EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis is more difficult to diagnose than respiratory tuberculosis. However, late detection leads to disabling consequences. Children from 4 to 11 years old are at risk for tuberculosis due to increased communication skills. It seems relevant to isolate urinary tract tuberculosis (UTTB) in children of these age groups in the structure of all forms to improve its diagnosis.
Purpose of the study. Isolation of urinary tract tuberculosis to determine the significance and improve the diagnosis of this localization of tuberculosis in the structure of all forms and localizations of tuberculosis in children of preschool and primary school age.
Materials and methods. The cohort comparative study included 303 children aged 4 to 6 years and 306 children aged 7 to 11 years who had tuberculosis in the period from 2000 to 2018. The results were statistically processed using the Microsoft Office 2007 software package, Biostat 2009. Differences between the groups were determined using the Х2 test. The hypothesis of the absence of a statistically significant influence of the factor was rejected at p > 0.05.
Results. Respiratory tuberculosis (RTB) was diagnosed in children of preschool and primary school age in most cases (94.7% and 89.9%; p < 0.05), bacteriological confirmation was found in 6.3% and 3.6% (p > 0.05) children in the compared age groups. Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic lymph nodes (TBILN) prevailed (85.7% and 75.3%; p < 0.05) in the structure of RTB. Primary tuberculosis complex (PTBC) was more often diagnosed in children of primary school age (23.3%) than in preschoolers (13.2%; p < 0.05). The registration frequency of isolated extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis was 1.3% and 5.6% (p < 0.05), bacteriological confirmation of the diagnosis was 25,0% and 35.3% (p > 0.05). Most of the detected cases of isolated extrapulmonary tuberculosis accounted for UTTB - 50,0% and 64.7% (p > 0.05), all cases were confirmed bacteriologically. Generalization of the tuberculous process was noted in 4.0% and 4.6% of cases (p > 0.05). Most cases of generalized tuberculosis in children from 4 to 11 years old were associated with a combination of tuberculosis primary forms, mainly (TBILN) and in one case of PTBC, with UTTB (83.3% and 85.7%; p > 0.05). These cases of combinations were confirmed bacteriologically.
Conclusion. Children of preschool and primary school age were diagnosed most often with TBILN. Isolated extrapulmonary tuberculosis was rare; UTTB predominated with frequent bacteriological confirmation. Isolated extrapulmonary tuberculosis was rare, UTTB of the predominated with frequent bacteriological confirmation. Generalization of tuberculosis in children 4-11 years old was rare; isolated forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis were more often diagnosed. Most of the cases of combined localizations were due to a combination of TBILN and UTTB. UTTB was confirmed by the detection of M. tuberculosis in urine cultures. Physicians of primary health care and specialized services should be aware of the possibility of developing UTTB in children from 4 to 11 years old and search for the pathogen in patients with chronic UTIs and infected with M. tuberculosis.
Introduction. There remains a need to introduce new methods of treating kidney stones, given the increasing incidence of urolithiasis. Considering the proven efficacy and safety of retrograde electro-pulse lithotripsy, its use in the treatment of stones in the ureter, kidney and bladder, the need to expand the scope of this method is substantiated. Namely, the use in the treatment of kidney stones and the ureteropelvic junction with percutaneous approach.
Purpose of the study. Assessment of the destruction effectiveness of kidney stones using an electro-pulse lithotripsy apparatus through antegrade (percutaneous) approach.
Materials and methods. 229 percutaneous nephrolithotripsies were performed in patients with different locations of kidney stones in Siberian State Medical University Clinics (Tomsk, Russia) period from 2014 to 2019. We used the Urolit-105M electro-pulse lithotripter (Lithotech Medical, Israel, MedLine LLC, Russia) or the Calculase II laser lithotripter in some cases (Storz, Germany).
Results. Patients were aged from 24 to 81 (women - 59.8%). The stones average size was 22 mm (from 10 to 73 mm). The stones average density was 1051.1 HU (from 360 to 1720 HU). The operation average duration was 122.3 minutes (from 40 to 300 minutes). The incidence of complications was 14.3%. The complete stones destruction occurred in 76% cases and that in combination with the laser went up to 89.95%. The overall response rate in redo operations reached 98.2%.
Conclusion. Application of the electro-pulse method of kidney stone destruction with the percutaneous approach is makes a great effect, which is much higher when the stones is treated by the laser energy. Furthermore, combing with flexible endoscopes enables to apply the electro-pulse lithotripsy antegradely in hard-to-reach spots of the kidney cavitary system with no extra access to be provided. The method also enables to fight efficiently with the ureter upper part stones, also in combination with the retrograde approach to the stones.
