ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. The implementation of an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol may improve quality of life in patients undergoing subtotal cystectomy followed by intestinal reconstruction.
Objective. To evaluate the outcomes of subtotal cystectomy with intestinal reconstruction and postoperative recovery in patients managed using a tailored ERAS protocol.
Materials & methods. The study included 99 patients who underwent subtotal cystectomy for microcystitis with subsequent intestinal augmentation. The primary group, managed with the ERAS protocol, comprised 29 patients, while the control group included 70 patients.
Results. Utilisation of the ERAS protocol significantly reduced the incidence of postoperative complications according to the Clavien-Dindo classification. The ERAS group showed a higher proportion of patients with improved glomerular filtration rate (65.5% vs. 27.1%). A functional capacity of the neobladder exceeding 200 ml was more frequently observed in the ERAS cohort (69.0% vs. 34.3%). Residual urine volume greater than 100 ml was absent in the ERAS group but present in 20% of controls. Passage of flatus occurred on average 16h postoperatively in the ERAS group, compared to 25h in controls. Mean time to first defecation was 35h in the ERAS group and 49h in the control group.
Conclusion. Application of the ERAS protocol in patients undergoing augmentation ileocystoplasty substantially decreases postoperative complications, facilitates better renal function recovery, achieves superior functional voiding parameters, and accelerates restoration of bowel motility.
Introduction. The issue of concomitant renal parenchyma damage during extracorporeal shock wave exposure (ESWE) remains relevant due to the lack of a unified concept regarding the mechanism of renal parenchyma injury.
Objective. To elucidate the mechanisms of renal injury and protection during ESWE considering histomorphological and functional changes in experimental animals.
Materials & methods. The study was conducted on 50 sexually mature non-linear male white rats weighing 240–290 grams. The animals were randomly divided into two groups: an intact animal group (control group, n = 10) and a group of animals (n = 40) that underwent a single ESWE. Subsequently, euthanasia was performed on the animals after ESWE at 1 (n = 10), 3 (n = 10), 7 (n = 10), and 14 (n = 10) days under general anaesthesia via decapitation. Blood sampling was performed via cardiac puncture for research purposes. The kidney subjected to ESWE was used for homogenate preparation and histomorphological studies. Markers of free radical oxidation were studied: protein carbonyl groups (PCG) and malondialdehyde (MDA), reflecting the degree of damage to the renal tubular epithelium. Additionally, antioxidant defence (AOD) enzymes in the renal homogenate were determined, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), and reduced glutathione (GSH), reflecting the degree of renal antioxidant protection. Functional renal impairments in experimental animals after ESWE were assessed by measuring urea and creatinine levels in blood serum. Histomorphological assessment of changes in the kidneys under the influence of RSWE was carried out when collecting material at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after ESWE. The excised material was subjected to light optical and microscopic examination.
Results. Following ESWE to the kidney, from days 1 to 3, there is an activation of free-radical oxidation processes of proteins and lipids in the nephroepithelium (protein carbonyl groups, malondialdehyde), accompanied by a decrease in the activity of antioxidant defense enzymes (SOD, GPx, GR, GSH). This ultimately leads to membrane-destructive changes, cell death of the nephroepithelium, and alteration of kidney tissue. By day 7, pronounced histomorphological changes contribute to impaired renal function, as evidenced by increased urea and creatinine levels in the blood serum. Only by day 14 do markers of kidney damage, its histomorphological structure, and functional capacity approach normal levels. The analysis of indicators of free-radical oxidation of proteins and lipids in the nephroepithelium, assessment of antioxidant enzyme activity, and renal functional capacity, along with histomorphological changes after ESWE on days 1, 3, 7, and 14 of the study, allowed for clarification of the mechanism and stages of damage and recovery of the structural and functional renal parameters in experimental animals.
Conclusion. Mechanisms and temporal stages of kidney damage and recovery after ESWE have been identified in experimental animals.
Introduction. Drainage of the upper urinary tract using a temporary internal ureteral stent is frequently associated with significant stent-related symptomatology in many patients and constitutes a major contributor to functional impairment during the stent indwelling period.
Objective. To evaluate temporary disability in patients with ureteral stent. To compare clinical symptoms, the nature of work, the patient’s subjective assessment of his ability to work, medical and social confirmation of the temporary disability.
Materials & methods. The study included 134 officially employed patients whose duration of upper urinary tract stenting did not exceed two months. Patients were asked to respond to five questions regarding their assessment of well-being and work capacity during the stent indwelling period. Responses to the questions were obtained from all respondents.
