ORIGINAL ARTICLES
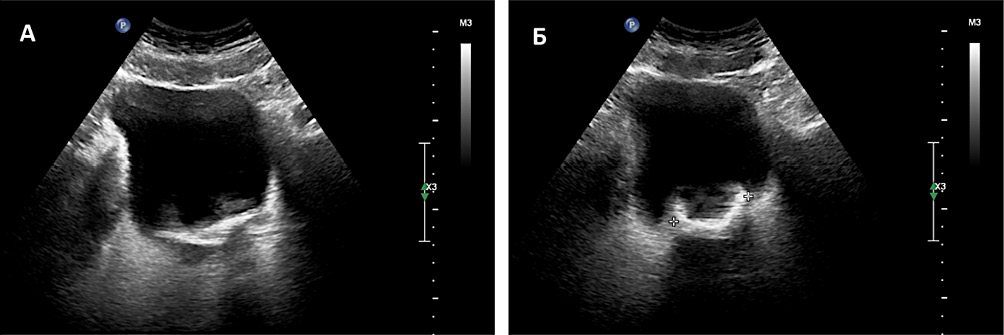
Introduction. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is considered the gold standard for treating renal stones larger than 2 centimetres. The initial stage of PCNL involves retrograde catheterisation of the pelvicalyceal system (PCS) with contrast enhancement. Direct-guided puncture is a modification of standard PCNL, where puncture of the PCS is performed without retrograde enhancement of the PCS.
Objective. To compare the efficacy and safety of standard PCNL (miniPCNL/mPCNL) versus direct-guided puncture PCNL (dgPCNL).
Materials & methods. The study involved 67 patients who were recruited between September 2021 and March 2023. They were divided into two groups. Group 1 (n = 35) underwent standard PCNL, while group 2 (n = 32) received dgPCNL. We compared the following parameters: surgery duration and puncture time, visualization (using the Likert scale), stone-free rate (SFR), blood loss (post-op haemoglobin level decrease), renal function (post-op creatinine variations), and postoperative complications. To assess SFR, patients underwent abdominal computed tomography (CT) on the first post-op day. Postoperative complications were assessed using the Clavien-Dindo classification.
Results. The average surgery time in group 2 was 16 minutes, which was significantly less than that in group 1 (p < 0.001). We believe this reduction is due to the absence of the first stage. The puncture time did not differ between the two groups (p = 0.739), with an average puncture time of 2 minutes. There was no significant difference in SFR between the groups, with 91.4% in group 1 and 93.8% in group 2 (p > 0.999). Similarly, there were no significant differences in haemoglobin loss and creatinine changes between the groups (p = 0.32 and p = 0.442, respectively). No severe complications were observed, as classified by Clavien-Dindo III and IV.
Conclusion. dgPCNL is safe and effective compared to standard PCNL, offering the advantage of reduced operative time. Blood transfusions were not required in either group.
Introduction. Differential diagnosis of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) is a complex, multi-stage process. It is known that men with BPH and PCa have significant differences in their sexual activity throughout life.
Objective. To devise a model for predicting the risks of developing PCa or BPH, considering male sexual activity, and to construct a calculator based on this model to distinguish between the two conditions.
Materials & methods. An open prospective non-comparative сross-section study involved 47 men aged 49–71 years with BPH and 87 men aged 47 – 70 years who had been newly diagnosed with PCa. The patients underwent testing for serum PSA levels, total testosterone, and prostate volume. The results of the survey based on the “Rostov Integral Assessment of Male SExuality Questionnaire — RIAMSE” were evaluated.
