ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Today there is many highly effective surgical approaches in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). New technologies in the treatment of BPH continue to be implemented. Despite this in some patients the results of surgical treatment for short-term and long-term monitoring is unsatisfactory.
Purpose of research. Тo improve the results of treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia
Materials and methods. The functional state of the urethral sphincter was studied in 123 patients with symptomatic BPH. According to the treatment method, all patients were separated into groups. Group 1 - patients with established standard indications for surgical treatment. After surgery, patients with persistent obstructive urination received therapy with a central muscle relaxant for three months. Group 2 - patients with uncomplicated BPH, having hypertonic urethral sphincter and receiving drug therapy according to the established urodynamic patterns.
Results. Our analysis of the efficacy of surgical treatment of patients with BPH demonstrates a significant correlation between negative outcomes of surgery for BPH with increased tone of the external urethral sphincter. So, in 70.1% of cases, symptomatic obstructive Low Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in BPH were accompanied by increased tone of the urethral sphincter from standard parameters. We believe that these changes were related to the anatomical characteristics of nodular hyperplasia.
Conclusions. Exactly this fact, that these patients had urethral sphincter dysfunction in 14.5% of cases made for poor effect of surgical treatment of BPH. Use of muscle relaxants centrally acting drug therapy in these cases, significantly improves the urodynamics of lower urinary tract, which is accompanied by regression of LUTS.
Introduction. The main method of treating patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer remains radical cystectomy (RC). In recent years in RC along with open access are used laparoscopic and robot-assisted approaches.
Purpose of research. Describe main steps of robot-assisted RC.
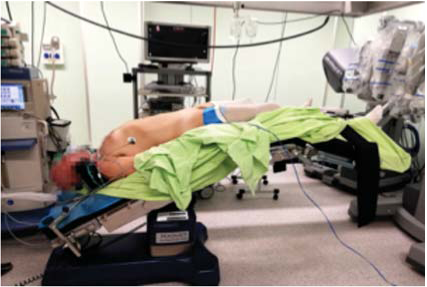
Materials and methods. From June 2018 to November 2019 10 patients were underwent robot-assisted RC with intracorporeal orthotopic ileocystoplasty. There were 8 male, and 2 female. Age of patents ranged from 54 to 76 years. Body mass index was 25.6±4.5 kg/м2. Preoperative examination included USI and CT of abdomen and pelvis, lchest CT, laboratory analyses. Procedure performed in Tredelenburg position. RC included next steps: mobilization of distal part of ureters, posterior dissection of bladder, lateral dissection of the bladder, vesicle pedicle is clipped by Hem-o-Lok clips, dorsal venous complex stitch and dissection of the urethra.
Results. No conversion to open surgeries. Operative time of RC ranged from 100 to 240 min (mean – 120 min). Blood loss volume ranged from 259 ml to 800 ml (mean 370 ml), and generally blood loss was noted during mobilization of a prostate and a dorsal venous complex. The haemotransfusion was carried out to 3 patients. Morphologic examination is revealed T2 stage in 6 patients, T3 in 4 patients. Three patients also had adenocarcinoma of prostate. Lymph nodes were negative in all patients.
Conclusion. Robot-assisted RC is a mini-invasive method for treatment of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Stage-by-stage approach during performing RC allows to reduce time of operation and quantity intra-and postoperative complications.
Introduction. The prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men with chronic kidney disease stage V is from 60 to 80%. At the same time, the prevalence of erectile dysfunction in patients after kidney transplantation remains high at up to 60%. One of the possible causes of erectile dysfunction after kidney transplantation is considered a decrease in arterial inflow to the cavernous bodies of the penis.
Objectives. Тo evaluate the results of treatment of ED in patients after KT, depending on the vascular anastomosis.
