ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. There are various data in the literature regarding the boundary values of the width and length of the neck, as well as the angle between the pelvis and infundibulum. These parameters distinguish between patients with high and low risk of residual fragments.
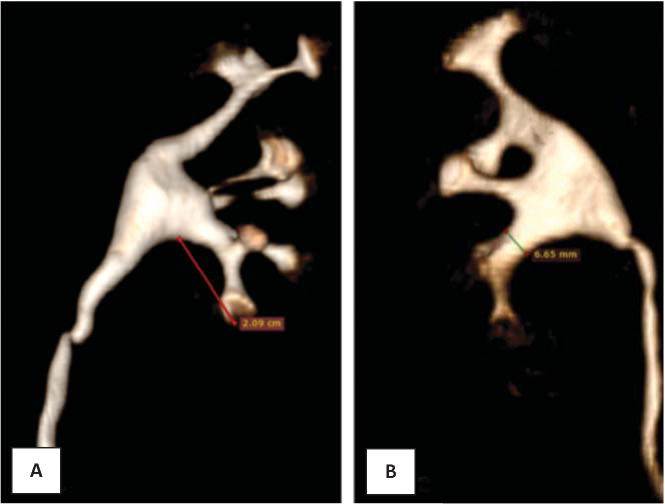
Objectives. The purpose of this study is to examine the lower calyceal group anatomy of patients without kidney stones and to compare the obtained results with previously published one. Materials and methods. Retrospective stage: Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen was obtained in 120 patients (which was performed on them from March 2018 to 2019). CT scans of 100 patients (200 kidneys) were included in analysis after exclusion of inappropriate data. The infundibulopelvic angle was measured using the two most common methods by Sampaio and by Elbahnasy. Also, the length and width of the lower infundibulum were measured. All results were divided into four groups depending on the Sampaio classification of pyelocaliceal system (PCS). Results. The average value of the infundibulopelvic angle according to the Elbahnasy’s method is 74.1±15.1, and according to the Sampaio method is 101.8±20.1. When measured by the Elbahnasy method, an angle of more than 90 ° is more likely to occur with A1 structure variant, and less than 90 ° is more likely to occur in the PCS corresponding to the A2 variant. The average length of the lower infundibulum is 20.7±2.8 mm. The higher value of the lower infundibulum width was in group A1. Conclusion. In our study, all parameters were out of risk of both the low success of the operation and the development of kidney stone indicated in previously published studies. This fact can confirm the influence of the anatomy of the lower calyceal group on the development of kidney stones.
Background. During a long time, men appraise the problem of overweight as a natural process of aging in the conditions of social demand and physical inactivity. Therefore, there is usually no reason to see a doctor and conduct a clinical examination. In this regard, obesity-associated metabolic diseases are often diagnosed late in the complication stage.
Objective. Assessing the effects of obesity and androgen deficiency on the development of metabolic disorders in men.
Materials and methods. 120 men with obesity aged 29–56 years who considered themselves healthy were examined. The patients were divided into two groups: in-group 1 included 56 people with a normal level of total testosterone (T), in-group 2 included 64 people with a level of total T less than 12.1 mmol / l, accordingly. The main indicators of carbohydrate, lipid, purine metabolism, and the level of sex hormones were investigated.
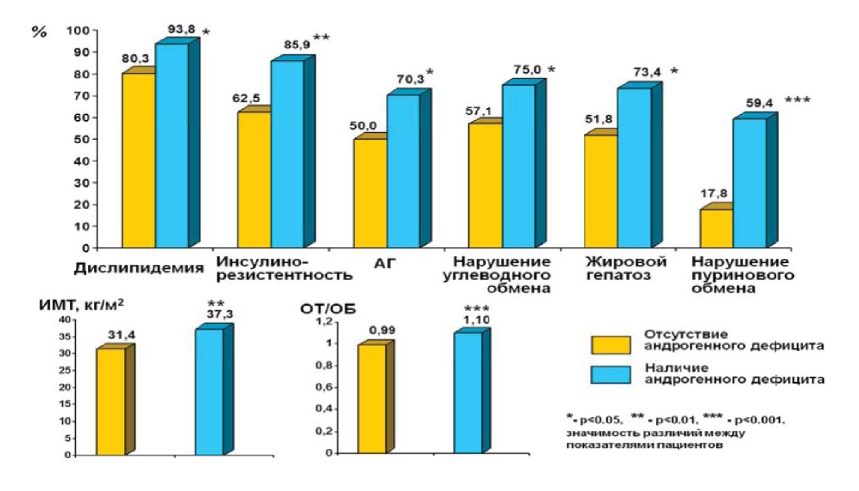
Results. Аnalysis of the metabolic status of obese men who considered themselves completely healthy revealed a high incidence of dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension, insulin resistance (IP), carbohydrate metabolism disorders and purine metabolism, and fatty hepatosis. The most significant changes were identified in the group of patients with testosterone deficiency.