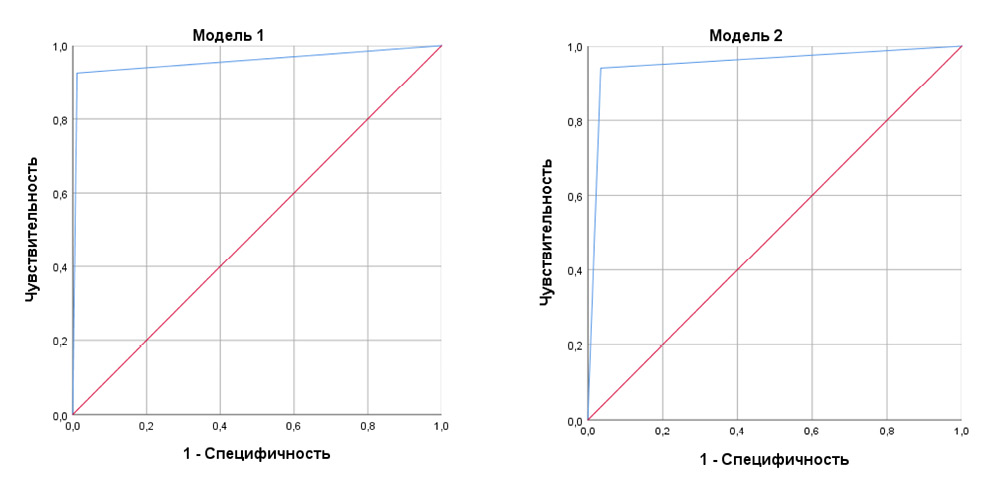
Results. Logistic regression techniques have shown that a patient's sexuality, prostate volume, and PSA level can be predictive of a patient's risk of having either a BPH or an PCa. A 1-point increase in sexuality increases the odds that a patient will be diagnosed with BPH rather than PCa by an average of 1.08 times. If the volume of the PSA increases by 1 cm3, the odds of being diagnosed with BPH increase by an average of 1.15 times. A 1 ng/ml increase in PSA level decreases the odds of detecting BPH compared to PCa by a factor of 0.13. A differentiation calculator was developed based on the results of mathematical modelling.
Conclusion. The simple calculator presented in the study has a sensitivity and specificity > 0.90 and can be evaluated in upcoming clinical trials.
Introduction. At present, the progress in reconstructive urology demonstrates high efficiency rates in treating urethral strictures (US), ensuring satisfactory urination parameters. Meanwhile, there is a need to maintain a high quality of life associated with male sexual function.
Objective. To evaluate the erectile function in males suffering from US considering the presence of risk factors for erectile dysfunction (ED), characteristics of US and surgical techniques employed.
Materials & methods. The study involved 153 sexually active patients with US who underwent surgical treatment. The assessment of erectile function was carried out using the IIEF-5 questionnaire, while considering the presence of risk factors for ED in patients (age, smoking, coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus), stricture parameters (primary/recurrent, length) and surgical technique (transecting and non-transecting techniques). Evaluation time points: baseline (before surgery), 3, 6, and 12 months after urethroplasty.
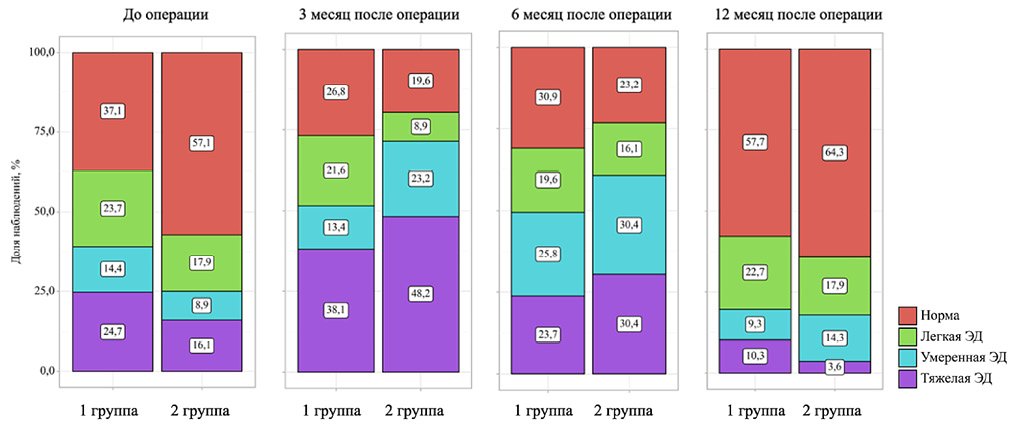
Results. The mean age of the patients was 53.0 years, and their baseline erectile function scores were 19.0 points. Regardless of the parameters under study, a decline in erectile function was observed in all study groups by the 3-month follow-up, which regressed over the one-year follow-up period. The duration of recovery and severity of erectile dysfunction were associated with age, smoking, the presence of coronary heart disease and arterial hypertension, US length, and recurrent nature of strictures. No significant differences were found in erectile function indicators after surgery, depending on the grade of transection of the spongy body. According to multivariate analysis, predictors of ED development after surgery include age (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] 1.082; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.038–1.127; p < 0.001), arterial hypertension (AOR 4.608; 95% CI 1.089–19.511; p = 0.038), and baseline erectile function status (AOR 0.046; 95% CI 0.013–0.160; p < 0.001).