Materials and methods. 84 patients with a functioning kidney after transplantation were examined. All patients were divided into 3 groups: Group I – 38 patients undergoing KT with arterial vascular anastomosis with an internal iliac artery; Group II – 46 patients undergoing kidney transplantation with arterial vascular anastomosis to external iliac artery; Group III – 35 healthy volunteers (control group) with no history of urological diseases or surgical interventions on the pelvic organs. International Index of Erectile Function Index (IIEF-5) was used to assess erectile function. An ultrasound study with dopplerography of the penile arteries was performed before and after intracavernous pharmacological stress. For treating patients with erectile dysfunction after kidney transplantation were used PDE-5 inhibitors (Tadalafil® 5 mg daily for 3 months, then at a dose of 20 mg “on demand”), a special set of exercises for the muscles of the pelvic floor, vacuum therapy and physiotherapy with the device “Androgyne”.
Results. Significant erectile function disorders were detected in 26 (68.4%) patients of group I, and in 31 (73.9%) patients of group II, according to data from the IIEF-5 questionnaire. Group I 27 (71.1%) patients were satisfied with sex life, group II – 39 (84.8%) by the end of the year. According to the Doppler ultrasound, after 12 months in patients of group I, the maximum systolic velocity of blood flow in the right and left cavernous artery of the penis was 25.0 ± 3.44 cm / s and 33.0 ± 3.56 cm / s, respectively. The difference in arterial inflow of 8 cm / s indicates a pronounced arterial perfusion of the penis in group I patients. At the same time, in patients of group II, the maximum systolic velocity was significantly higher than in group I and amounted to 40.1 ± 2.66 cm/s and 40.0 ± 2.77 cm/s, respectively.
Conclusion. The data obtained indicate a decrease in the arterial inflow to the penis along the right cavernous artery in patients from group I, who underwent an arterial vascular anastomosis with an internal iliac artery during kidney transplantation.
Introduction. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is an urgent and widely discussed problem in the medical community. Despite the efforts made by a wide range of specialists, there is currently no universally accepted universal approach to the diagnosis and treatment of this condition. The article provides a description and results of applying its own approach to the management of patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Purpose of research. The aim of the work was to improve the practical results of treatment of patients suffering from chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
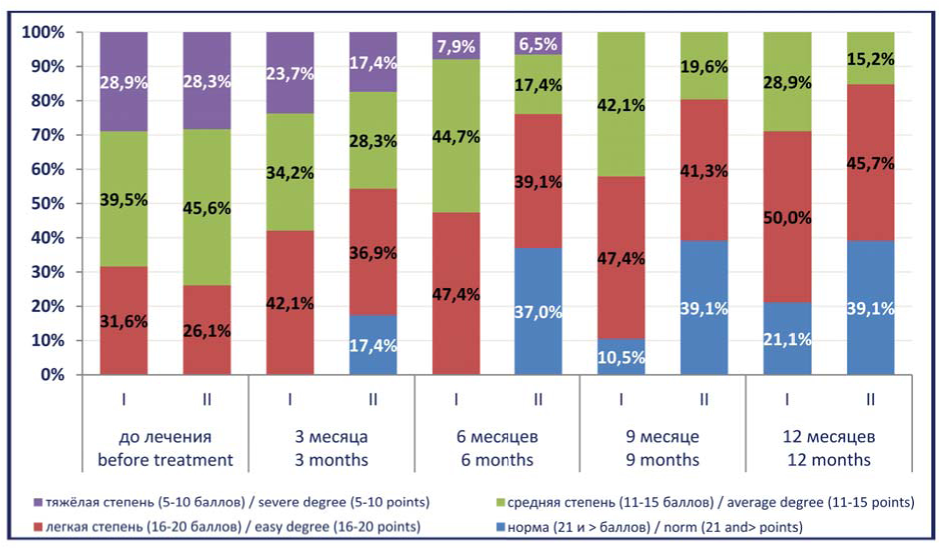
Materials and methods. The results of the examination and treatment of 46 men aged from 26 to 57 years are presented. The leading complaint of the patients was the long-term pain in the pelvic and / or perineal region. According to the survey results, 43.5% of patients showed signs of inflammation in the prostate gland, 56.5% showed no symptoms.