Introduction. The frequency of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) progression associated with prostatic hyperplasia in elderly men is increasing despite improvements in early diagnosis methods and the emergence of new drugs. Questionnaires are used to assess the patient's condition on primary admission and to monitor the effectiveness of medical procedures to diagnose the severity of LUTS in clinical practice.
Purpose of the study. To compare the effectiveness of LUTS diagnosis in elderly men using different scales: the International Prostate Symptom Index (IPSS) and the Visual Prostate Symptom Scale (VPSS) for differential analysis of the cognitive impairment degree.
Materials and methods. The study included 56 men, residents of the Trans-Baikal Territory, over the age of 50 with LUTS of varying severity. All patients completed the VPSS and IPSS questionnaires (IPSS1) independently. Subsequently, the IPSS questionnaire (IPSS2) was completed in cooperation with the urologist. Additionally, respondents were questioned using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCa-test) to determine the degree of dementia and other cognitive impairments.
Results. All patients were divided into 3 groups after analyzing the results of the MoCa test: I — patients with signs of dementia, II — with cognitive impairments, III — no cognitive impairments. The predicted differences were obtained when comparing the results of IPSS1 / IPSS2: the greatest differences were in the patients of the first group (76.47%; p < 0.05), the smallest in the third group (12.5%; p > 0.05); there was an increase in the severity of LUTS with self-completion of questionnaires (IPSS1). When evaluating a similar indicator on the VPSS questionnaire, compared with a more objective response with the participation of a physician (IPSS2), statistically significant differences were not obtained in all groups of participants.
Conclusion. The dependence of the objectivity of filling out the questionnaires for the diagnosis of LUTS on the severity of cognitive impairments and the age of the respondents was revealed. A reliable correlation of VPSS indicators with the indices of the validated IPSS scale was established. The new questionnaire may be in demand in the clinical practice of a urologist to assess the degree of LUTS in elderly men, as an alternative to the generally accepted IPSS scale, especially in patients with age-related dementia and other cognitive impairments.
Introduction. Nephrectomy (NE), heminephrectomy (HNE) and the formation of ipsilateral ureteroureteroanastomosis (UUA) do not exclude the possibility of preserving the distal ureter. The remaining ureteral stump can cause the formation of ureteral stump syndrome (USS) in the form of recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI), hematuria, pain syndrome, and stump empyema in some cases.
Purpose of the study. To assess the incidence and treatment approach of USS in children after NE, HNE and UUA performed using open and laparoscopic access in different Russian clinics.
Material and methods. The study is based on the results of treatment of 778 patients from 9 clinics in the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus in the period from 1998 to 2020. Patients underwent NE, HNE and UUA by open or laparoscopic access. The ureter was not removed completely, its stump was left. Open access was used in 313 (40.2%) children, laparoscopic in 465 (59.8%) cases. USS was detected in 27 (3.5%) patients. The ureteral stump was removed in 26 (96.3%) children. Open removal of the ureteral stump was performed in 11 (42.3%) patients, through laparoscopic access in 13 (50.0%) and vesicoscopically in 2 (7.7%) children.
Results. There were 12 boys (44.4%) and 15 girls (55.6%) among the patients with USS. USS was detected on the right in 13 (48.1%) children, on the left - in 14 (51.9%). The median age of the patients was 25 [12; 42] months at the time of USS detection. Ureteral stump was sutured and ligated in 15 (55.6%) children during the primary operation, the stump was left open after excision in 4 (14.8%) children, it was not indicated how the stump was processed in 8 (29.6%) patients. Reflux to the stump was detected in 13 (48.1%) patients, USS against the background of obstruction was detected in 14 (51.9%) children. It was determined that the frequency of SCM is lower (9 (1.9%)) with the use of laparoscopic access than with open (18 (5.8%)) operations (p < 0.004). Clinical manifestations occurred in 85% of patients with USS within a year after surgery.
Conclusion. USS is a rare complication (3.5% of cases) in patients who have undergone NE, HNE and UUA with the distal ureteric stump preserving. Performing these operations by laparoscopic access allows carrying out total ureterectomy and significantly reduces the likelihood of USS development.
Introduction. The problem of extended urethral strictures treatment remains relevant due to the complexity of the supervision of such patients and the high frequency of disease recurrence after surgical treatment.
Purpose of the study. Evaluation of the effectiveness of one-stage buccal urethroplasty according to the Kulkarni technique using two flaps for extended anterior urethral strictures.
