ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Globalization contributes to the increase in cases of “exotic” bacterial and parasitic infections importation from the countries of the tropical belt to the territory of our country and to European states.
Purpose of research. Study and analysis of data on the methods of diagnosis and treatment of urogenital schistosomiasis at the present stage
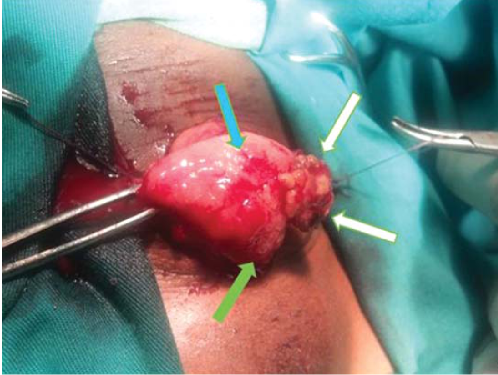
Materials and methods. The study includes an analysis of the examination and treatment results of 181 patients with urogenital schistosomiasis (US) living in the province of Benguela, Republic of Angola. In 39 (21,5%) cases are revealed schistosomal bladder cancer. All patients with schistosomal bladder cancer (SBC) were operated. 142 patients (78.5%) were divided into two groups. Group I (n = 74) consisted of patients with uncomplicated MS, into group II (n = 68) patients had granulomatous proliferative inflammatory changes in the bladder.
Results. Patients with US (n = 142) were examined on an outpatient basis. Cytological exmination of urine sediment (CEUS) showed that eggs of schistosomes were detected in 38 (26.8%) patients. Ultrasound showed specific granulomatous changes in the mucous membrane of the urinary bladder in 28 (19.7%) patients. In 7 (4.9%) cases it showed hydronephrosis, calcification. Bladder wall thickening were detected in 10 (7%) and 99 (69.7%) cases, respectively. Endoscopic examination showed the presence of granulomatous changes in the bladder in 68 (47.9%) patients. Patients of group I (n = 74) received «Praziquantel» in combination with oral antibiotic therapy, which resulted in the relief of macrohematuria and urination disorders. All patients of group II (n = 68) also underwent antibacterial and antiprotozoal therapy. In addition, 35 (24.6%) patients underwent transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB). The results of control observations showed the restoration of bladder mucous layer. Of the 33 (23.2%) patients in Group II who received only antibacterial and antiprotozoal therapy, granulomatous changes persisted in 7 (4.9%) patients. In connection with this, TURB was performed for these patients. Subsequent control studies showed regression of the formations in this group of patients
Conclusions. CEUS and ultrasound are not sufficient for diagnosis of US. Cystoscopy is suitable for all patients with MS. It allows to estimate the volume of the bladder lesion, and to determine the indications for performing TURP in addition to the use of antiparasitic and antibacterial therapy.
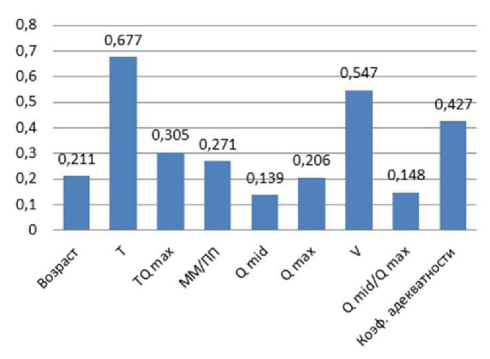
Introduction. In the practice of an urologist, it is customary to assess the type of urination by two parameters: most often it is the effective volume of the bladder (V) and the maximum volume rate of urination (Qmax). Since the expert assessment of the digital characteristics of urine flow is often ambiguous, they are not taken into consideration by some doctors and often remain without due attention. Today there is a tendency in medicine to objectify by quantification of clinical parameters. The main technology used to solve the tasks of data processing and analysis, as well as their classification and forecasting, are artificial neural networks. The aim of the work was to develop an expert system of urine flow rate data recognition based on neural network classifier.
Materials and methods. The training of an artificial three-layer neural network of direct distribution occurred according 210 uroflowgrams and a multidimensional vector, characterized by 9 input parameters.
Results. The system was tested on 40 examples ‒ uroflowgram data of patients who did not participate in neural network training. Despite this fact, the neural network has identified all the proposed examples correctly.