Results. Stent-associated symptomatology was observed in 76.1% of patients. Throughout the entire duration of upper urinary tract drainage, 61.9% of patients remained functionally incapacitated. Notably, 25.3% of those classified as incapacitated were asymptomatic with respect to the presence of the stent. Conversely, 64.9% of all patients reported preserved work capacity. The proportion of patients formally exempted from physically demanding occupational activities exceeded that of those excused from mentally demanding work (59.3% vs 45.3%, respectively).
Conclusions. Drainage with an internal stent in most cases justifies assigning the patient a temporary disability status. When determining temporary incapacity for work, the physician should base their decision on the following parameters: presence of local symptomatology, nature of the patient's occupational activity, and the patient's subjective assessment of their condition.
Introduction. Laparoscopic transvesical adenomectomy (LTA) is the method of choice for managing large and giant BPH. This method is characterised by effective correction of bladder outlet obstruction, low incidence of hemorrhagic complications and incontinence, reduction of postoperative recovery time, as well as improvement of patients' quality of life.
Objective. To determine the functional state of the detrusor pre- and post-LTA in patients with large and giant BPH.
Materials & Methods. This retrospective study is based on the results of treatment of 36 patients who underwent LTA for BPH. Inclusion criteria: prostate volume over 80 cc, maximum urine flow rate (Qmax) below 15 ml/sec, no history of lower urinary tract infection and neurogenic urination disorders; no history of transurethral surgery. All patients underwent filling and voiding cystometry immediately before surgery and again 3 to 6 months postoperatively.
Results. The mean age of the patients was 65.8 ± 4.21 years. The average prostate volume was 148.5 ± 17.9 cc, and the mean total IPSS score before treatment was 19.4 ± 2.3 points. Qmax ranged from 3.2 to 11.3 ml/s, with a mean value of 6.2 ± 1.6 ml/s. No patients experienced complications greater Clavien-Dindo I in the early postoperative period. Postoperatively, there was a statistically significant decrease in detrusor pressure from 20.29 (± 2.9) to 11.24 (± 2.9) cm H₂O, as well as an increase in Qmax from 6.24 (± 1.61) to 25.1 (± 5.05) ml/s.
Conclusions. LTA is an effective and safe method of surgical treatment of BPH both from the perspective of common complications and from the perspective of functional detrusor disorders.
Introduction. Ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) is the most common indication for surgical intervention in the upper urinary tract in paediatric patients. We conducted a comparative analysis of outcomes following robotassisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty (RAP) using the da Vinci Xi system versus conventional laparoscopic pyeloplasty (LaP).
Objective. To comparatively evaluate the outcomes of RAP and LaP in children.
Materials & Methods. The study included 40 patients who underwent pyeloplasty. Patients were divided into two groups: Group 1 comprised 20 patients treated with RAP, and Group 2 comprised 20 patients treated with LaP. All procedures were performed by the same surgeon.
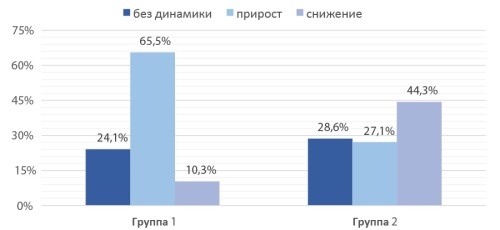
Results. There were no conversions in either group. In the RAP group, the mean operative time was 144.2 ± 25.9 min; docking time averaged 21.7 ± 2.6 minutes; and console time for the surgeon was 87.8 ± 20.4 min. In the LaP group, the mean operation duration was 121.8 ± 39.9 min; average surgeon time was 90.0 ± 20.0 min. The mean postoperative hospital stay was 6.6 ± 1.4 days after RAP and 7.5 ± 2.8 days after LaP (p = 0.198). At six months post-pyeloplasty, the mean anteroposterior renal pelvic diameter was 18.3 ± 11.3 mm in Group 1 and 19.7 ± 6.1 mm in Group 2 (p = 0.632).