Materials and methods. The study included 18 men with an extended anterior urethral stricture, who underwent buccal urethroplasty by perineal access using the Kulkarni dorsolateral onlay technique using two flaps from January 2018 to March 2020, and a postoperative follow-up period of at least 6 months. The study was prospective. Control examination was carried out 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months after surgery. The criteria for the recurrence of urethral stricture were the presence of complaints of deterioration in the quality of urination in combination with a decrease in the maximum urinary flow rate of less than 12 ml/sec and the presence of residual urine in an amount of more than 100 ml, as well as the need to perform any surgical intervention to restore the normal passage of urine.
Results. The age of the patients ranged from 32 to 72 years (median 58 years). The length of the stricture ranged from 6 to 11 cm (median, 8 cm). The stricture was localized in the penile segment in 11 (61.1%) cases and the penile and bulbar urethra in 7 (38.9%) cases simultaneously. An iatrogenic cause of urethral stricture occurred in 11 (61.1) patients, idiopathic in 5 (27.8%) patients and inflammatory in 2 (11.1%) patients. The stricture was primary in 12 (66.7%) cases and recurrent in 6 (33.3%). Spontaneous urination was preserved in 6 (33.3%) patients, cystostomy existed in 12 (66.7%) patients. The follow-up period after surgery ranged from 3 to 24 months (median - 12 months). Recurrence of urethral stricture was noted in 3 (16.7%) cases. The use of this technique for recurrent forms of the urethral stricture (recurrence after the previous urethroplasty) is the most significant risk factor for treatment failure. 1 (5.6%) case of erectile dysfunction and stress urinary incontinence has taken place of the late postoperative complications.
Conclusions. The Kulkarni operation using two buccal flaps for extended strictures of the anterior urethra allows to achieve high rates of efficacy and safety of a treatment, however, the risk of failure increases significantly when used for the treatment of recurrent types of strictures.
Introduction. The incidence of kidney cancer (KC) in the world is increasing and today is about 3%, but the death rate from this type of malignancy does not increase proportionally. According to research by many authors, more than half of the patients are over 65 years old at the time of diagnosis. Patients at this age have a high incidence of high comorbidity and risk of death from cardiovascular or other intercurrent pathology that exceeds the risk of death from KC. Recently, there has been a positive trend in the detection of the disease in the early stages up to 61.80%. Most of the primary detected kidney tumours are diagnosed randomly as asymptomatically small (less than 4 cm) tumours without signs of visceral metastasis. These tumours have a high degree of differentiation and rarely require surgical treatment in addition to their small size, and in the case of surgery, these pathomorphological results are benign. Due to the slow progredient growth of kidney formations and an asymptomatic course, the method of dynamic observation of kidney tumours is relevant in elderly patients and avoids unnecessary risks of surgical treatment of localized KC.
Purpose of the study. To trace the growth rate of kidney tumours accumulating contrast agent using the method of dynamic observation. This study will allow us to differentially approach the choice of surgical treatment, which is optimal for elderly patients with low somatic status.
Materials and methods. In the Multidisciplinary clinical medical centre «Medical City» (Tyumen) database all cases of radiographically verified space-occupying lesions of the kidneys that accumulate contrast were selected in the period from 2009 to 2019. We studied 50 people: 23 women (46%) and 27 men (54%), aged from 58 to 90 years. The study group included patients with kidney neoplasms of size < 7cm. Patients whose follow-up period was less than 12 months were excluded from the analysis. Regularly, every 3 to 6 months, patients underwent computed tomography to assess the growth dynamics. The size of the tumour, which was assumed to be its diameter in the largest dimension, was carefully studied. The growth rate of the tumour was calculated as the average change in diameter for 1 year during the entire observation period.