Conclusion. Visceral obesity in men is a high-risk factor for the formation of metabolic disorders. Androgen deficiency completed obesity leads to the formation of more severe metabolic changes in patients and the development of erectile dysfunction. Men with visceral obesity, even in the absence of actively complain need careful examination. It should include, along with the assessment of biochemical indicators of metabolic status, also control of the level of total serum testosterone.
Background. Patients with first diagnosed prostate cancer, kidney cancer and bladder cancer, more than 25% of cases are diagnosed at stage IV disease at the primary visit in clinics. A characteristic feature of these types of tumors is a predisposition to bone metastasis. Bones failure at the treatment stages is diagnosed in 80% of patients already.
Objectives. Determine the most effective palliative analgesic radiotherapy regimens.
Materials and methods. Case histories of 41 patients with a diagnosis of osteolytic bone lesion were analyzed. The male / female ratio is 32/9. All patients underwent radiotherapy in the Radiological Division of the Rostov District Oncological Dispensary for the period from 2015 to 2018
Results. The direct effectiveness of the analgesic effect of large-fraction radiotherapy is slightly higher than that of single-fraction radiotherapy. However, the opposite trend was observed a month after the R-therapy end. It was determined that higher analgesic effect corresponds to higher values of a single focal dose (SFD).
Conclusion. This method deserves closer attention despite the low direct efficiency of single-fraction radiation. This is due to the high and persistent analgesic activity and the short duration of the course
DISCUSSION PAGE
Many publications in foreign and domestic papers are devoted to pyelonephritis in pregnancy. At the same time, aspects of the upper urinary tract (UUT) drainage, indications / lack of indications, and the duration of UUT drainage during kidney infections in pregnant women are bypassed. Etiological treatment of this pathology is well described in the European Association of Urology guidelines and American Urological Associations guidelines in accordance with the recommendations of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, there are no references to the management of patients with UUT dilatation, associated with pyelonephritis in pregnant women. The Russian Clinical Guidelines for Urology (2018) also contains very brief information on this issue. Thus, each urological clinic of the Russian Federation has formed its own views on the draining tactics for pyelonephritis in pregnant women, which our colleagues have been following for years and decades. This publication presents an analysis of the literature sources focusing on the current state of the problem of pyelonephritis in pregnancy and the «neсessity» of the UUP drainage. It is intended to initiate a review of the established «tradition» and avoid a significant number of catheter and stent-related complications.
Diagnosis and optimal treatment of urological conditions in pregnant have lots of controversy due to a lack of objective and evidence-based data. This is equally true in for acute gestational pyelonephritis patients, particularly in the context of indications for upper urinary tract ‘de-obstruction’/ draining, and catheter stay in situ time. This review is a compilation of current scientific data concerning upper urinary tract draining in patients with acute gestational pyelonephritis, as well analysis of our own data and results.
