EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Despite numerous methods of treating infertility including methods of assisted reproductive technology a significant proportion of patients remains with infertility.
Purpose of the study. Improving the efficiency of the diagnosis of couples with two or more missed pregnancies in history.
Materials and methods. We examined 38 patients aged from 22 to 38 years with a diagnosis of infertility.
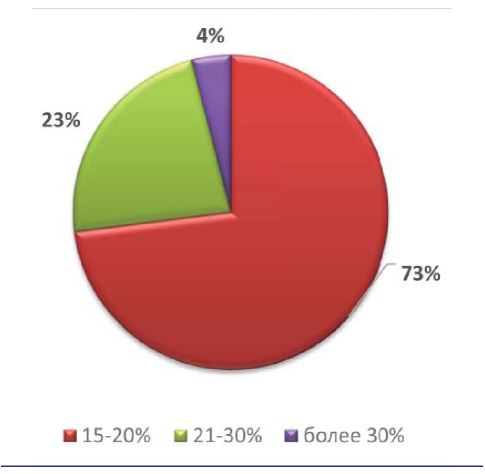
Results. The most common form of prospermia with missed abortion is teratozoospermia (53%), asthenozoospermia occurs in 21% of cases, asthenoteratozoospermia - 8%. Normosaospermia is recorded in 18% of patients. When determining the DNA of semen fragmentation, it turns out that only about 20% of the subjects do not have this pathology.
Findings. The results indicate the need for further study of the contribution of prospermia, and in particular teratozoospermia, and DNA disruption of semen fragmentation to reproductive loss.
Introduction. Currently, indications for intracorporeal lithotripsy of ureteral stones with sizes up to 10 mm inclusively of different localization are established. However, there is no consensus was reached on the preferences of this type of surgery over other existing one in the case of proximal ureteral obstruction by a stones greater than 10 mm in size. Endoscopic ureterolithotripsy is associated with existing studies on the effectiveness and safety of this method. Thus, it is important to continue conducting comparative studies in this direction.
Materials and methods. 54 patients with proximal ureteral stones larger than 10 mm in size were investigated. All patients underwent Semi-Rigid Ureteroscopy and Laser Lithotripsy (SRULL) using a semi-rigid ureteroscope. Patients was stratified into several groups in accordance with the size of stones according to the actual AUA classification: group A (n - 46), the dimensions of ureteral stones from 11 to 20 mm inclusive and group B (n - 8), the size of stones over 20 mm. Criterion for the effectiveness of treatment was to achieve the "Stone Free" level after performing lithotripsy. Indicator of treatment failure was the impossibility of complete removal of ureteral stone within one surgical procedure without its expansion. Statistical data processing was performed using non-parametric data analysis methods applying the STATISTICA 10 (StatSoft Inc., USA) software package.
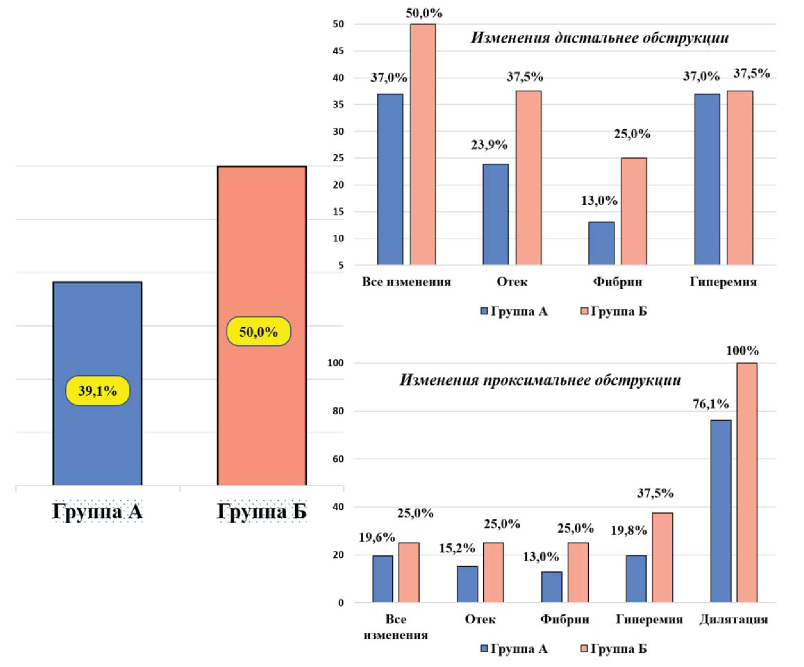
Results. Larger stones compared to higher density. Obstruction symptoms such as hydronephrosis, nausea and vomiting, gross hematuria were more common with stones > 20 mm. Treatment duration in patient groups is similar despite differences in the number of complications and the incidence of postoperative ureteral stenting. At the same time, operation time depended on stone size and density. Surgery efficacy in patient groups was comparable and met 78.3% in group A versus 75.0% in group B.