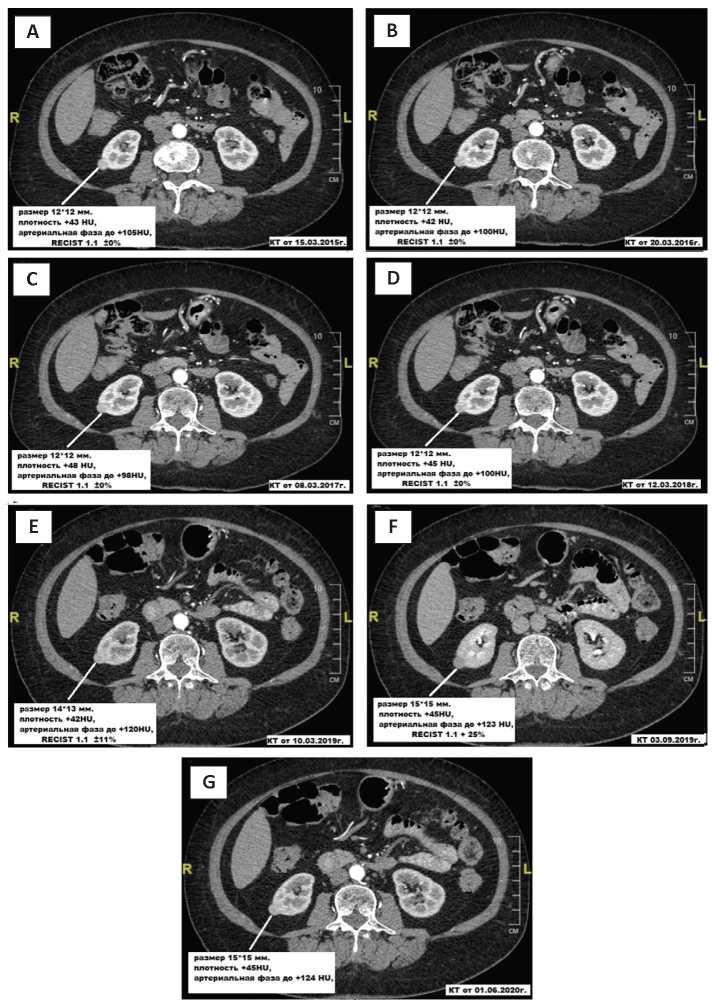
Results. The average age of patients was 74.8 ± 7.4 years according to the results of the study. The age of patients at the time of diagnosis also had no prognostic significance for the rate of growth of kidney tumours (p > 0.05). The primary diagnosis was made in 32 patients (64%) using CT, in 18 (36%) using ultrasound. The average size of the tumou at the time of detection was 35.0 ± 6.9 mm. Percutaneous kidney biopsy was performed in 2 patients for morphological verification of the tumour type. Moderate-differentiated light-cell renal cell carcinoma pT1bN0M0 was detected in both patients according to the results of histological differentiation. The average linear growth rate of the tumour was 6.6 ± 2.4 mm / year. The size of the tumour at the time of diagnosis was not correlated with the growth rate (p > 0.05). There was no correlation between the rate of increase in the size of formations depending on their structure — solid (median 6 mm / year; average — 10 mm / year) or cystic-solid (median 7 mm / year; average 9 mm / year; p > 0.05). The absence of tumour growth dynamics during the entire observation period was detected in 22 (44%) people, including 10 (20%) men and 12 (24%) women. Visceral metastasis was diagnosed in 3 cases: to the liver, spleen, and the appearance of a second tumour on the contralateral kidney. Surgical treatment was performed in 4 patients (8%), in 2 (4%) cases, the indication for surgery was the progression of the tumour in the form of the appearance of visceral metastases. One patient had chromophobic KC pT1bN0M1, the other had renal cell carcinoma, a light-cell variant of pT1bN0M1. The operation in the volume of kidney resection was performed in 2 (4%) patients, in both cases, morphologically confirmed renal cell carcinoma, light-cell variant pT1aN0M0. The presence of a cystic-solid component and the initial size of the tumour were potential radiographic signs that could predict the dynamics of an increase in renal parenchyma neoplasm.
Conclusion. The tactic of actively observing the growth rates of kidney tumours that accumulate contrast material allowed us to better understand the biological behaviour of KC. It was found that most kidney malignancies have a slow growth rate when determining the linear growth rate of the tumour. This conclusion allows us to differentially approach the choice of surgical treatment, which is optimal for elderly patients with low somatic status. Because prognostic signs of KC have not yet been identified and are not fixed in international treatment protocols, all patients who are suitable candidates for surgery are shown operative treatment.
Introduction. The most common type of lower urinary tract dysfunction is an overactive bladder (OAB). Today there is a need to search for new effective methods of treating this disease.
