EDITORIAL
The article summarises the guidelines of the International Continence Society (ICI-7) for the management of male and female urinary incontinence. The author's opinion on the state of the problem from the perspective of its relevance in the field of modern practical urology is expressed.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
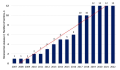
Introduction. Until recently, open ureteral reimplantation was considered the gold standard for the surgical treatment of ureterovesical junction (UVJ) pathologies. The introduction of minimally invasive ureteral reimplantation (MIUR) for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) and primary obstructive megaureter (POM) in children started in the 1990s. However, studies describing national trends in the use of minimally invasive and open approaches in the surgical treatment of UVJ pathology in children are limited.
Objective. To describe changes in the use of MIUR and open ureteral reimplantation (OUR) between 2007 and 2022 in some regions of the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus and compare the results and complication rates of the two surgical approaches.
Materials & methods. The study includes 1273 patients (1793 ureters), operated on for UVJ pathology in the period from 2007 to 2022. MIR was performed in 1356 (75.6%) ureters (913 for VUR and 443 for POM). The studied parameters included an annual amount of reimplantation, the age of patients, the frequency of intra- and postoperative complications, as well as the medium-term results of operations.
Results. The use of MIUR techniques has increased significantly over time, and in 2022, seventy-five percent of surgeries were performed using MIUR. Analysis of the rate of adoption of MIUR by clinics showed that those that began using it first experienced a significant increase in frequency of use after 4 to 6 years, while those that started later took 2 to 3 years to achieve a significant positive trend. There were 5 (0.4%) intraoperative complications in the MIUR group. All these complications were classified as grade I according to the Satava grading system. There was no significant difference between MIUR and OUR in terms of postoperative complication rates (6.6% vs. 7.6%, p = 0.8). The efficiency of reimplantation was 96.6% in the MIUR group compared to 95.9% in the OUR group for POM and 96.2% in the MIR group compared to 94.6% in the OUR for VUR.
Conclusion. In the regions of Russia involved in the study, there has been a trend towards completely replacing open surgery with minimally invasive techniques. Regarding complication rates and efficacy, MIUR is not significantly different from OUR.
Introduction. The method of choice for surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with a volume of more than 80 сс is holmium enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP). However, laser enucleation of the prostate is associated with limitations that carry both a clinical and financial burden. Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy (LSP) has now emerged as an alternative to transurethral procedures. In addition to ensuring clinical efficacy, optimal approaches to surgical management of large-volume BPH must also be financially viable, which underlines the significance of this study.
Objective. To conduct a comparative economic analysis of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate and laparoscopic retropubic simple prostatectomy combined with temporary clamping of the internal iliac arteries and vesicourethral anastomosis (LSP + TCA + VUA).
Materials & methods. An economic analysis of the results of HoLEP (214 people) and LSP + TCA + VUA (215 people) was conducted in a multicenter, open-label study. The economic analysis aimed to calculate the direct costs associated with surgery, as well as indirect costs related to hospitalization. A comparative analysis of drug prescriptions was conducted, including an assessment of costs for conservative treatment during hospitalization and the postoperative period. The economic losses associated with the duration of patients' temporary disability were calculated as the total loss in gross domestic product (GDP) production.
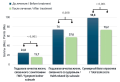
Results. The cost of basic surgical equipment was 15,701,000.0 and 36,927,827.0 rubles (₽) for LSP + TCA + VUA and HoLEP, respectively. The median direct costs for performing LSP + TCA + VUA and laser enucleation HoLEP was 54,990.6 [49,870.5; 67,850.8] and 69,158.9 [65,005.9; 72,351.7] ₽, respectively. The median of indirect costs in the LSP + TCA + VUA and HoLEP groups was 71,251.0 [68,039.0; 73,103.0] and 80,451.0 [74,423.0; 83,501.0] ₽, respectively. The indicators of lost profits in GDP production per person were 5,398.4 and 6,167.9 ₽ in the LSP + TCA + VUA and HoLEP groups, respectively.
Conclusion. The rationale for the use of LPA + VPA + UCA in the surgical treatment of large-volume BPH is based on economically justified advantages compared with HoLEP.
Introduction. Teaching the skill of renal cavity puncture remains a pressing issue for both resident trainees and practicing physicians. Because patient-based training is ethically questionable and can be unsafe in terms of complications, training models have been created to practice skills.
