EDITORIAL
The article presents historical aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of acute pyelonephritis. The features of surgical approaches and management tactics for patients with acute pyelonephritis in the 70-80s in the USSR and later in Russia are revealed. The author presents his view of the problem. The author presents the research data aimed at studying the pathophysiology of acute pyelonephritis, which cardinally changed the ideas of that time about the principles of disease management. The author's contribution to the issues and organization of care for patients with acute pyelonephritis is also reflected.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Cryptorchidism is a common disease in pediatric urological and andrological practice since the issues of tactical approaches and its optimal treatment remain extremely relevant. Cryptorchidism makes a significant contribution to the structure of male infertility.
Objective. To conduct a retrospective analysis of treatment results in children and adolescents with cryptorchidism.
Materials & methods. This study summarises the treatment results of 8308 patients with cryptorchidism aged from 6 months to 17 years who underwent inpatient treatment in the Russian Federation and the Republic of Uzbekistan.
Results. It was revealed that from 2015 to 2019, patients were admitted for surgical treatment evenly over the years. The ratio of right-sided / left-sided / bilateral cryptorchidism was 4.6 : 4.4 : 1 The inguinal form prevailed more than 6 times over the abdominal location. At the same time, 26.1% of the patients underwent surgery at the optimal time, and 9.8% were older than 10 years. More often, children are operated from an open inguinal access (95.0%), much less often — laparoscopically and percutaneously. Stage-by-stage treatment was carried out in 6.0% of patients.
Conclusion. Thus, the approach presented in the study in the surgical treatment of cryptorchidism provided good treatment results. The number of disease relapses was 1.9% (mainly among children over 7 years old). Most surgeons are very reserved about primary orchidectomies (only 3.8% were performed).
Introduction. The primary focus for improving medical care is introduction of inpatient-replacement forms of healthcare for patients, particularly, with prostate cancer (PCa). Day-care facilities at outpatient institutions and hospitals are considered the most cost-effective and convenient for patients. It is expected that the introduction of new survey methodologies and the optimization of their use in day-hospitals of outpatient clinics will reduce the use of other diagnostic procedures, including invasive ones, and will allow the specialist to determine the treatment tactics and method.
Objective. To improve the quality of PCa diagnosis with the use of high-tech advanced outpatient medical care.
Materials & methods. To assess the appropriateness and effectiveness of transrectal prostate biopsies (TRPBs) in the day hospital, we have compared the statistics obtained in outpatient clinics with inpatient hospital divisions of the corresponding urban district. A comparative analysis of the data obtained using a standard examination algorithm was carried out: prostate-specific antigen analysis, digital rectal examination and transrectal ultrasound examination with a group of men who used multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) in the examination algorithm prior to TRPB.
Results. The average annual number of TRPBs performed in inpatient urology divisions (three сapital hospitals from Western urban district) was 344, and the PCa detection was 142 (41%). In the outpatient urological unit of the Branch No. 2, Moscow Outpatient Clinics No. 195 for the period from 2010 to 2017, the average annual number of TRPBs was 440, and the PCa detection was 153 (35%) Thus, from the above data, it appears that with inpatient-like PCa detection, one large outpatient urological unit performed on average 24% more TRPBs (440 versus 344) than three inpatient urological divisions in a comparable period of time. When comparing histological data obtained after TRPBs in the absence and presence of pelvic mpMRT, a reliable difference (42% vs 35%) was found in PCa detection, respectively.
Conclusion. mpMRI due to its high sensitivity and specificity in PCa diagnosis, which can be recommended as a mandatory diagnostic step before TRPB. In addition, mpMRI can significantly reduce the number of unnecessary TRPBs, increase the effectiveness of timely PCa diagnosis at the early stages.
Introduction. It is known that women are significantly more likely to suffer from lower urinary tract infections (LUTIs) than men. Nowadays, there is growing evidence to demonstrate the impact of vaginal microbiota on the development of recurrent LUTIs.
Objectives. To demonstrate the impact of vaginal microbiota disorders on the development of recurrent lower urinary tract infections.
Materials & methods. Seventy-five women with recurrent LUTIs 19 – 76 years old were enrolled in this study. The examination was performed according to the algorithm developed in the Department of Urology and Surgical Andrology, Russian Medical Academy of Continuous Professional Education. Real-time PCR of vaginal epithelial cell scrapings (Femoflor 16) was performed to comprehensively evaluate the vaginal microbiota.