Patients with proven inflammatory changes in the prostate gland were divided into two groups: the first group received the “standard” therapy of chronic prostatitis (antibiotics, prostate-tropic drugs, microcirculation and immunocorrection enhancers, physiotherapy), in the second group the patients received the “standard” treatment in combination with myofascial blockades and neuropathic pain therapy. Patients without inflammatory changes in the prostate were combined into a third group and received only myofascial blockade and neuropathic pain therapy.
Results. Pain in chronic pelvic pain syndrome is most often localized in the perineal region and in the inguinal zones, while the presence or absence of a proven inflammatory component in the prostate gland does not significantly affect the localization and degree of pain, nor the assessment of quality of life. The pelvic myofascial syndromes are detected in the majority of patients with CPPS and their targeted correction in the framework of complex therapy has a positive effect on the results of patient treatment.
Conclusions. Correction of musculo-tonic disorders in chronic pelvic pain syndrome was accompanied by a statistically significant reduction in pain on a 10-point numerical rating scale for pain, a decrease in the I-PSS index.
Introduction. Much attention in ccRCC development is paid to VHL-HIF1α pathway genes. Numerous genes involved in the pathogenesis of ccRCC are targets for miRNA. Alteration in the nature of interaction with miRNA binding site as a result of a single nucleotide substitution may promote change the expression of target genes involved in the genesis and development of tumors.
Purpose of research. Analysis of the role of polymorphic variants in the miRNA binding sites of the VHL-HIF1α gene pathways in ccRCC development.
Materials and methods. We used 225 DNA samples isolated from the venous blood of ccRCC patients who are hospitalized to the Clinic of the Bashkir State Medical University, and 298 healthy individuals. The genotyping of miRNA binding site polymorphisms in VHL-HIFα-dependent pathway genes (rs10982724 of the DEC1 gene, rs406271 of the TFRC gene, rs10491534 of the TSC1 gene, rs1642742 of the VHL gene, rs3025033 of the VEGFA gene) was performed using Taq-man assays.
Results. The frequency distribution of alleles and genotypes of rs1642742 of the VHL gene showed that rs1642742 *GG is a marker of the increased risk for ccRCC. In addition, rs10491534 * C allele was found to be the marker for severe ccRCC (p = 0.044; OR = 1.72 (CI = 1.012-2.911)), and rs10491534 * TT genotype (p = 0.044; OR = 0.55; (95% CI = 0.31–0.98)) of the TSC1 gene was shown to be a protective marker for ccRCC of severe duration.
Conclusions. The study indicated the association of miRNA binding sites polymorphisms with the risk of ccRCC development and severity of disease. However, further studies of the genes are needed to establish their functional significance and role in the pathogenesis of ccRCC.
Introduction. Contemporary diagnosis of prostate cancer is crucial to the patient’s further fate. Difficulties in the histological verification of the final diagnosis and false-negative results of biopsy research are often associated with the similarity of the prostate adenocarcinoma`s micromorphological picture and its benign lesions.
Purpose of the study. Comprehending the possibilities of immunohistochemical identification of tumor cells and the basal epithelial layer of prostate glandular structures in prostate cancer suspected cases.
Materials and methods. A biopsy material was taken from 134 patients. Prostate adenocarcinoma was verified by routine histological examination in 72 samples, in 62 samples there were no signs of malignant transformation. Subsequently, immunohistochemical analysis of biopsy specimens was performed using antibodies to α-methylacyl-CoA racemase, nuclear p63 protein and high-molecular cytokeratin.
Results. The AMACR-positive reaction of malignant cells and a negative reaction of the basal epithelium to nuclear p63 protein antibodies and high-molecular cytokeratin were detected during prostate adenocarcinoma.