Conclusion. ED following surgical treatment of urethral strictures is predominantly transient, with regression observed by the 12-month follow-up period. The recovery of erectile function is adversely affected by advanced age, smoking, cardiovascular diseases, the length and recurrent nature of US.
Introduction. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are prevalent among children, particularly those with anatomical anomalies such as vesicoureteral reflux (VUR). The diagnosis of VUR typically follows an episode of UTI, highlighting the importance of early detection of VUR in case of UTIs to prevent renal complications. The management of a first febrile UTI remains a subject of debate among medical professionals. Pediatricians often recommend diagnosing VUR after recurrent UTIs, while urologists advocate for early imaging and prophylaxis. Antibiotic prophylaxis (ABP) before surgery can reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs; however, it also induces antibiotic resistance and alters the microbiota.
Objective. To evaluate the microbiota of bladder urine in children before surgery for VUR.
Materials & methods. The study included 40 children (12 boys — group 1, 28 girls — group 2) diagnosed with MTCT after symptomatic urinary tract infection. The control groups were 18 healthy boys (group 3) and 16 healthy girls (group 4). Urine was collected and cultured using an expanded set of nutrient media (10–12) for culturing aerobic and anaerobic taxa of microbiota.
Results. The median age of VUR-patients in the study groups was 3.6 years. A statistically significant predominance of girls was observed (p < 0.001). The urine samples from VUR-children were unsterile, and a total of 27 taxa of microorganisms were detected. Among them, 16 taxa were aerobes, and 11 taxa were anaerobes. The dominant taxa differed between the groups: Enterobacterales, Peptococcus spp., and Anaerococcus spp. predominated in VURboys, while coagulase-negative staphylococci, Corynebacterium spp., and Peptococcus spp. dominated in VUR-girls. Most microorganisms were found in associations. The median bacteriuria level was mostly 10² CFU/ml. In total, 29 microbiota taxa with dominant aerobic-anaerobic relationships were identified in healthy children and VUR-patients. There were more significant correlations between different taxa of the urine microbiota in VUR-patients compared to healthy children.
Conclusion. Bladder urine from VUR-children contains aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. It is yet to be determined whether bacterial associations with a bacteriuria of 10² CFU/ml increase the risk of UTIs in VUR surgery, but urinary dysbiosis should be investigated as a possible risk factor for UTIs. Further studies are needed to justify the feasibility and suitability of selective ABP in the treatment of VUR.
Introduction. Despite the selective patient screening and improvements in surgical techniques for radical prostatectomy (RP), the incidence of erectile dysfunction (ED) remains relatively high. The efficacy of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i) in patients undergoing nerve-sparing RP can vary from 35% to 75%. One of the issues in penile rehabilitation after RP is its duration. Currently, there are no standardised guidelines on the length of PDE5i therapy, with authors providing conflicting and insufficient data to recommend specific timelines for penile rehabilitation. Therefore, further research is required to determine the optimal duration of PDE5i-based rehabilitation.
Objective. To compare the efficacy of long-term PDE-5i administration for restoring erectile function in patients undergoing nerve-sparing RP versus a short 3-month course in the early postoperative period.
Materials & methods. A prospective analysis of data from 81 patients with localized prostate cancer who underwent laparoscopic nerve-sparing RP was carried out. In the postoperative period, patients were divided into two groups using simple randomisation. Group 1 received PDE5i for 11 months as part of penile rehabilitation, while group 2 received them for three months.
Results. The severity of ED three- and 12-months following RP was comparable in both groups. A long-term course of PDE-5i showed no advantages at the one-year stage of the study in terms of erectile function compared to a threemonth therapy course. The same trend was observed in the results of the nocturnal penile tumescence test. In addition to developing irreversible ED, gradual penile shortening after surgery can cause the patient's inability to urinate while standing and, as a result, lead to serious psychological problems. When assessing the penile length in both groups, a tendency towards its shortening at the annual stage of the study was noted, which indicates insufficient effectiveness of both the annual and three-month rehabilitation course with PDE-5i.
Conclusion. Long-term use of PDE-5i compared to a short-term rehabilitation course did not demonstrate any advantages in restoring erectile function one year following nerve-sparing RP.
Introduction. Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), sexual dysfunction and psychological disorders coexist in the lives of older men. Evaluation of the prevalence of mood disorders and sexual dysfunction after surgical treatment is important to ensure a high quality of life for patients with LUTS.
Objective. To analyse the incidence and severity of affective disorders in patients before and after laser enucleation of the prostate and to determine their association with LUTS and erectile dysfunction.