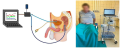
Objective. To compare two non-biological simulators for renal cavity puncture under ultrasound guidance: “UROSON”, GEOTAR, Russia and the kidney phantom “SafeToAct”, Estonia.
Materials & methods. The study involved 40 young doctors with no experience in kidney puncture. Group 1 (20 people) practised on the UROSON simulator (GEOTAR, Russia). Group 2 (20 people) trained on a kidney phantom (SafeToAct, Estonia). Both simulators were evaluated by doctors before and after practice, as well as in the long-term period for 3 and 6 months. The assessment was carried out using a Likert scale.
Results. The UROSON was rated higher (p < 0.05) according to the results of the comparison of the parameters (colour and consistency, visualisation of the cavity and calyx on ultrasound). Renal cavity visualisation of the UROSON simulator was rated as "good" throughout the study. Visualisation deteriorated by 6.9% after six months of use. Meanwhile, the SafeToAct kidney phantom showed a 64% deterioration in visualisation after one month of use. The SafeToAct kidney phantom was not evaluated later point because it became unusable. Both simulators had "tracks" after punctures. The UROSON had 30% and the SafeToAct kidney phantom 100% (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion. The UROSON simulator can be used for training, master classes and accreditation of specialists. This simulator can be used for a long time.
Introduction. Numerous studies have suggested that lower urinary tract infections may be involved in the development of overactive bladder (OAB) in patients who are resistant to standard treatment. In these cases, treatment targeting all stages of disease progression could be beneficial.
Objective. To evaluate the efficacy of Vesusten® in management of OAB in women with chronic recurrent cystitis.
Materials & methods. The study involved 40 patients diagnosed with OAB and chronic recurrent cystitis. All patients received Vesusten® as therapy for OAB. They received 5 mg of the medication intramuscularly three times per week for a total of 10 doses. The study included three stages: a screening period lasting up to 14 days; the stage for assessing the effectiveness of therapy (42 days from the start of therapy, including the therapy period + further follow-up after the end of therapy); follow-up period — 180 days + 14 days from completion of treatment.
Results. It was revealed Vesusten® clinical effectiveness on the severity of OAB symptoms and the quality of life of patients. hree weeks after the end of treatment, there was a statistically significant decrease in the severity of OAB symptoms on the Patient Perception Index of Urgency and Symptoms (PPIUS) (2.2 ± 1.0 vs 0.95 ± 1.0 points) and TUFS (28.4 ± 11.6 vs 5. 1 ± 6.4 points), a decrease in the number of urinations during the day (11.5 ± 2.2 vs 8.8 ± 2.7 episodes) and at night (3.5 ± 1.8 vs 1.4 ± 1.5 episodes) time (p < 0.001). The nighttime urination frequency decreased by more than 2.5 times, while the proportion of patients who did not wake up at night for urination increased from 10 % to 35%. Evaluation of the Overactive Bladder Questionnaire (OAB-Q) after the completion of treatment compared with the initial data showed a statistically significant improvement in quality of life related to the severity of OAB symptoms (24.8 ± 7.5 vs 15.7 + 6.4 points; p < 0.001), and with general health status (74.0 ± 31.7 vs 57.6 ± 22.1 points; p = 0.0087). The average duration of the relapse-free period, including the course of Vesusten® treatment and the follow-up period, significantly increased to 42.90 ± 9.64 weeks in comparison with the duration of the relapse-free period before patients’ inclusion in the study — 17.96 ± 7.75 weeks (p < 0.001). During the clinical study, eight women experienced exacerbations of chronic cystitis (20%).
Conclusion. Study results suggest that the drug Vesusten® may be an effective treatment for OAB in combination with chronic recurrent cystitis. Based on our findings, we believe that Vesusten® can be considered as a potential treatment option for patients with chronic cystitis.
Introduction. Post-coital cystitis is not a separate nosologic unit, but belongs to recurrent urinary tract infection. Surgical interventions are only recommended in cases where conservative treatment fails to provide relief.
Objective. To evaluate the results of post-coital cystitis prophylaxis in urethral transposition.
Materials & methods. A retrospective study of 46 patients who underwent surgical treatment in the volume of transposition of the distal urethra from 2011 to 2013 was conducted in the clinic of Urology of MSUMD based on the Spasokukotsky Moscow Clinical Hospital.
Results. Based on subjective reports from patients, urethral transposition was found to be effective in 71.7% of cases. Half of the participants reported no recurrence of cystitis within the past year, and over half (67%) reported no inflammatory episodes after undergoing surgery.