Conclusion. If prostate cancer is suspected, immunohistochemical assays with monoclonal antibodies to AMACR, p63 and high-molecular cytokeratin greatly facilitate the detection of adenocarcinoma.
Introduction. Purulent pyelonephritis is a complicated urinary tract infection with one of the most severe currents. It represents a serious clinical problem associated with the complexity of the choice of diagnosis and the optimal active treatment strategy, as well as the need for subsequent rehabilitation of this category of patients.
Purpose of the study. Studying of the immediate and remote results of the kidneys` functional state in patients who have undergone purulent pyelonephritis using a differentiated approach to treatment tactics.
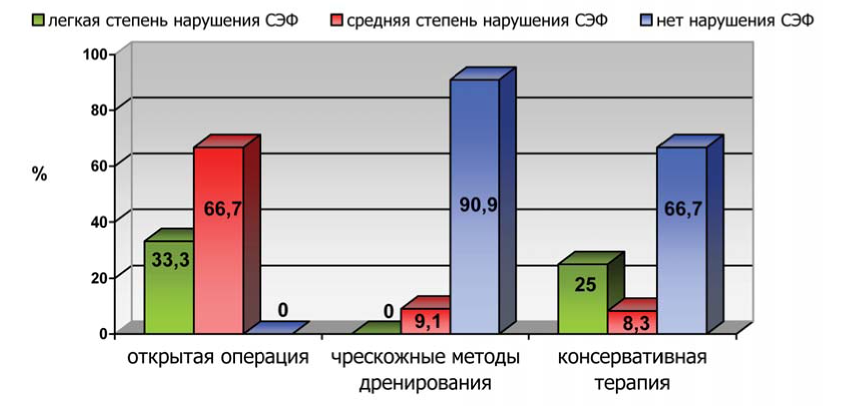
Materials and methods. The study included 84 patients who underwent purulent pyelonephritis at the age of 15 to 70 years old and were treated at the Botkin City Clinical Hospital from 1999 to 2007. The patients were divided into three groups depending on the method of treatment: group 1 - open surgery of 18 patients (21.4%); group 2 - percutaneous drainage methods - 38 (45.3%); group 3 - conservative therapy - 28 (33.3%) patients. Examination of patients included dynamic nephroscintigraphy and complex ultrasound. It was performed in time after treatment after 12, 36 and 60, 84 months.
Results. During the 7-year observation of patients, it was found that a more pronounced renal dysfunction and perfusion occurred during all periods of observation after undergoing open surgery according to Doppler sonography. Restoration of renal function occurred in shorter observation periods after the use of percutaneous kidney drainage and conservative treatment.
Conclusion. Based on the data obtained, it can be concluded that a differentiated approach to the choice of tactics for the treatment of patients with purulent pyelonephritis is reasonable. Accordingly, it should be introduced into clinical practice of urological departments that provide emergency care to urological patients.
HISTORY OF UROLOGY
LECTURES
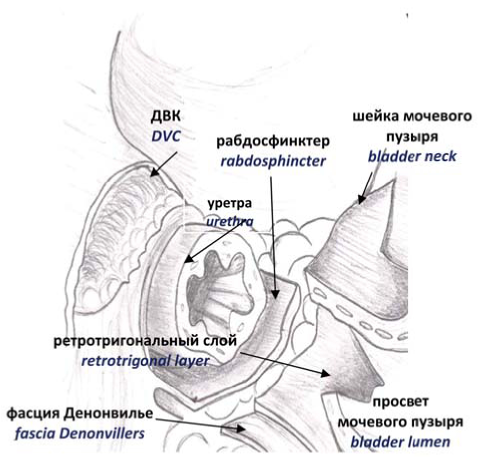
This lecture describes the preoperative preparation, the course of the operation and the management of patients in the early postoperative period when performing a radical robot-assisted prostatectomy. The material was developed for the purpose of methodological assistance to surgeons in the development of this operational method.