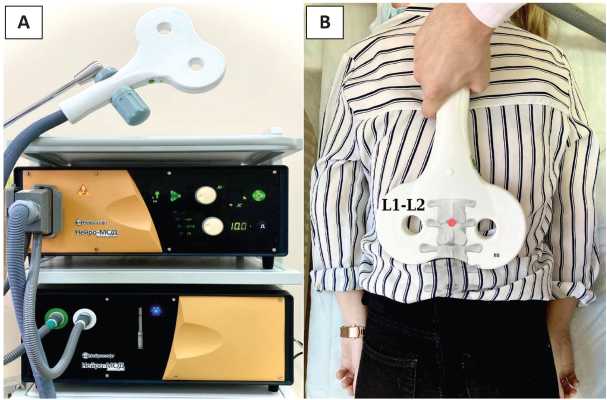
Purpose of the study. To evaluate the effectiveness of transvertebral magnetic neuromodulation (TMN) of the lumbar spine in patients with OAB.
Materials and methods. 26 patients were enrolled in the clinical study. The treatment course consisted of 15 procedures (3 times a week for 5 weeks). Before and after treatment at 1, 3 and 6 months, complaints were assessed using the ICIQ-SF and OAB-q SF questionnaires. Objective parameters were assessed by urodynamic tests before and 6 months after treatment.
Results. We observed a significant improvement in patients subjective clinical status at all points of assessment. Transvertebral magnetic neuromodulation had the greatest influence on such urodynamic parameters as the first sensation, the first desire, strong desire, maximum cystometric capacity. Patterns of phase hyperactivity were absent in 60.8% of patients after treatment and terminal hyperactivity in 41.7% of patients.
Conclusions. This small study observed a significant therapeutic effect of TMN in patients with OAB. Further large placebo-controlled trials are needed to develop universal effective protocols for lower urinary tract dysfunction treatment.
Introduction. Lymphatic cysts (LC) are the accumulation of free lymphatic fluid in a limited space (between tissues and organs), in the place where the lymphadenectomy was performed. They are the most frequent complications in pelvic oncourology. LC are divided into symptomatic and asymptomatic.
Purpose of the study. To assess the influence of the anatomical localization of symptomatic lymphatic cysts (sLC) on the clinical appearance.
Materials and methods. 203 radical prostatectomies (RPE) and 42 radical cystectomies (RC) were performed with pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) in the N.I. Pirogov City Clinical Hospital № 1 from January 2017 to March 2020. Of 203 patients, 13 (6.4%) developed SLC, and of 42 patients, 6 (14.3%). All patients who developed complications underwent complex ultrasound studies and multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) of the retroperitoneal space, abdomen, and pelvic area to assess the localization and volume of the sLC.
Results. Four anatomical localizations of the sLC can be distinguished after analyzing the clinical picture of 19 patients with sLC and comparing the obtained data with MSCT: paravasal-iliac, paravesical, prevesical, and pelvic-retroperitoneal. The frequency of paravasaliliac sLC was higher, they developed in 13 (68.5%) patients. The clinical picture included: pain in the pelvic area, lymphedema of the lower limb, body temperature ≥ 39.0 °C, due to LC infection and compression of the iliac vessels. Paravesical sLC were found in 2 (10.5%) patients. There was a failure of the urethrovesical anastomosis, according to retrograde cystography, due to displacement of the bladder. Prevesical sLC were found in 2 (10.5%) patients. Patients noted progressive urinary incontinence and pain above the pubic symphysis. Pelvic-retroperitoneal sLC was observed in 2 (10.5%) patients, with the clinical appearance of nagging pain in the lumbar region, body temperature ≥ 38.0 °C, due to ureteral compression and the development of obstructive pyelonephritis, as well as compression of the inferior vena cava by a lymphatic cyst. The repeated intervention was performed in 18 cases: percutaneous drainage of the LC under ultrasound guidance in 12 (63.2%) patients, laparoscopic marsupialization of the LC in 3 (15.7%) patients, an open technique in 3 (15.7%). In 1 patient (5.4%) the treatment was conservative.
Conclusion. Symptomatic LC can be classified according to 4 anatomical locations, which define their clinical symptoms. Most sLC require reoperation.
Introduction. Sling urethropexy is considered the «gold standard» surgical treatment for stress urinary incontinence in women. However, the long-term results of such operations have not yet been fully studied.
Purpose of the study. To evaluate the results of using various options for sling operations at different periods of postoperative follow-up.