Materials & methods. The study included 136 patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia treated with laser enucleation between 2018 and 2023. All the male participants were sexually active, and their erectile function was assessed at 11 points or higher according to the IIEF-5 scale. In addition to standard examination methods, all patients completed the IPSS, IIEF-5, and HADS questionnaires prior to surgery and 18 months postoperatively. The first stage of the study involved an investigation into the prevalence and severity of affective disorders both before and after surgical intervention, as well as determining their correlation with LUTS. The second stage focused on examining the relationship between affective disorders and sexual dysfunction. Patients were categorized into two groups based on the absence or presence of negative influence of LUTS on their quality of sexual life: group 1 (n = 70) — no influence, group 2 (n = 66) — influence is present.
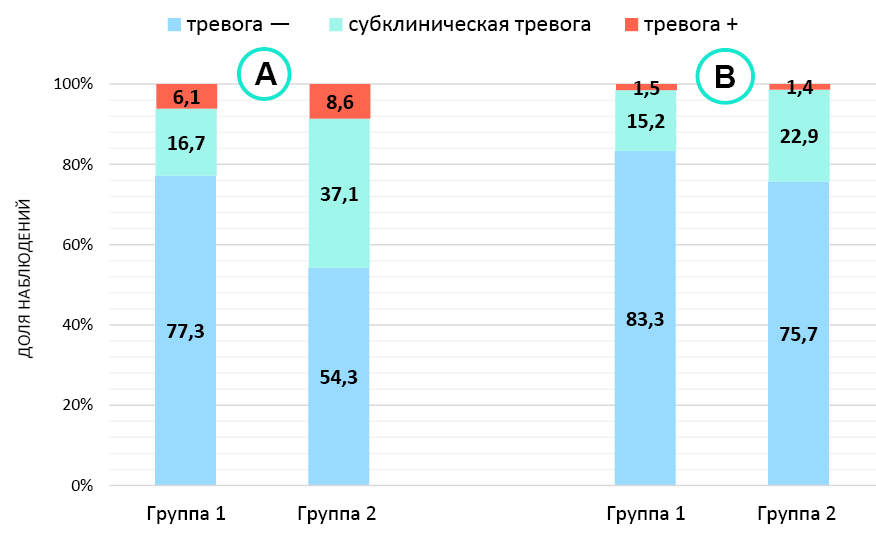
Results. Anxiety and depressive disorders of varying severity were found in 48 (35.3%) and 46 (33.8%) patients, respectively. It was found that the severity of both anxiety (r = 0.574; p < 0.001) and depressive disorders before surgical treatment correlated with LUTS (r = 0.590; p < 0.001), but after surgical treatment only anxiety disorder scores had a correlation with LUTS (r = 0.742; p < 0.001), and with irritative symptoms (r = 0.475; p < 0.001). Group 2 patients had lower IIEF-5 scores (18.0 vs. 21.0 points; p < 0.001) and were more likely to have anxiety and depressive disorders before surgical treatment (45.7 and 44.3% vs. 22.8 and 22.7%; p < 0.05), with significant improvement in erectile function and affective status after surgery, in contrast to group 1 patients, whose IIEF-5 scores and incidence of affective disorders did not change significantly.
Conclusion. Patients with a predominantly irritative LUTS profile and a negative impact of urinary disturbances on sexual life are more susceptible to anxiety and depressive disorders. Consequently, evaluating their affective state is essential when treating men with LUTS to enhance their quality of life.
Introduction. Implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is the main treatment method of surgical treatment in men with moderate to severe stress urinary incontinence. Despite its efficacy, implantation is sometimes accompanied by the development of complications, which in some cases necessitate revisions and removal of the entire device or its components.
Objective. To evaluate the outcomes of AUS implantation regarding safety and the need for re-interventions at long-term follow-up.