Conclusion. The findings suggest that urethral transposition is an effective and relatively safe treatment option for patients with post-coital cystitis who have failed to respond to conservative treatments.
Introduction. There is evidence of a connection between infectious and inflammatory lesions of the lower urinary tract and bladder cancer (BCa). However, there is virtually no data on the urine microbiota of middle-aged and elderly men with suspected BCa. This knowledge is extremely important from the point of view of studying the role of the infectious-inflammatory hypothesis in the genesis of BCa.
Objective. To conduct a comparative assessment of the microbiota of bladder urine obtained during natural urination and bladder catheterization through standard and extended cultural studies in men with a presumptive diagnosis of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
Materials & methods. The prospective comparative study with consecutive patient recruitment included 23 men older than 45 years with suspected NMIBC based on clinical, laboratory and sonographic data, as well as with no history of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, including sexually transmitted infections and recurrent infections of other organs and systems. A midstream urine samples and catheter-drained urine immediately before urethrocystoscopy were subjected to bacteriological analysis. Urine culture study was carried out using a standard set of nutrient media under aerobic cultivation conditions and an expanded set of nutrient media under aerobic and anaerobic cultivation conditions.
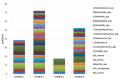
Results. An anaerobic spectrum of microorganisms was predominantly detected in the urine of patients with suspected NMIBC. Moreover, Peptococcus spp. was more often found among anaerobic taxa. (70%), Eubacterium spp., Propionibacterium spp. (45% each, respectively), among representatives of the aerobes — Corynebacterium spp. (60%), S. lentus (up to 45%), S. haemolyticus (35%) and E. faecalis (30%). Data from a comparative analysis of the detection frequencies of microorganisms depending on the method of collecting material and the set of media for cultivation showed that more isolates are isolated in the midstream urine samples than in the study of catheter urine (2.9- and 1.9-fold with the standard and extended sets of media, respectively). In addition, when performing an extended bacteriological study compared to the standard method, the detection of microorganisms is 3.5-fold higher when examining an average portion of urine and 5.1-fold higher when examining catheter urine. The average number of microorganisms per one patient is also higher when using the extended method (midstream portion — 4.7 ± 1.9; catheterised urine — 2.3 ± 1.0) in comparison with the standard one (midstream portion — 1.3 ± 0.9; catheterised urine — 0.3 ± 0.5).
Conclusion. Middle-aged and older men with NMIBC are characterized by asymptomatic bacteriuria in the form of a wide range of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms. The urine pattern obtained with a urethral catheter contains a significantly narrower range of bacteria compared to the sample obtained through natural urination. It is advisable to carry out an extended cultural urine examination to study the characteristics of the microbiota / microbiome of the urine of the bladder immediately before the urethrocystoscopy procedure by collecting urine with a urethral catheter.
Introduction. In patients with suprapubic tube (SPT) surgical restoration of voiding is not 100% successful. Sometimes urination is inadequate or not recovered at all.
Objective. To determine factors influencing the outcomes of benign prostatic hyperplasia / benign prostate obstruction (BPH/BPO) surgery in patients with cystostomy drainage.
Materials & methods. The study included 52 men with suprapubic tube initially placed for urinary retention caused by prostate hyperplasia. Afterwards, all patients underwent transurethral resection of the prostate. The age of the patients ranged from 48 to 85 years old. Clinical and urodynamic data of the patients were analysed, restoration of adequate urination after surgery was evaluated as well. We took into account patients age, IPSS scores, bacterial growth in the urine culture test, number of episodes of urinary retention, volume of urinary retention prior to cystostomy, prostate volume, intravesical prostate growth, detrusor overactivity and ability to void in the presence of SPT.
Results. We were unable to achieve adequate bladder emptying after transurethral resection of the prostate in 4 (7.6%) patients. These patients required continued bladder drainage after surgery. In 48 (92.4%), adequate urination was restored after surgery and cystostomy drains were removed. Patients with one or more of the following characteristics were more likely to experience a failure of surgical treatment: age over 80, residual urine volume over 1500 mL, and absence of overactive bladder.
Conclusion. The study indicates that use of cystometry prior to BPH/BPO surgery is reasonable in such patients. Feasibility of BPH/BPO surgery for this group of patients should be considered individually.