Conclusion. Comparative analysis of the efficacy and safety of RAP and LP for UPJO in children reveals comparable results in operative duration and postoperative regression of pelvicalyceal dilatation in both groups. A key advantage of RAP over LaP is the preservation of the surgeon’s physical condition throughout anastomosis formation, enabling maximal precision and avoiding compromises between desired intracorporeal suture quality and actual outcomes, which are otherwise limited by the inevitable physical fatigue associated with laparoscopic access.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
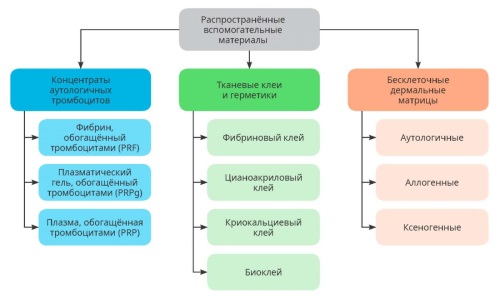
Hypospadias is the most prevalent congenital malformation of the male urogenital tract and the most common penile anomaly. This literature review delineates the most frequently performed hypospadias repair techniques and highlights the evolving paradigms in its surgical management. In recent years, significant attention has been directed towards the application of adjunctive biomaterials in hypospadias surgery. These materials are employed to provide an additional layer over the neourethra and the suture lines, particularly in cases where optimal local tissues, such as the dartos fascia or tunica vaginalis, are deficient or unavailable. Analysis of published evidence and statistical data indicates that autologous platelet concentrates, specifically Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), yield the most favourable outcomes. The use of PRP presents novel avenues for advancement in urethral reconstructive surgery. Investigations into its mechanism of action suggest that PRP can stimulate tissue regeneration, modulate anti-inflammatory responses to expedite wound healing, promote neoangiogenesis within the affected tissues, and enhance their vascularisation. This evidence points to the potential efficacy of topical PRP application in managing patients with compromised wound-healing potential and significant alterations in the morpho-functional characteristics of the urethral tissues.
Introduction. Lichen sclerosus (LS), also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO), is a chronic inflammatory dermatosis affecting the skin and mucous membranes, frequently with genital involvement. In men, LS induces sclerotic changes of the foreskin, glans penis, and urethral meatus. This can lead to phimosis and meatal stenosis, and in severe cases, to the development of urethral strictures.
Objective. To evaluate current treatment methods for BXO-associated urethral strictures and their outcomes.
Materials & Methods. A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA protocol (PROSPERO CRD420251005196). The review included 18 studies that met the following eligibility criteria: male patients with urethral strictures secondary to histologically confirmed BXO, a minimum of 5 patients per study, and reported treatment outcomes. Reviews, case reports, and publications without differentiated BXO-specific data were excluded. A meta-analysis was performed to calculate the pooled efficacy of various treatment modalities (both conservative and surgical). Subgroup analyses were conducted (comparing, for instance, one-stage vs two-stage urethroplasty), with assessment of heterogeneity (using the I² statistic) and potential publication bias (utilising a funnel plot).
Results. The pooled data from the 18 studies, encompassing over 600 patients, were analysed. Conservative management, such as urethral dilatation and intracavitary steroids, provided temporary symptomatic relief in a significant proportion of patients, with a reported success rate of 80–90% at 2–3 years. However, disease progression requiring reconstructive surgery was observed in 10–20% of cases. One-stage urethroplasty with buccal mucosal graft demonstrated high efficacy, with a pooled success rate of 85% (95% CI 80–90%) over a mean follow-up of 3 – 5 years. Twostage urethroplasty was reserved for cases with extensive stricture disease; its outcomes were comparable (75 – 85% success), although some case series reported a risk of stricture recurrence between stages. As a palliative measure, perineal urethrostomy achieved a durable restoration of voiding, with a long-term success rate exceeding 90%. The principal complications included stricture recurrence (up to 15 – 20% at 5 years) and isolated cases of fistula formation and neomeatal stenosis; severe complications were uncommon. The meta-analysis found no statistically significant difference in outcomes between single-stage vs two-stage reconstructions (relative risk of recurrence 0.95; p > 0.05). The use of adjunctive postoperative topical steroid therapy was associated with a reduced incidence of recurrence.
Conclusion. BXO-associated urethral strictures are characterised by higher recurrence rates compared to strictures of other aetiologies, necessitating a distinct management approach. Conservative management may be suitable for a select group of patients, particularly those with contraindications to surgery or awaiting reconstruction; however, definitive cure is only achieved through surgery. Single-stage urethroplasty with buccal mucosa graft transplantation is the treatment of choice for BXO-associated strictures and provides optimal functional and cosmetic outcomes. In cases of extensive stricture disease, a staged reconstructive strategy or urethrostomy should be considered. A multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists is essential for the postoperative control of underlying BXO disease activity. Further research, including RCTs, is required to optimise medical therapy for BXO and to improve the long-term success of reconstructive surgery.
Introduction. Retrograde ejaculation (RE) has many well-described causes, ranging from pharmacological disturbances to interference with innervation mechanisms during surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Objective. To explore the anatomical and physiological aspects of retrograde ejaculation (RE) and to critically evaluate published evidence regarding the preservation of antegrade ejaculation following various ejaculatory-sparing procedures, drawing on the latest medical literature.