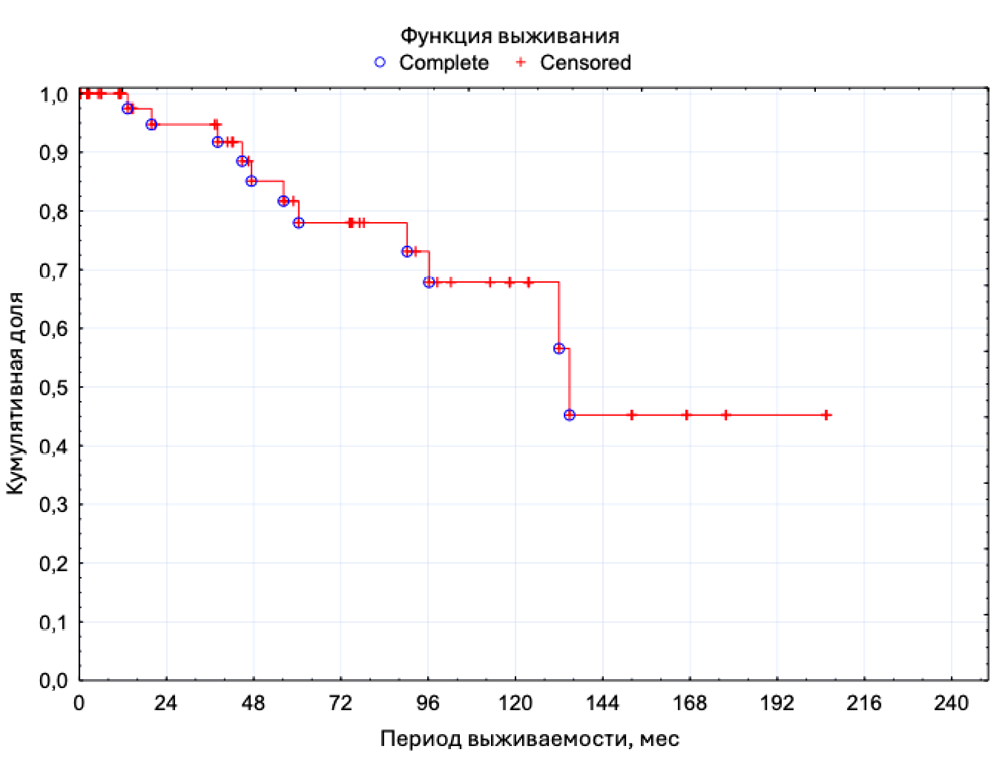
Materials & methods. From 2004 to 2023, AUS was implanted in 62 patients with severe stress urinary incontinence. Complications are described according to the Clavien-Dindo classification. Revisions followed replacement of components or the entire AUS in the absence of signs of infection and revisions followed components or entire AUS explanation in case of infection were registered.
Results. The mean patient age at the time of implantation was 67.4±8years. With amedian follow-up time of 73.5months (IQR 14.8 – 118.3 months), complications were noted in 22 (35.5%) patients, and 33 revisions were performed. The median time to complication requiring replacement of the AUS or its components was 60 months (IQR 50 – 94 months). The median time to complication requiring removal of the AUS or its components was 31 months (IQR 8 – 83 months). A statistically significant effect of type 2diabetes mellitus on AUS component replacement was revealed (OR 4.9, p<0.05).
Conclusions. AUS implantation is associated with the development of complications that necessitate revision. These complications account for roughly one-third of all AUS interventions. Revision operations contribute to restoring AUS functionality and enhancing patients' quality of life. Given the inadequacy of applying the general surgical classification of complications to men undergoing surgical treatment for urinary incontinence, there is a need to modify the documentation and classification of such complications.
Introduction. Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) are common urogynecological diseases that cause serious damage to the psychoemotional state of patients and have an extremely negative impact on their quality of life. The study of the medical and social profile of patients with these pathologies contributes to the choice of treatment tactics, informed decision-making on surgical treatment and shortening the period from the moment of the first doctor's recommendation about the need for surgery to the time of its implementation.
Objective. To study of the medical and social profile of patients with POP/SUI who have indications for reconstructive surgery. Conducting a comparative analysis of profiles in patients with POP and SUI. Determination of the factors that influenced the timing of patient’s decision on surgical treatment (decision-making period, DMP).
Materials & methods. The current single-center prospective study included 1176 patients with POP (n = 860) or SUI (n = 316) requiring pelvic floor reconstructive surgery. Upon admission to the department, all patients filled out a questionnaire specially designed for this study, which included socio-demographic information, information about previous treatment, gynecological and obstetric history, region and place of residence, labor status, financial situation, anthropometric indicators, physical activity level, sports/gymnastics, smoking status, and diet.