Introduction. The gold standard of treatment for intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB) in combination with intravesical therapy. However, this procedure may cause serious complications. At the same time, studies of various lasers for the treatment of NMIBC have demonstrated their safety and efficacy. Despite this, the topic has not yet been fully explored and is not widely practiced in clinical oncology, making further research necessary.
Objective. To compare thulium and holmium lasers with conventional TURB for management of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
Materials & methods. In our study, depending on the treatment approach, 84 NMIBC-patients were divided into three groups. Group 1 included 27 patients (34.14%), who underwent laser thulium bladder resection; group 2 included 25 patients (29.76%), who underwent laser holmium bladder resection, and group 3 included 32 patients (38.1%), who underwent standard TURB. Prior to surgery, all patients received a standard set of preoperative general clinical and instrumental examinations for bladder cancer, and the choice of surgical approach was based on informed patient consent, taking into account the benefits and risks of the three treatment options. All surgeries were performed in accordance with established protocols.
Results. In the TURB group, the surgery time was the longest and totalled in 20.5 ± 7.4 min. Laser technologies reduce the surgery time to 16.3 ± 5.3 min for a holmium laser and to 14.7 ± 5.2 min for a thulium laser. Also, in groups 1 and 2, a shorter duration of postoperative bladder irrigation was noted (4.4 ± 1.8 and 4.7 ± 1.6 hours) and shorter periods of postoperative bladder catheterisation (1.5 ± 0.08 and 1.6 ± 0.08 days) compared to group 3, where these indicators were 16.4 ± 2.5 hours and 2.5 ± 0.13 days, respectively. Among patients undergoing either holmium or thulium surgery, a higher rate of disease-free survival has been noted. Independent prognostic factors that influence the prognosis of NMIBC in all groups include the type of surgery, history of bladder tumors, and pathological stage.
Conclusion. The use of laser technology, such as thulium and holmium laser, in bladder wall resection for NMIBC shows promising results and provides a good clinical outcome that is comparable to (and in some cases, superior to) standard TURB.
Introduction. For the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome (OAB), injection of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) has been shown to be effective. However, there is a need for a less invasive method for administering BoNT-A, which could significantly expand the treatment options for OAB.
Objective. To assess the impact of tizol on the absorption of BoNT-A by the bladder mucosa and compare it to the individual absorption of BoNT-A.
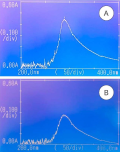
Materials & Methods. Dialysis through the mucous membrane of the сalf bladder was used as an experimental model to study changes in bioavailability of BoNT-A complexed with tisol (BoNT-A + T) and pure BoNT-A solution during in vitro experiment. After dialysis, the BoNT-A concentration in both samples was determined using a spectrophotometer. Dialysis curves were plotted according to the data obtained. Kruvchinsky equilibrium dialysis method was used to determine botulinum toxin A bioavailability. The UV spectrophotometry method was used to determine the concentration of BoNT-A in the acceptor medium by reaction of BoNT-A with Benedict's reagent.
Results. It was established that the maximum concentration of BoNT-A diffused into the acceptor medium from the blend of the test substance with tizol after nine hours. The area under the curve for dialysis of BoNT-A + T exceeds the area under the curve of pure BoNT-A by almost 20%, suggesting an improvement in the drug's bioavailability when blended with tizol.
Conclusion. Based on our experiment, it was found out that the BoNT-A + T has greater bioavailability than a solution of pure BoNT-A. However, the diffusion rate of the component mixture is sufficiently low.
Introduction. Radical prostatectomy (RP) stands the gold standard method of treatment for localised prostate cancer. Pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) is a common surgical procedure that can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Lymphocele is the most common complication after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) and PLND.
Objective. To develop a surgical technique aimed at reducing the incidence of lymphocele in patients who underwent RARP with TL and to evaluate its efficacy and safety.
Materials & methods. The study included 49 patients who underwent RARP and PLND. The patients were divided into 2 groups: group 1 — patients with free peritoneal flap fixed to the pubic bone after RARP and PLND (n = 25) and group 2 — control group «without peritoneal flap fixation» (n = 24). The average follow-up period was 3 months.
Results. No significant differences in clinical parameters were observed between the groups in perioperative period. In postoperative period lymphocele was diagnosed in 5 (10.2%) patients: group 1 — 1 (4%) patients, group 2 — 4 (16.7%). There were no significant differences in lymphocele volume between the groups. In group 1 lymphocele had no clinical manifestation. Symptomatic lymphocele was diagnosed in 1 patient (4.2%) from the control group.