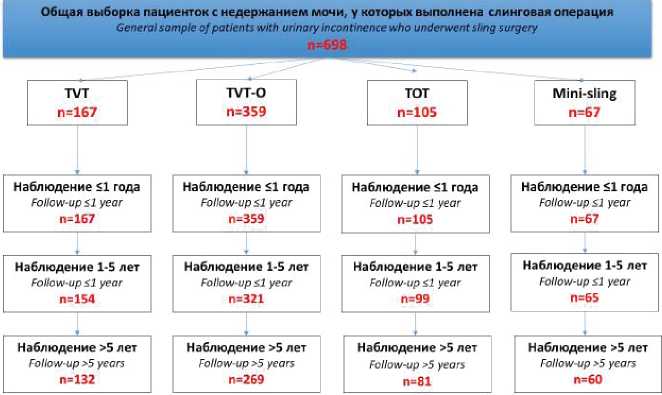
Materials and methods. In 698 women aged 42 - 68 years (median — 54 years) suffering stress incontinence were used 4 variants of sling operations according to the database of the S.P. Botkin City Clinical Hospital: TVT retropubic technique; transobturator technique TVT-O («inside-out»); transobturator technique TOT («outside-in»); mini sling system. The period of postoperative follow-up was 6 - 139 months (median 79 months). Evaluation of treatment results was carried out according to the following periods of postoperative follow-up: short-term (up to 1 year inclusive); mediumterm (a period from 1 to 5 years inclusive); long-term (over 5 years). The success of the treatment was determined by the criterion of the absence of urine involuntary loss during the cough test and the 1-hour pad test.
Results. Treatment success in the entire sample of patients was 96.1% (671 / 698) for the short-term criterion, 93.1% (591 / 635) for the medium-term criterion and 86.2% for the long-term criterion (467 / 642). The effectiveness of short-term treatment after TVT was 97%, TVT-O — 95.8%, TOT — 96.2%, mini-sling system — 95.5%, in medium-term — 92.2%, 93.1%, 90.9% and 92.3%, respectively, for long-term — 87.1%, 86.2%, 85.2% and 85%, respectively. There were no significant differences between the indicated variants of sling operations in terms of treatment efficacy for all observation periods (p > 0.05). Intra and early postoperative complications were noted in 51 (7.3%) cases, late — in 79 (11.3%). There were no significant differences in the incidence of both categories of complications between the surgical techniques used (p > 0.05). Only surgical experience significantly affects the risk of recurrent urinary incontinence after surgery, early and late postoperative complications.
Conclusions. The success of surgical treatment for stress urinary incontinence in women does not significantly depend on the type of sling surgery but depends mainly on the surgical experience. Therefore, it is advisable to use sling operations in hospitals with extensive experience in this area.
Introduction. Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder (IC / BMP) is a rare, chronic, and disabling disease. Treatment of IC / BMP is empirical in the scope of physiotherapy procedures, taking antidepressants, pentosan sodium salt sulfate, intravesical administration of lidocaine and heparin, as well as various types of surgical interventions — mainly aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease. The effectiveness of the latter does not exceed 60%, and symptoms return even when a period of remission seems to have occurred. The article presents the experience of our clinic in treating women with IC / BMP using hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO).
Purpose of the study. To study the effectiveness of HBO in complex therapy patients suffering IC / BMP in the form of ulcerative lesions.
Materials and methods. The study included 40 women, average age 60.1 ± 10.5 years, with the classic form of IC / BMP. All patients were examined and included in the study according to the NIDDK criteria. The patients were divided into 2 groups: Group I — women who received complex therapy with HBO (n = 20), Group II — only complex therapy (n = 20). Group I women received treatment: transurethral coagulation of Gunner's lesion zones, bladder hydrodistension, tricyclic antidepressants, intravesical instillations of lidocaine, dimethylsulfoxide, and a course of HBO. HBO consisted of 10 sessions (40 min, 2 ATM). Group II patients received the same IC / BMP therapy as the group I women, to the same extent, but without HBO.
Results. Indicators of the PUF scale after 6 months of therapy in Groups I and II were 14.2 and 21.2 points, respectively. The average score in Group I was 3.48, in Group II — 5.13 according to the visual analogue pain scale. The cystometric capacity of the bladder in both groups after treatment was stable, its value was at least 320 ml. The number of urinations after combined therapy with HBO after 1, 3 and 6 months was 12 times a day. Whereas it was 14 times a day in Group II after 1 month, and it was 15 times a day after 3 and 6 months.
Conclusions. The index of IC assessment, indicators of the visual-analogue pain scale, the cystometric capacity of the bladder, and the number of urinations improved after standard treatment but were significantly worse than in patients who received HBO additionally. Treatment with HBO leads to a statistically significant improvement, only in combination with the therapy, both according to questionnaires, and the function of accumulation and emptying of the bladder. For patients with IC/BMP who had ineffective standard treatment, it makes sense to conduct HBO, which can be an important stage of therapy and contribute to a longer remission of the disease.