Conclusion. Inflammatory and destructive changes in the ureter wall are more common with stones greater than 20 mm, which affects the incidence of postoperative complications. Increasing the operation duration and frequency of proximal fragments' migration are determined by increasing of the stones' size and density. SRULL important feature is the lack of statistical difference in the effectiveness with the different sizes of stones. In addition, the achievement of "Stone Free" level for various size's stones does not exceed one day. Performing a SRULL of proximal ureter's large stones on the first day of a patient's hospitalization is accompanied by greater treatment efficacy. It statistically reliably determines the reduction in the frequency of postoperative complications.
Introduction. The effectiveness of methods for treating chronic prostatitis, which are aimed at improving the hemodynamics of the pelvic organs, has been proven by numerous studies conducted over more than thirty years. At the same time, pelvic myofascial syndrome can lead to impaired pelvis' hemodynamics.
Purpose of research. This study aimed to determine the effect of myofascial syndromes on the blood circulation in the prostate in patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis, as well as an assessment of the dynamics of changes in blood flow in the prostate on the treatment of concomitant myofascial syndrome.
Materials and methods. 59 men 34-52 years old with various clinical manifestations of myofascial syndrome (patients of the neurological clinic) were examined to assess the dynamics of blood circulation in the prostate. In addition, 127 men aged 28-52 years (mean age 38 years) with typical clinical manifestations of chronic prostatitis, who repeatedly and unsuccessfully received treatment for this disease, evaluated the effect of treatment of concomitant myofascial syndrome on prostate hemodynamics
Results. The results suggest violations of microcirculation in the prostate in patients with chronic pelvic pain with myofascial syndrome. At the same time, hemodynamic impairment in the prostate is directly associated with impaired pelvic hemodynamics in general. The state of microcirculation in the prostate depends on the severity of pain symptoms in nonspecific chronic pelvic pain, and the treatment of nonspecific chronic pelvic pain leads to a reduction in the main symptom of the disease (pain) and to the normalization of microcirculation in the prostate.
Treatment of concomitant myofascial syndrome in patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis allowed to achieve the disappearance of clinical manifestations of the disease and normalization of hemodynamics in the prostate, as well as a decrease in laboratory signs of inflammation.
Conclusions. Concomitant myofascial syndrome in patients with chronic pelvic pain is a cause of pelvic hemodynamic disorders and because of the development of the inflammatory process. The severity of hemodynamic disturbances directly depends on the intensity of painful manifestations of the myofascial syndrome. Treatment of myofascial syndrome in patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis is accompanied by the disappearance of disease's clinical symptoms and the restoration of prostate's blood circulation, as well as the reduction or disappearance of inflammation's signs.
Introduction. Urinary tract infections of any localization are rarely considered in the context of the endogenous relationship of patient's urine microbiota and the microbiota of nearby biotopes. Nowadays, there are attempts to study the microbial interrelationships of the urinary system with nearby biotope to find fundamentally new solutions in the study of the etiology and pathogenesis of diseases, but now this problem remains almost unexplored.
Purpose of the study. Analysis of the correlations between various taxa of the microbiota isolated from urine, vagina and intestines in patients with upper urinary tract infection.
Materials and methods. According to the inclusion criteria, bacteriological examination of cystic urine, feces and posterior vaginal fornix discharge was performed on 60 women (18-65 years old) with acute obstructive pyelonephritis. The material was taken, transported and examined by standard methods, but with some modifications of nutrient media. Statistical calculations were performed in R "R ver 3.2" ("R Foundation for Statistical Computing", Vienna, Austria) with generally accepted significance coefficients.