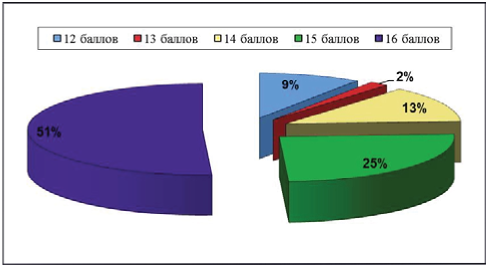
Conclusions. A neural network method for recognition of uroflowmetry data of various diseases of the lower urinary tract is proposed. The space of informative features influencing the assessment of uroflowmetry data is formed. An expert system that classifies diseases (3 types of disorders) of the lower urinary tract with a 95% degree of confidence has been developed.
Introduction. May-Thurner syndrome is a complex disease diagnosed. Most often this disease manifests itself in chronic pelvic and testicular pain or pain in the left leg. Also, this syndrome can cause an unstable erection and cause infertility against a tense varicocele.
Purpose of the study. Optimization of the management strategy for patients with recurrent varicocele.
Materials and methods. The study included 254 patients with varicocele at the age of 34.8 ± 13.3 (16-44) years. Recurrent varicocele detected in 31 (12.8%) patients. May-Thurner syndrome was confirmed in 8 (3.15%) patients. In 40% of cases the syndrome of May-Thurner had identified at a recurrence to a varicocele
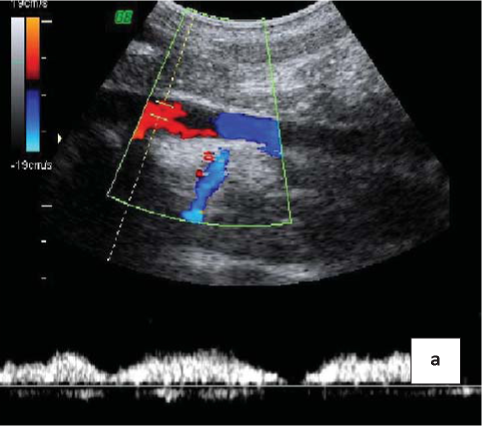
Results. If you suspect a May-Thurner syndrome diagnostic algorithm appropriate to start with a search of the asymmetry of blood flow in the iliac veins according to Doppler ultrasound.
Conclusion. The optimum therapeutic tactics in these patients will be intravascular stenting of the left iliac veins in identifying positive pressure gradient in it more than 10 mm Hg compared with the vena cava inferior.
Introduction. Etiology of the Bladder pain syndrome/Interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) remains completely unknown. BPS/ IC is a chronic disease in which bladder biopsy specimens show varying degrees of inflammation`s severity, detrusor fibrosis and mastocytosis. With BPS/IC, cellular mechanisms of inflammation and processes leading to tissue damage and fibrosis are still not entirely clear. However, the results of studies have shown that fibrosis and mastocytosis of the detrusor are associated with the need for various types of treatment and suggest the failure of standard therapy.
Purpose of research. The aim of the study is to determine the relationship between the anatomical capacity of the bladder and detrusor fibrosis with the clinical course of BPS/IC.
Materials and methods. 110 patients with BPS/IC were examined from 2010 to 2014 in the University Urological Clinic MSMU, A.I. Evdokimov Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry. Patients` pain severity was assessed by a 10-point Visual Analogue Pain scale (VAS). Clinical manifestations of the disease were assessed using international questionnaires: an index of symptoms and quality of life of patients with interstitial cystitis (Interstitial Cystitis Symptom and Problem Indexes; ICSI, ICPI) and scales of symptoms of pelvic pain, urgency and frequency of urination (the Urine and Frequency Questionnaire, PUF), Female Sexual Dysfunction Index (FSDI), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. All patients underwent cystoscopy with general anesthesia for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Bladder biopsy was performed in 36 patients (33%) for the treatment of other bladder`s diseases, as well as for the degree`s pathological assessment of the inflammatory process and the severity of detrusor fibrosis.