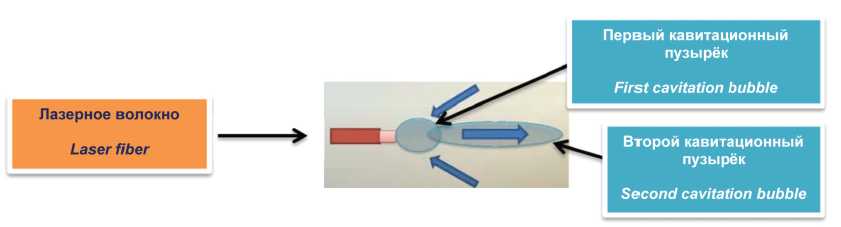
Introduction. The development of laser technologies in medicine and their introduction into everyday clinical practice determine the trend of using this type of energy in the treatment of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In the last decade, holmium laser enucleation (HoLEP) of the prostate has been claiming to be «the gold standard» in the BPH treatment. The advantages of HoLEP over alternative technologies (transurethral resection, bipolar enucleation) in the BPH treatment have been demonstrated in randomized trials. These advantages include the reduction of the patient's hospital stay, safety of manipulation and high quality of life for the patient after surgery. The use of electrical energy in resection techniques for the BPH treatment in most cases is limited by the prostate volume (80 cm3). A better understanding of the effect of laser radiation and its clinical efficacy has led to increased interest and widespread adoption of laser systems. The constant search and improvement of existing approaches encourages urologists and surgical equipment companies to research new laser systems. One type of improvement is a software update for laser pulse modulation that has been developed to improve the efficiency of laser equipment. For the further development of new laser technologies and widespread use in routine clinical practice, it is necessary to compare them with standard methods of BPH surgical treatment with an assessment of the effectiveness, as well as the pros and cons of the compared methods.
Purpose of the study. To evaluate the results of laser endoscopic treatment of patients with prostatic hyperplasia.
Materials and methods. The study included 50 patients with prostatic hyperplasia who underwent two different types of surgery — HoLEP (group I; n = 25) and HoLEP with MOSES (HoLEP-M) technology (group II; n = 25). Inclusion criteria were: the presence of moderate or severe obstructive symptoms of the lower urinary tract, prostate volume > 40 cm3, maximum urine flow (Q-max) < 12 ml/sec. Exclusion criteria were: the presence of cystostomy drainage, an oncological process of the urinary system, an active inflammatory process of the genitourinary system, previous surgical interventions on the urinary system. I-PSS, QoL and IIEF questionnaires data, the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), the maximum flow of the urine stream (Q-max) and the post-void residual volume were assessed at baseline and 3 months after the operation. The main indicators of the compared methods, the number and nature of complications were studied.
Results. Both methods of laser enucleation allow achieving a good functional result with a minimum number of complications. When comparing both methods in the group II of patients who underwent HoLEP-M, there was a statistically significant difference in terms of characteristics: the time of enucleation in group I (HoLEP) — 46.7 ± 15.0 min (31 - 80) vs group II (HoLEP-M) — 38.9 ± 7.6 min (30 - 60) (p = 0.03), but this did not affect the total time of surgery (p = 0.21), the level of haemoglobin postoperative changes in group I (HoLEP) — 7.5 ± 5.4 g/l (2 - 18) vs group II (HoLEP-M) — 5.0 ± 2.9 g/l (2 - 13) (p = 0.04) and irrigation time in the postoperative period, group I (HoLEP) — 17.6 ± 3.6 h (11 - 26) vs group II — 14.0 ± 4.3 h (5 - 21) (p < 0.001). Thus, the results of the study suggest that the HoLEP with the modified pulse MOSES technology has advantages over the standard HoLEP technique. HoLEP-M allows you to perform the enucleation stage faster, with better hemostasis and minimizes the effect of the laser on the surrounding tissues. Complications above level 2 were not observed in both groups according to the Clavien-Dindo scale.
Conclusion. HOLEP-M is a safe method of surgical treatment of prostatic hyperplasia from the point of view of surgical safety, efficacy, as well as the duration of the patient's recovery period and can serve as an alternative to the HoLEP standard technique.
Introduction. Tuberculosis remains a global problem of our time. Kidney tuberculosis, especially complicated by tuberculosis of the urinary tract, becomes a surgical disease if it diagnosed late or the therapy was not optimal.