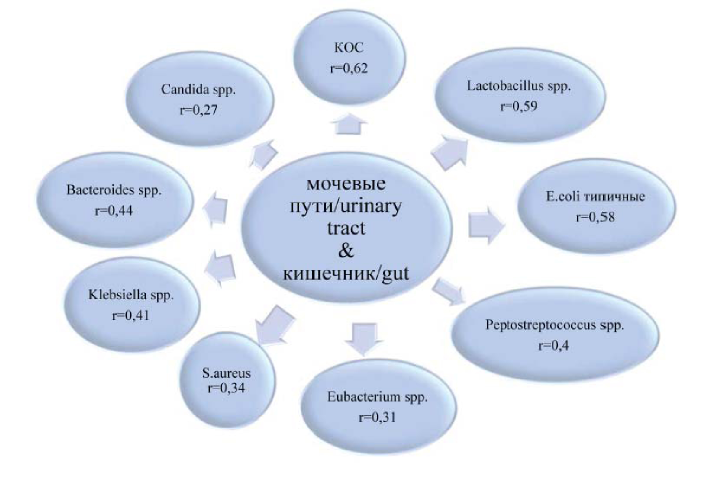
Results. 26 significant correlation coefficients were found in the urinary tract and the vagina when conducting a comparative correlation analysis between the microbiota taxa, and 21 in the urinary tract and intestine. Significant correlations between the general taxa were direct and a large proportion of them were in optional anaerobic microbiota. 28 significant correlation coefficients were found in most cases between aerobic and anaerobic taxa of microorganisms in the vagina and intestines.
Conclusion. The obtained significant correlation coefficients between various microbiota taxa in the three studied biotopes are evidence of the relationship of these loci. However, further research is needed on the phylotyping and genotyping of the microbiota taxa of the urinary tract, vagina and intestines of patients with urinary tract infection.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
Golubev V.Z. created a scientific basis for the study of microangioarchitecture of the kidneys. The principles outlined in his thesis mediated appearance of studies investigating juxtamedullary blood flow and renal blood circulation in normal and pathological conditions.
In acute cardiovascular diseases, the value of the juxtamedullary path of the blood flow increases and juxtamedullary shunting is observed. In chronic cardiovascular diseases, the juxtamedullary shunting initially increases and in the later stages of the disease, the sclerosis of the renal medulla causes a reduction and block of the juxtamedullary blood flow both the juxtamellular and the cortical blood flow deteriorating, which leads to a failure of the circulation to the heart flow. Through research Golubeva V.Z. modern information about the pathways of renal blood circulation prepared, allow to explain the mechanism of the development of various pathological conditions: acute blood loss, hydronephrosis, renovascular hypertension, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis and another nephrological and urological diseases, cardiogenic shock, cardiorenal syndrome in acute ischemic heart disease, hypertension, sudden coronary death, and others.
CLINICAL CASES
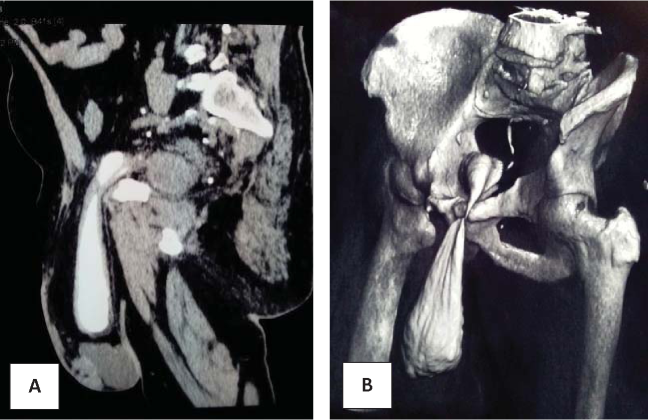
Data from a patient's medical history with a sliding inguinal-scrotal hernia with bladder involvement in the hernia sac was studied. The data of general clinical and instrumental examination, intraoperative data and the results of surgical treatment are presented. A large sliding inguinal-scrotal hernia with the involvement of the bladder in the hernia sac has been eliminated. Prostate adenoma of considerable size is preserved. In the postoperative period, a decrease in the severity of urinary disorders. Moved from the scrotum, the bladder is fully expanded. However, it remains unclear the functionality of that area of he bladder which was located in the hernial sac.