Results. In 65% of patients, the anatomical capacity of the bladder was 200-350 ml, and in 5% of cases, its reduction to 100 ml was found. The average capacity of the bladder was 297 ± 90.2 ml. The results of the study suggest a significant decrease in the anatomical capacity of the bladder due to progressive inflammation and fibrosis in the bladder`s wall an essential factor affecting the clinical course of the BPS/IC, causing the severity of the organ-specific symptoms of the disease. A direct correlation was found between the indicators of the nature of alterative changes in urothelia, the severity of inflammatory infiltration and the severity of pain, symptoms of dysuria, in particular, frequency of urination and imperative urges, quality of life and mental health. The severity of fibrosis, the presence of perineuritis and mastocytosis are directly dependent on the duration of the disease.
Conclusions. Reduced bladder capacity and detrusor fibrosis are markers of bladder damage in BPS/IC. These changes are characteristic of a certain patients` subgroup who require endovesical treatment, unlike patients with a systemic phenotype and comorbid conditions.
Introduction. With CPPS / CP III, symptoms of sexual dysfunction and mental pathology are often simultaneously detected.
Goal. Analysis of sexual dysfunction in patients with CPPS / CP IIIA, CPPS / CP IIIB and the existing affective pathology, comparing these groups of patients with CPAP / CP IIIA and IIIB with each other.
Materials and methods. 65 men with type III CPAP / CP were examined, 41 patients were included, which comprised 2 comparison groups: 12 patients with CPPS / CP IIIA (group 1) and 29 patients with CPPS / CP IIIB - group 2. All patients did not have testosterone abnormalities, did not respond to standard urological therapy. Diagnosis of mental disorder and sexual dysfunction was established clinico-psychopathologically, the «International Index of Erectile Dysfunction» (ICEF) scale was applied; the severity of the pain was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS). Statistical calculations were performed in the R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, version 3.2.
Results. Patients of both groups were diagnosed with a primary depressive episode in the 1st comparison group - 75%, in the 2nd comparison group in 80%; depressive episode within the recurrent (recurrent) depressive disorder - in the 1 group 25%, in the 2 group 7%, in the bipolar affective disorder only in the 1 group - 7%; 1 obsessive-compulsive disorder (Table 1) was diagnosed in 1 patient (3%) in the 2nd group. In both groups, moderate episodes of moderate severity predominated-92% in group 1 and 62% in group 2; Depressive episodes of mild degree were 8% in 1 group and 28% in 2 comparison groups; A severe depressive episode was observed only in the 2nd comparison group at 7%. Erectile dysfunction was detected in 75% of patients in group 1, 93% in patients in group 2, premature ejaculation in group 1 in 58%, in group 2 in 45% of patients, reduction in libido in group 1 in 92%, in group 2 in 100%, pain during the ejaculation in group 1 was presented by 33%, in the 2nd group in 28% of men.
Discussion and conclusions. Erectile dysfunction and decreased libido prevailed in patients of both comparison groups, were observed against the background of depressive episodes and, possibly, can be regarded as symptoms of disruption of vital functions within the atypical depressive syndrome of depressive disorders in both groups. ED, decreased libido (sexual desire, desire and attraction), premature ejaculation, general dissatisfaction with sexual intercourse were observed in both groups of patients with CPPS / CP III against a background of depressive episodes, comparing the frequency of occurrence of symptoms of sexual dysfunction does not reveal significant differences in the compared groups. It is advisable to further study the symptoms of sexual dysfunction in CPPS / CP III and psychopathology, their development in the length of the disease, and the relationship for the development of comprehensive CPPS / CP III therapy.
Introduction. CCurrently, there are more and more new data that the urine of the healthy subject has its own unique microbiota and virobiota. Nevertheless, in the etiology and pathogenesis of the inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, the bacterial component is the most studied, but the viral component, as a rule, remains outside the scope of the standard clinical examination of patients. Objectives. To investigate the viral-bacterial associations in the urine of healthy subjects.
Materials and methods. The 20 healthy sexually active women and men were examined, which are divided into groups according to gender: Group I – women (n = 10), Group II – men (n = 10). The average age of the subjects was 22.4 ± 1.2 years.