Materials and methods. 93 patients with urogenital tuberculosis (UGTB) was included in this study who were admitted to the Novosibirsk Scientific and Research Institute of Tuberculosis consecutively. All of them underwent surgical intervention on the kidney. 51 patients underwent open surgery, and 42 patients underwent laparoscopic surgery. The results of treatment and the incidence of complications in both groups were analyzed and compared.
Results. The age of the patients ranged from 23 to 75 years, averaging 50.9 ± 6.7 years; there were 45 men and 48 women. Tuberculosis of the left kidney was diagnosed in 41 patients, on the right - in 52 patients. The indication for nephrectomy was polycavernous tuberculosis of the kidney with no function in 74 cases, while in 11 cases polycavernous tuberculosis was complicated by stage 4 bladder tuberculosis. In 9 patients, nephrectomy was performed with cystectomy simultaneously. In 2 patients with severe renal dysfunction, cystectomy for microcystis was not performed, preferring laparoscopic nephrectomy with heterotopic urine diversion. In the group of patients operated on with an open approach, complications developed in 14 patients (27.4%), in the group of laparoscopic operations - in 5 (11.9%). The laparoscopic approach made it possible to activate the patients much earlier: after 2.4 hours, while in the openaccess group - after 38.7 hours.
Conclusion. Due to the peculiarities of the pathogenesis of UGBT, it is accompanied by the local development of gross deforming scars, which significantly complicates the implementation of the surgical procedure - both open and laparoscopic access. Nevertheless, modern technology allows to perform the entire spectrum of operations laparoscopically to UGTB, and the complication rate is 2.3 times lower than in open operations. Early activation of the patient, less need for analgesics are also positive factors of minimally invasive surgery for UGTB.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
The article provides an overview of the most significant publications on the male infertility topic. The main selection criteria were considered the practical significance of the article, as well as the impact factor of the journal in which it was published, according to the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR). As a result, a list of 10 works published in the third quarter (July - September) of 2020 was formed. The review included articles on the following issues: redox balance in the male reproductive system, advanced paternal age, the effect of a new nasal form of testosterone on fertility, the correlation of PSA levels with infertility, as well as new data on the effect of COVID-19 on male fertility.
CLINICAL CASES
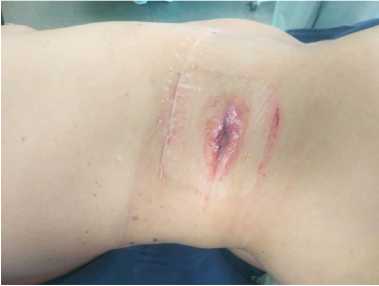
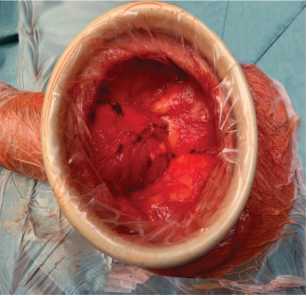
Penile prosthetics is the «gold standard» for treatment of severe or drug-induced refractory erectile dysfunction. One of the most formidable postoperative complications of penile prosthetics is periprosthetic infection. Currently, infusion and topical application of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs is used for the prevention of prosthetic infectious complications. One of the means for the prevention of postoperative infectious complications is the Alexis retractor (Applied Medical, Rancho Santa Margarita, CA). It is a port that is installed in the surgical area and limits the contact of the prosthesis components with the surrounding tissues and skin, achieving optimal wound visualization. The use of Alexis provides atraumatic retraction of the wound edges and 360-degree protection of the wound from the contact of the implant components with adjacent tissues and skin.
Nowadays, radical prostatectomy (RPE) is the «gold standard» in the treatment of localized prostate cancer (PCa). However, this intervention is associated with a high risk of developing iatrogenic erectile dysfunction (ED), which significantly reduces the quality of life of a man. One of the surgical solutions to this complication is the installation of a penile prosthesis. Nevertheless, it must be borne in mind that this manipulation is associated with certain risks of intra-and postoperative complications. During the operation, there may be complications such as perforation (cavernous, septal, urethral), crossover (intersection of rods or cylinders), haemorrhage, difficulties in suturing the operating wound, damage to the components of the prosthesis. The most common problem is an infection in the postoperative period. It is also worth noting the high cost of implants and artificial erection, which is crucial for some young patients. Countries around the world are searching for new methods to restore physiological erectile function in patients after RPE. Recently, the attention of specialists has been drawn to the possibility of restoring the innervation of the penis by transplanting a nerve graft. The study aimed to provide a general idea of the ED treatment in patients after RPE by nerve graft transplantation with the development and realization of our own described at the end as a clinical case.