Materials & Methods. A comprehensive literature search was performed across PubMed, MEDLINE, and Scopus databases for the period 1966–2024. Differential searches employed the keywords «benign prostatic hyperplasia», «retrograde ejaculation», «ejaculatory-protective techniques», «transurethral enucleation», «assessment of ejaculatory disorders», and «physiology of ejaculation». In total, 1126 sources were screened, with 51 articles included for review.
Results. The main perspectives on the anatomo-physiological basis of RE were identified, alongside the subjective methods used to assess ejaculatory disorders. Additionally, current ejaculatory-protective techniques and alternative surgical approaches for the treatment of BPH were highlighted. Advances in high-tech medical care for BPH have already provided patients undergoing transurethral procedures with the possibility of fathering children. Consequently, patient expectations today extend beyond mere symptom relief to include improved psycho-emotional wellbeing and enhanced quality of life in social aspects.
Conclusion. Implementation of ejaculatory-sparing surgical techniques markedly improves the psychosocial outcomes and overall quality of life for patients treated for BPH. Continued investigation into the mechanisms of RE, as well as the refinement of surgical methods, is warranted to further mitigate this complication and optimize patient-centred care.
CURRENT STATE-OF-THE-ART
The article presents data on factors contributing to impaired spermatogenesis and the development of semen disorders (SD). The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of SD and male infertility is demonstrated. Various therapeutic approaches to SD are outlined, with particular emphasis on the role of antioxidant therapy in its management. Evidence is provided highlighting the high efficacy of melatonin and its beneficial impact on semen parameters.
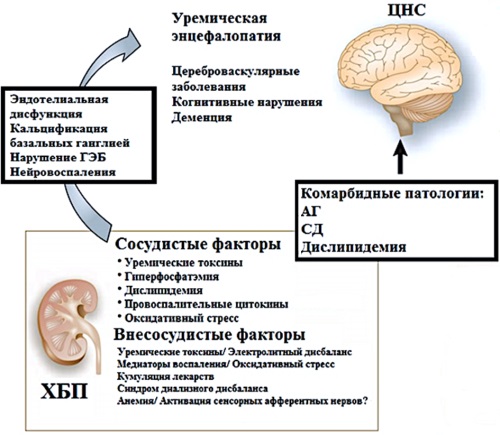
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most significant risk factor in the development of stroke; the latter remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally. CKD patients, especially at the end-stage renal failure and on dialysis, have a very high risk of stroke by 5 – 30 times, with a mortality rate reaching almost 90%. CKD is associated with both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. In addition to general risk factors, increased cerebrovascular risk is due to several mechanisms associated with CKD, such as platelet dysfunction, blood clotting disorders, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and an increased risk of atrial fibrillation. In addition, CKD can significantly affect the effectiveness of stroke treatment and prevention. Therefore, it is important to study the factors contributing to the development of stroke in this vulnerable population group to apply preventive strategies more effectively. This article examines the epidemiology and pathophysiology of the association between CKD and stroke, as well as the impact of CKD on stroke outcomes. The study aimed to review scientific articles published over the past twenty years on the relationship between CKD and stroke risk. To achieve this objective, a search was used for the keywords «chronic kidney disease», «stroke», «risk», «stroke risk factors» in the databases PubMed, Google Scholar and eLibrary.
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
The aim of this study was to develop the sixth set of guidelines in a series produced by the International Alliance of Urolithiasis (IAU), providing a clinical framework for the management of paediatric patients with urolithiasis based on the best available published evidence. All recommendations were synthesised following a systematic review and critical appraisal of the literature indexed in the PubMed database from January 1952 to December 2023. Each recommendation was graded according to a modified GRADE methodology. The guidelines were ratified by Panel Members after thorough review and discussion of the evidence. The recommendations address key topics including aetiology, risk factors, clinical presentation and symptoms, diagnosis, conservative management, surgicalinterventions, prevention, and follow-up. Notable parallels exist in the management of primary stone episodes between paediatric and adult patients, particularly regarding conservative treatment approaches and technological advancements facilitating less invasive stone removal. Additionally, preventive strategies aimed at reducing recurrence – such as adequate hydration, well-structured dietary modifications, and the selective use of pharmacological therapies – are anticipated to yield favourable outcomes in paediatric stone formers. Given the variability in the severity of metabolic abnormalities and anatomical anomalies, a meticulously planned, close follow-up programme is essential for each paediatric patient to mitigate the risk of future recurrences.