Conclusion. The surgical technique of a free peritoneal flap fixation to the pubic bone combined with PLND after RARP may reduce the incidence of lymphocele if compared to the standard technique.
Introduction. Male infertility is a complex condition with many potential causes, including hormonal imbalances, anatomical problems, genetic factors, lifestyle factors and more. But today, there is a fairly large group of infertile men with unknown causes of the disease.
Objective. To analyze the taxonomic microbial diversity of testicular tissue and the urogenital tract of infertile men and to identify correlations between the microbiome and mastocytes in the testicular parenchyma.
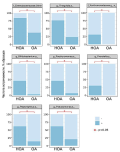
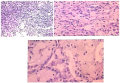
Materials & methods. The study was performed on testicular tissue samples from infertile patients with azoospermia (n = 33). All patients were divided into two groups based on the form of azoospermia: group 1 — infertile patients with non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) (n=21); and group 2 — infertile with obstructive azoospermia (OA) patients (n=12). The bacterial diversity of testicular tissue was studied by the method of high-performance new generation sequencing (NGS). Immunohistochemical staining with anti-MCT (Anti-Mast Cell Tryptase) was used to determine the IHC expression of mastocyte markers.
Results. The microbiome of patients with NOA differs markedly from the microbiome of patients with OA (p < 0.05). In group 1, representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae and Xanthomonadaceae families, the genera Finegoldia, Bifidobacterium, Porphiromonas, Prevotella, Peptoniphilus and Pseudomonas are significantly more often found. A distinctive feature of group 2 is the rare occurrence of the genus Prevotella. Histochemical analysis revealed mastocytosis in the in-between-canalicular stroma approximately in 83% of azoospermia cases. Mastocytes are found in tubule structures in 68% of cases and correlate with the microbiome of testicular tissue.
Conclusions. Injuries caused by mastocytes in the stroma and tubular structures are interrelated with the taxonomic diversity of testicular tissue. Moreover, the testicles of NOA-patients have a qualitatively and quantitatively more diverse spectrum both at the level of families and genera, unlike OA-patients.
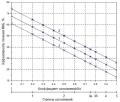
Introduction. Currently, single- and multifactorial criteria are employed to evaluate the quality of urolithiasis treatment utilizing lithotripsy. Among the most utilized single factors that influence the efficacy of urolithiasis therapy are the stone-free rate (SFR), the duration of lithotripsy, the level of intra- and post-operative complications, and hospital stay following lithotripsy. A more promising approach is the integrated indicator of the efficacy of urolithiasis management using the lithotripter, which considers all the aforementioned factors. It is an urgent task to determine the extent to which alterations in individual variables impact the value of an integrated assessment of the efficacy of laser lithotripsy-based urolithiasis intervention.
Objective. To study the dependence of the integral efficiency indicator on the magnitude of influencing factors in the treatment of urolithiasis using transurethral thulium lithotripsy.
Materials & methods. We used the method of mathematical modeling of the integral criterion for urolithiasis treatment efficacy using the Scilab v.6.02 software package to determine the extent to which individual factors influence the overall effectiveness of laser thulium lithotripsy.
Results. Graphical dependences of the index of urolithiasis treatment efficacy for lithotripsy on the complication rate (at different values of surgery time and dependence of urolithiasis treatment efficacy on SFR at different values of complication rate, surgery time and hospital stay) were obtained. A software system for determining the integral index of urolithiasis treatment efficiency for lithotripsy was developed.
Conclusion. The resulting dependencies of the index of urolithiasis treatment efficacy for lithotripsy can be used to evaluate the impact of the complication grade and the SFR on the value of the efficacy index and to devise measures to enhance it. The software developed for the calculation of this index allows to obtain the required value at different input influencing parameters.
Introduction. Urinary incontinence is a common complication of radical prostatectomy. The development of surgical techniques when performing radical prostatectomy that improve the function of urinary continence after surgery is actual.
Objective. To compare urinary continence functions in long-term follow-up after open and laparoscopic radical prostatectomy when only posterior or combined (anterior + posterior) reconstruction of the pelvic fascial spaces is performed.