Pyelonephritis in pregnant women is an urgent problem for urology. In the Russian clinical guidelines, there are disagreements on the classification of pyelonephritis. This is probably the cause of its overdiagnosis in pregnant women, as evidenced by the increase in the statistical frequency of pregnant pyelonephritis. This situation is the reason for the unjustified etiotropic therapy of pyelonephritis in this category of patients. On the other hand, the diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis can cause an underestimation of the severity of the patient’s condition and increase the risk of an adverse outcome of the disease. Along with this, the literature has accumulated data on the absence of a morphological substrate of inflammation during periods of so-called remission, and that pyelonephritis should be considered as reinfection. All this call into question the eligibility of the term chronic in relation to pyelonephritis. In the available literature there are few data on the physiology of the urinary tract in pregnant women. Nevertheless, the accumulated experience indicates the safety of excretory function despite dilatation of the upper urinary tract. In addition, there are no studies indicating the benefits of drainage of both asymptomatic and symptomatic hydronephrosis in pregnancy. All this does not allow associating pregnant pyelonephritis with obstructive in non-pregnant patients, and asymptomatic dilatation of the upper urinary tract should be interpreted as a physiological state.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
It performed the analysis of literature data on modern approaches to the treatment of vas deference spermatic obstruction caused by epididymis cyst (EC). High medical and social significance of male infertility was noted, one of the etiological factors of which may be EC. It is shown that at present, minimally invasive methods of treatment of EC are widely used, not inferior in effectiveness and safety to traditional types of surgical treatment of this pathology. As one of such approaches, sclerotherapy of EC is considered an affordable and low-impact method, the use of which does not require large economic costs and can be used in young men of reproductive age. The results of studies showing high clinical efficacy and safety of EC sclerotherapy. It was noted that information on the this assesment of the impact on men fertility is practically absent in the available literature, which indicates the need for further clinical trials to studу on the possibility of sclerotherapy in the EC treatment.
CLINICAL CASES
A 26-year-old patient with cryptozoospermia turned to the International Center for Reproductive Medicine for infertility. The man underwent surgical treatment for right-sided cryptorchidism in childhood. Subsequently, he was repeatedly examined and treated for scrotal pain. An ultrasound examination of the scrotum revealed bilateral testicular microlithiasis and signs of neoplasm of the left testicle that was not detected by palpation. Based on the research data, the patient underwent left orchifuniculectomy. Based on a histological examination, the diagnosis was established: a mixed germ cell tumor seminoma and teratoma against the background of intratubular germ cell neoplasia. A case from practice allows us to justify the expansion of indications for ultrasound of the scrotum in the non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome (scrotal pain).
Prostatitis is a chronic disease that does not respond well to therapy. It is prone to frequent relapses and does not have a clear and unambiguous clinical picture, which can lead to diagnostic failure. A case of overactive bladder and myofascial syndrome described. The clinical picture was interpreted as «chronic prostatitis» erroneously. Differentiated analysis of the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and NIH-CPSI (National Institute of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index) questionnaires, as well as palpation of trigger points made it possible to establish the correct diagnosis. The following drugs were prescribed: Trospium chloride (Spasmex® ) 15 mg twice a day, Baclоfen (Baclophenum) 10 mg daily, Combilipen (B vitamins multicomplex) intramuscularly, Nimesulide (Nimesulide) orally, and locally low-intensity laser therapy. The patient noted a marked improvement after 14 days: the pain intensity decreased from 8 points to 1, urination urgency was not noted, nocturia stopped. The quality of life (QoL) accordingly improved to 1 point on the IPSS scale. The total score for domains III and IV decreased from 11 to 3 according to the NIH-CPSI symptom scale of chronic prostatitis. The pronounced positive dynamics of the patient’s state of health has confirmed the accuracy of the diagnosis and treatment.
We analyzed the experience of a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunting – migration of the abdominal catheter into the scrotum through the non-obliterated vaginal scion with the development of acute symptoms from the scrotum. The case histories of two patients with short-term complications of ventriculoperitoneal shunting were studied, general clinical and instrumental examination data were presented, and surgical tactics for this condition were analyzed. The problem of these complications is shown as related, requiring the collective participation of urologists, surgeons, neurosurgeons This review provides general guidelines for managing patients with the described complication based on published data and our own experience.
STATEMENTS OF RESEARCH AND EDUCATIONAL EVENTS
This is a report on the 30th World Congress of Video Urology held in June 2019 in Seoul, South Korea. Over 200 experts attended this congress from 40 countries from around the world. Twenty live and semi-live interventions were performed.