Results. The average age of the patients was 57.6 ± 11.7 years. When analyzing the data obtained, the following differences were found between the groups of patients with POP and SUI. Patients with POP are older than patients with SUI (p < 0.001). In the SUI group, the proportion of women with higher education (p = 0.023), working patients (p < 0.001), not following proper nutrition and not exercising (p < 0.001), as well as living a sexual life (p < 0.001) is higher. The duration of complaints related to POP / SUI averaged 6.7 ± 6.4 years. This period is longer in the group with SUI (p < 0.001). The duration of the decision-making period is significantly longer in the SUI group (p < 0.001). On average, the preparation for the operation took 3 ± 5.3 years. The decision-making period (DMP) is longer in patients with POP compared to those with SUI (p < 0.001). We have found differences in DMP duration depending on patients' level of education and employment. Women with higher education have a shorter DMP (p = 0.018 for the whole sample; p = 0.008 for the POP group). Retired women have a longer DMP compared to non-working women of working age (p = 0.028 for the entire sample; p = 0.026 for the POP group). For patients with stages POP 3 and 4, the duration of DMP is significantly longer than for women with stage 2 POP (p = 0.007). For women with SUI, there is no correlation between DMP and the degree of urinary incontinence at the time of surgery (p > 0.05).
Conclusion. In this study, the medical and social characteristics of patients in need of reconstructive surgery were demonstrated. These factors must be considered to make an informed decision about surgical treatment.
CLINICAL CASES
Buccal ureteroplasty is a surgery that is now increasingly encountered in urological practice. There are various techniques for performing this surgical procedure, which require further improvement. This article presents a clinical case and the immediate results of ureteroplasty utilising the oral mucosa via the augmentation anastomosis technique in a 40-year-old patient with an extended recurrent ureteral stricture having an obliteration site.
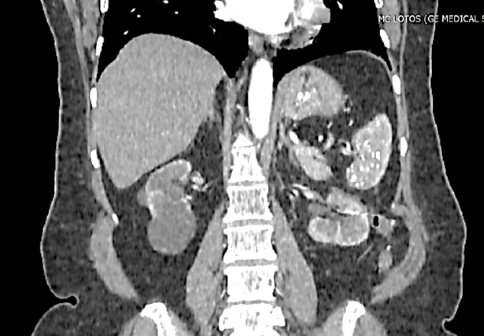
The basic treatment approach for clinically localized and locally advanced renal cell cancer (RCC) is surgery. Kidney resection is the preferred organ-preserving approach to surgical treatment. For high-risk patients with operative treatment or with somatic contraindications to surgery, an alternative treatment option like stereotactic radiotherapy may be considered. The article presents a clinical case of a 63-year-old patient with the diagnosis: Left kidney cancer T1aN0M0, stage I. C3a CKD. In April 2021, a course of stereotactic radiotherapy was performed on the kidney tumor up to SOD 45 Gy. In June 2022, left kidney resection was performed for PCC progression. Recurrence-free and cancerspecific survival rate was 20 months.
Incrusting cystitis is an extremely uncommon form of chronic bladder inflammation. It is characterised by wall calcification and associated with urease-producing microorganisms, most commonly Corynebacterium urealyticum. The enzyme urease triggers a cascade of urea cleavage into carbon dioxide and ammonia, thereby leading to hyperammoniuria and urine alkalisation within the first 24 hours. These conditions result in hypersaturation favourable for the formation of struvite and apatite crystals encrusting the bladder wall. The most significant predisposing conditions and risk factors for the development of encrusting cystitis are foreign bodies in the urinary system, such as urethral catheter, nephrostomy tube, internal ureteral stents. Additionally, a history of endoscopic surgery on the urinary tract is of special importance. This article presents a clinical case of successful treatment of encrusting cystitis in a man after transurethral resection of the prostate.
LECTURES
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an integral part of modern medicine, including urology. This article examines key approaches to implementing AI in diagnostics, treatment, and patient management. The focus is on the potential of neural networks, such as convolutional and recurrent networks, for medical image analysis, outcome prediction, and automation of routine tasks. Particular attention is given to the application of deep learning algorithms in identifying and segmenting urological pathologies in ultrasound, CT, and MRI images. Successful examples of AI use in diagnosing prostate and bladder cancer, predicting complication risks, and developing personalized therapeutic strategies are discussed. The advantages and limitations of AI in urological practice are explored, including the need for high-quality data for model training, challenges in algorithm interpretation, and ethical considerations. The article provides practical recommendations for urologists on integrating AI into clinical activities, emphasizing its role in improving healthcare quality and enhancing decision-making accuracy. The article serves as a practical guide for urologists seeking to integrate AI into clinical practice, emphasizing the importance of combining AI technologies with clinical expertise to optimize the quality of medical care. On the threshold of a new era in urology, those who are the first to master artificial intelligence will not only transform approaches to treatment but also shape the future of the profession.