Materials & methods. The study included 130 patients aged 63.0 [59.0; 68.0] years with local prostate cancer (сT1a-2сN0-xM0; 1 – 4 ISUP groups), subjected to non-nerve-sparing retropubic radical prostatectomy with posterior reconstruction and non-nerve-sparing extraperitoneal laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with isolated posterior or combined (anterior + posterior) fascial reconstruction of the pelvic fascial spaces. Postoperative continence function was studied at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months following surgery using a standard pad test.
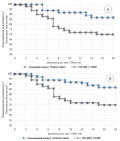
Results. The incidence of urinary continence was higher at all follow-up periods during laparoscopic surgery. From the 6-months follow-up, these patients did not have severe urinary incontinence. At the same time, the rate of growth of some patients who began to retain urine did not depend on the method of reconstruction of the pelvic fascial spaces. The use of combined reconstruction of the pelvic fascial spaces at 12-months follow-up showed an advantage in urinary continence over performing only posterior reconstruction. Such patients achieved urinary continence in 90% of cases compared to 80.0% of cases. At the same time, the restoration of urinary continence at all periods of observation had a relatively uniform linear rate of increase in the indicator.
Conclusion. Reconstruction of the pelvic fascial spaces during open and laparoscopic radical prostatectomy allows one to achieve satisfactory continuation in the postoperative period. However, higher efficiency is achieved when using a combined reconstruction technique.
CLINICAL CASES
Introduction. Partial nephrectomy is the treatment of choice for small renal tumors. There are other indications include tumors in a solitary kidney, multiple and bilateral tumors.
Сase presentation. A 67-year-old male presented with left flank pain and lower urinary tract symptoms. Computed tomography for abdominal and pelvis showed bilateral renal masses. After doing the essential laboratory tests and investigations, he underwent bilateral open simultaneous partial nephrectomies. After two days, he was discharged with no complains. Follow-up after three months showed no recurrence and acceptable renal function.
Discussion. Partial nephrectomy is increasingly used for the management of renal masses. The preservation of renal function with reduced morbidity and equivalent oncologic outcomes led to a paradigm shift away from radical nephrectomy.
Conclusion. Bilateral partial nephrectomy is feasible with both clinical and oncological good results.
Cross or transverse testicular ectopia is a rare congenital condition of the reproductive system that involves the migration of a testicle into the opposite inguinal canal, along with the presence of an inguinal hernia on the same side as the ectopic testicle. In the modern literature, there are discussions about diagnostic issues, particularly the use of ultrasound scanning and magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose this condition. However, it is the results of laparoscopic examination that determine the most accurate criteria for surgical treatment. Many publications discuss the choice of surgical tactics, including separate transabdominal orchiopexy, with or without laparoscopic assistance; transeptal orchiopexy on both sides of the scrotum; and rare cases of orchiopexy for both testicles on one side of the scrotum. Ultimately, the choice of surgery depends on the individual characteristics and needs of the patient, and the surgeon should make the decision based on these factors. The article describes, for the first time, a case of familial testicular ectopia with bilateral inguinal hernia in siblings who underwent surgery using laparoscopic assistance. The method used was single-trocar laparoscopic access with transscrotal transeptal orchiopexy and simultaneous bilateral puncture of the inguinal ring and suture. During the long-term follow-up period (50 and 20 months after surgery) in both siblings, there were no signs of malformation or atrophy of the gonads.
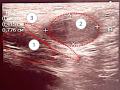
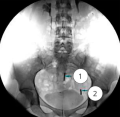
Introduction Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are widely used worldwide. One of the rare but serious complications is uterine perforation and the penetration of an IUD through the uterine wall into the bladder. In this report, we present two cases of IUD removal from the bladder wall.
Clinical case. Two patients were referred for recurrent episodes of dysuria. Medical imaging and cystoscopy revealed a foreign body in the bladder wall, which was confirmed to be an IUD that had been inserted into the uterine cavity several years prior and partially migrated into the bladder lumen. Both patients underwent successful transurethral surgery, with complete removal of the IUD without fragmentation.
Discussion. The removal of the IUD through the bladder did not cause any complications, and the patients were discharged from the hospital after five days. The translation of the IUD is possible if there is partial or complete damage to the wall of the cervix, isthmus or uteral body during the installation of the device.
Conclusion. Patients with an IUD in place and frequent episodes of acute cystitis should have a cystoscopy to rule out bladder perforation caused by the IUD. The removal of the IUD through the urethra using an cystoscope and forceps is a relatively simple procedure that does not usually cause any intraoperative, immediate or delayed postoperative complications.