HISTORY OF UROLOGY
This article presents the important scientific achievements of S.P. Fedorov as a urologist. S.P. Fedorov is the author of over 120 scientific papers. It was noted that in 1892 he was the first in Russia to prepare and use cholera antitoxin for the treatment of patients, then tetanus toxin and antitoxin, found that antitoxin protects against tetanus if it is administered simultaneously with the toxin. Abroad S.P. Fedorov studied the system of aseptic mode of operation from K. Schimmelbush, and L. Casper studied the method of cystoscopy and catheterization of the ureters and other endoscopic methods that appeared at that time. It was shown that S.P. Fedorov developed new surgeries — in situ pyelotomy, subcapsular nephrectomy, and new surgical instruments were proposed. He is rightly called the father of Russian urology. The circumstance is analyzed that the main direction of S.P. Fedorov's scientific activity was the problems of surgery of the urinary and biliary tracts. He summarized the extensive experience of the surgeon in the Atlas of Cystoscopy and Rectoscopy (1911), the Surgery of the Kidneys and Ureters (1923-1925), and others. Galpernom edition of the surgical journal «New Surgical Archive», essentially the first Soviet surgical journal, created in the difficult years of the Civil War and post-war devastation. He was the editor of the 1st edition of the BME, together with S.S. Girgolavom and A.V. Martynov was the editor of the multivolume Guide to Practical Surgery. S.P. Fedorov created a major domestic surgical school, from which dozens of specialists, heads of surgical departments of medical universities in various cities of the USSR graduated. The name of S.P. Fedorov was given to the department of hospital surgery of the Military Medical Academy. S.M. Kirov. It is noted that he was the first of the Soviet surgeons to be awarded the Order of Lenin (1933).
The article marks the main years of the life and work of Professor A.P. Frumkin. It is shown that since 1926 for 36 years he worked in the hospital to them. S.P. Botkin (first as resident, and then head of the urology department). In 1939 he defended his doctoral thesis on the topic «Intravenous pyelography». From 1946 to 1962 He headed the Department of Urology at the CIU doctors. During the Great Patriotic War, he was the chief urologist of the Soviet Army. A.P. Frumkin is the author of over 150 scientific papers, including 4 monographs on various issues of urology. The fact that A.P. Frumkin was engaged in the development of methods for urethrography, intestinal plasty of the ureter and bladder (intestinal plasty), surgical treatment of urinogenital fistulas, treatment of purulent processes in the kidneys. It was noted that he introduced into practice a number of original urological operations: resection of the bladder neck in cancer, upper pyelolithotomy, subcapsular pyelotomy, bladder creation operation in extrastrophy, and others. A.P. Frumkin was the editor of the Urology department of the 2nd ed. BME, the deputy. editor of the Journal of Urology, editor of the Department of Urology of the Encyclopedic Dictionary of Military Medicine (1946), editor of the 13th volume of the Experience of soviet Medicine in the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945. It is noted that since 1949, A. P. Frumkin was the permanent chairman of the All-Union and Moscow Urological Societies, an honorary member of the Royal Swedish Medical Society, the Society of Urologists of the German Democratic Republic and Poland. It is emphasized that the progressive development of the school created by A.P. Frumkin, and the dialectical continuation of his ideas in the works of his students, are the best monument to the creative activity of the scientist.
LECTURES
The article presents information about the prostate's zonal structure, prostate preparation after radical prostatectomy, cancer incidence in different prostate areas. This provides an overview of the WHO classification (2016) of prostate tumors, the changes are noted, approaches to the diagnosis of cancer variants, Gleason score assessment, gradation determination, clinical prognostic risk groups for prostate cancer, primary tumor assessment according to the international classification of prostate cancer according to the TNM system (AjCC 8th ed.), which was supplemented and revised in 2017. Prognostic factors for acinar carcinoma and the role of immunohistochemical diagnosis in the morphological material were determined. In conclusion, the main significant parameters are indicated, which should be reflected in the Protocol of in vivo pathoanatomical study of the prostate samples after radical prostatectomy.