Results. Bacteriological examination showed that in the urine of healthy women predominates Lactobacillus spp. (90,0%), Peptococcus spp. (80.0%), Propionibacterium spp. (70.0%), and in the urine of healthy men - Eubacterium spp. (70.0%) and Peptostreptococcus spp. (40.0%). During the polymerase chain reaction of urine were detected the papilloma (HPV) and herpetic (HSV) viruses in 40.0% of cases. In group I were verified HPV (20.0%) and HSVII (10.0%), in group II was found only the HPV (10.0%). In all cases, when viruses were detected in the urine, they were recorded as part of virus-bacterial associations. In one healthy woman in the urine were found HPV + HSVII associations
Conclusions. The findings about of verification different taxa of viruses in the urine of healthy subjects are the basis for understanding and detailing the etiological structure of infections of the urinary system. The further studies should be aimed for increasing the cohort of healthy subjects in order to obtain the correct factograms of bacterial and viral patterns which present in their urine.
Introduction. The choice of antibiotic for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTI) is mainly carried out empirically. At the same time, it should correspond to local data on the sensitivity of uropathogens to antibacterial drugs. If the level of uropathogen resistance in the region is more than 10-20% to any antibiotic, its use should be limited to empirical therapy.
Purpose of research. Identify the structure of pathogens of uncomplicated UTIs and determine the dynamics of their sensitivity to the most commonly used antibacterial drugs.
Materials and methods. This article presents a summary data of Russian multicenter epidemiological on the etiology of uncomplicated UTIs and the resistance of pathogens to antibiotics. The study are included female outpatients meeting the following criteria: 1) non-pregnant women over 18; 2) the presence of lower UTIs (acute or exacerbation of chronic cystitis); 3) uropathogen isolation > 103 CFU/ml with a positive test results for the presence of leukocytes in the urine and >105 CFU/ml for any test results for the presence of leukocytes in the urine.
Results. The most frequent uropathogen causing uncomplicated UTI is E. coli, which is excreted in 72.4% - 90.6% of patients. Cephalosporins of the third generation (cefixime), Nitrofurantoin, Fosfomycin have a high microbiological activity against E. coli, the frequency of resistant strains to them is 0%, 0-1.9% and 0%, respectively. The persistently high resistance of E. coli strains is determined to Ampicillin (33.1% - 41.5%) and Co-trimoxazole (19.3% - 26.2%). For non-fluorinated and fluorinated quinolones, there is a tendency to increase the proportion of resistant strains during the study period.
Conclusions. High generation Cephalosporins (cefixime), Nitrofurantoin, Fosfomycin have high activity against uropathogens сausing uncomplicated UTI. Ampicillin and Co-trimoxazole cannot be considered the drugs of choice for the treatment of uncomplicated UTI according to currently established criteria.
LECTURES
Laparoscopic (including robot-assisted) radical prostatectomy has become an alternative to open radical retropubic surgery. The main surgical techniques for reducing the period of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy are aimed at preserving, reconstructing and strengthening the structures that provide a complex mechanism for urine retention, namely, the pubo-prostate-vesicular ligaments, bladder neck, Denonvilliers` fascia, in procuring the functional length of the urethra, etc. Despite advances in the study of urinary continence mechanism there exists a large number of problems that need to be discussed. Therefore, researchers continue to search for solutions to create an optimal technique that ensures the earliest possible of urine retention, which is one of the main tasks in the social and medical rehabilitation of a patient who has undergone radical prostatectomy. This article describes the main modern techniques and methods for performing radical laparoscopic prostatectomy, which are aimed at achieving the earliest possible recovery of the urine retention mechanism.
STATEMENTS OF RESEARCH AND EDUCATIONAL EVENTS
On 5–7 September 2018 the fifteenth annual meeting of EAU Robotic Urology Section (ERUS) took place in Marseille, France. ERUS meeting is regarded as a scientific platform for every urologist who is interested in latest technical advances and continuous progress of urological science and practice. Among the widely discussed topics were organization of surgical care in hospitals equipped with surgical robot, education and training of robotic urological surgeons, use of early recovery protocols in robotic urology and many others. Prototypes and concepts of new robotic surgical systems soon to appear on the market were demonstrated at ERUS-2018. During the live surgery session worldwide-known urologists demonstrated about 20 surgical interventions with comments and explanations for every step in real time.
The article presents a report on the conference of the Russian Society of Oncological urology in the South and North Caucasus Federal Districts «New Trends in the Treatment of Oncological Diseases», which was held in Volgograd on September 7, 2018.