the SSC RAS for 2018. The state registration of the project № 01201363192. The author declares no conflict of interest.
Introduction. Generally recognized critical moments in kidney resection are the time of ischemia and the adequacy of hemostasis. Until now, one of the main contraindications to nephron-sparing treatment is the inability to provide hemostasis in middle-segment tumors, especially when they are intrarenal.
Purpose of research. To evaluate the effectiveness of open resection of the kidney.
Materials and methods. For the period 2005 to 2018 us made 152 open partial nephrectomy (OPN) for renal cell carcinoma. The algorithm OPN included extra peritoneal lumbotome access in the IX intercostal space with resection of the X rib resection under conditions of warm ischemia for compression of the blood vessel, in 92.8% of cases completed the clamping of segmental or aberrant arteries. Resection was performed, retreating from the tumor 0.5-1 cm within the unchanged renal parenchyma.
Results. The mean age of patients was 55.4±16.2 years; male/female ratio was 52.6/47.4%; right-sided/ left-sided tumor localization was 42.1/57.9%, respectively. The duration of the operation was 109.6±56.7 min, the time of partial ischemia was 15.1±8.3 min, the volume of blood loss was 258±93 ml the Discharge along the drains lasted for 4-12 hours after the operation and averaged 35.7±22.1 ml. Patients were activated after 24 hours, when the urethral catheter was removed, in 59 (38.8%) cases, bladder drainage was not performed. Average postoperative hospital stay was 10.1±4.2 per day.
Conclusion. The technique of open resection of the kidney with a margin from the border of the visible tumor and visual control of the surgical edge provides good oncological results, does not require the «Express» histology and is an alternative to nephrectomy in patients with high risk of complications, calculated on morphometric scales.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
HISTORY OF UROLOGY
The article notes that James Israel and Max Nitze have successfully developed European medicine for more than 30 years of their scientific and practical activities, enriching it with both experimental and large clinical experience. Their scientific achievements greatly contributed to the development of modern clinical urology throughout the world. Based on an analysis of the results of more than 1000 nephrectomy operations for tuberculosis, Izrael made a conclusion about the effectiveness of surgical treatment of this disease. In addition to kidney surgery, J. Israel developed questions of rhinoplasty. He participated in the International Congress of Physicians in Moscow (1897), where he reported on 191 kidney operations. He was an honorary member of the German Society of Surgeons, the Berlin Society of Urology, President of the International Congress of Urology (Paris, 1908). The main merit of M. Nitze is the invention of a cystoscope, in which for the first time an electric light source for illuminating the bladder was located at the end of a tool inserted into the bladder. The invention of the cystoscope contributed to the development of urology as an independent clinical discipline and marked the beginning of endoscopic studies of various organs and body cavities. It is analyzed the fact that the history of medicine gives rich material not only to understanding evolution, but also to the possibility to foresee its further development. The current state of clinical urology is determined by the progress of basic research in biology, physics, biochemistry, bacteriology, immunology, pharmacology. At the same time, it was noted that the personality of the scientist-physician, his observation, the non-standard view, the ability to see the opening perspectives, to bring up worthy students, to create a scientific and clinical school of urologists, is of utmost importance, at the same time, to the full compliance of the great German urologists J Israel and M. Nitze.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The author declares no conflict of interest.
The article notes that the problems of urology of the first half of the XX century were worked out by joint efforts of surgeons and urologists who distinguished their discipline as a narrow specialty from clinical surgery. Domestic medicine, improving and developing narrow specialties in those years, created the best conditions for improving the skills of the relevant specialists, but at the same time considered it necessary to proceed from the principle that a sharp delimitation of diseases and treatment by organs can not always serve the benefit of science and the patient. Special mention should be made of special methods of research – cystoscopy, catheterization of the ureters, pyelography, etc. – have become generally accepted for urologists and surgeons. Domestic urologists developed methods of operative access to the kidney, methods of intracapsular removal of it, methods of plastic restoration of the urino-genital organs. The author analyzes significant achievements in the treatment of congenital malformations of the genitourinary system in children, especially in the transplantation of ureters into the gut with ectopia of the bladder. When injuring the pelvic bones, rational surgical treatment of the wound at the first stages of evacuation, taking into account the anatomical features of the cellular spaces of the pelvis and the functions of the pelvic organs, was the main method of preventing subsequent complications. It is shown that in those years one of the important sections of the work of the urological departments of surgical hospitals was the treatment of gunshot injuries of the urethra. To treat these injuries, we used all sorts of developed ones before the Second World War. Domestic surgery in the first half of the XX century conducted an in-depth study of the main issues of theoretical and practical surgeons and urology. Surgical disciplines, including urology, began to approach the study of pathogenesis and the entire picture of the disease, guided by the teachings of Academician I.P. Pavlov on the role and significance of the central nervous system in the life of a living organism.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The author declares no conflict of interest.
LECTURES
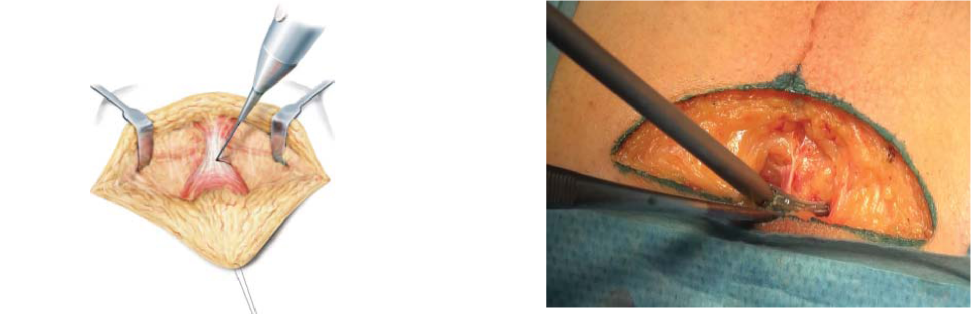
Lecture is devoted to the main provisions of perineal prostatectomy. At present, laparoscopic and robotic prostatectomy techniques have been widely developed. Nevertheless, the use of perineal access surgery remains indisputable for carefully selected patient groups. Undoubtedly, this type of intervention has obvious advantages, which are described amply in the lecture, in particular such as minimally invasive and economical expediency. The article presents modern functional and oncological results of perineal radical prostatectomy. This lecture will be useful for urologists and oncologists for improving their skills in performing this type of radical prostatectomy.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The author have declared no conflicts of interest.
STATEMENTS OF RESEARCH AND EDUCATIONAL EVENTS
In this article presented the report about the world meeting on sexual medicine, joint congress 21st World Meeting of the International Society for Sexual Medicine (ISSM) and 20th congress of the European Society for Sexual Medicine (ESSM), held in Lisbon from 28 February to 3 March 2018.
Disclosure: The study did not have sponsorship. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.