Results. Vaginal dysbiosis was detected in 47/75 (62.7%) women with recurrent UTIs: moderate vaginal dysbiosis was detected in 25/75 (33.3%) women and severe dysbiosis — in 22/75 (29.3%) women. A moderate correlation between the presence/absence of vaginal dysbiosis and the number of LUTI recurrences over 6 months was found (r = 0.310; p = 0.007). Vaginal dysbiosis was significantly more common among peri- and postmenopausal women with recurrent LUTIs than reproductive women (OR = 4.85; 95% CI = 1.45 – 16.17).
Conclusion. Vaginal dysbiosis contributes to the development of recurrent LUTIs with more relapses. Vaginal microbiota disorders and, consequently, recurrent LUTIs are more common in peri- and postmenopausal women than reproductive women.
Introduction. Genital herpes is a chronic sexually transmitted infection characterised by recurrent self-limiting genital ulcers caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) or type 2 (HSV-2) and can be associated with chronic prostatitis (CP).
Objective. To determine the efficacy of cytokines-antimicrobial peptides complex in therapy of patients with herpes virus-associated chronic prostatitis.
Materials & methods. The pilot, open, prospective, non-comparative study included 23 patients who were followed up for CP for a mean of 9.7 ± 4.2 years. All were diagnosed with abacterial CP / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) with signs of inflammation and detection of HSV DNA in urethral swabs by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Prescribed therapy: Tab. Valaciclovir 500 mg b.i.d. p.o. for 10 days, Tab. Ketoprofen 100 mg q.d. for 5 days, Supp. Superlymph 10 IU q.d. p.r. q.h.s. for 20 days. The results were evaluated at the end of therapy, 3 and 6 months after its completion.
Results. At the end of therapy, the leukocytes count in prostate secretion decreased by almost five times and remained stable throughout the entire follow-up period. The total symptom scale score at the end of therapy decreased from 22.96 ± 6.01 to 6.61 ± 3.71 points (p < 0.05). There was also a change in the perception of pain on a visual analog scale. If, before the start of treatment, 14 patients (60.9%) assessed the pain intensity as “severe” and only two (8.7%) had “weak” pain intensity, then after the end of therapy, none of the patients had severe pain, 21 (91.3%) patients noted "mild" pain and in 2 patients (8.7%) the intensity of pain was regarded as "average". Quality of life improved from baseline 8.23 ± 1.91 points to 2.43 ± 1.41 points immediately after completion of therapy (p < 0.05). Three months after therapy, patients assessed the quality of life as 2.43 ± 1.41 points, and six months later, as 2.81 ± 1.21 points. During the first three months, one patient experienced a HPV-relapse; one more — within the next three months. These patients underwent a second course according to a similar scheme. None of the patients reported significant side effects on any component of the therapeutic complex.
Conclusion. In abacterial CP/CPPS, a herpes infection should be identified. Being neurotropic, HSV can cause / exacerbate the pain characteristic of CP/CPPS. In case of persistent pain, HSV infection should be excluded. In the treatment of patients with herpes virus-associated abacterial CP, Supp. Superlymph showed good immediate and long-term results.
Introduction. Many methods have been proposed for the surgical treatment of varicocele, the most of which is of historical significance. At present, there is no consensus in favor of one or another method of surgical treatment of varicocele, which determines the relevance of further research.
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness of a new minimally invasive method of surgical treatment of varicocele using the author's method.
Materials & methods. The study enrolled 763 patients aged 18 – 46 years (mean age 26.3 years) with varicocele who underwent testicular vein subinguinal ligation according to the author's technique. Inclusion criteria: varicocele grades 1 – 3, aged ≥ 18 years, semen abnormalities according to semen analysis and dilated spermatic cord veins according to ultrasound, retrograde blood flow according to Doppler ultrasound. Exclusion criteria: previously operated patients with recurrent varicocele, patients with May-Thurner syndrome and bilateral varicocele. The examination included eight control points: before surgery and 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 months after surgery. Physical scrotal examination with Valsalva test, semen analysis, and Dopper scrotal ultrasound were performed at the control dates.
Results. The average surgery time was 15 min (10 – 30 min). All patients were discharged 1 to 2 days after surgery. At follow-up for 60 months, patients showed improvement in spermatogenesis / or no progression of semen abnormalities during follow-up after surgery based on clinical, laboratory and instrumental studies (semen analysis, ultrasound / Doppler ultrasound); no data on testicular hypotrophy, hydrocele were revealed. A scrotal haematoma was detected in one patient in the early postoperative period. Recurrent varicocele (1.4%) was detected in 11 patients during the follow-up period.
Conclusion. The technique is effective, easily reproducible, characterised by a low rate of recurrence and postoperative complications.
Introduction. Patients often request maintenance of antegrade ejaculation, and try to find the clinic, surgeon, and treatment to store it. Despite an established technique, the long-term results of ejaculation-sparing operations at a large prostate volume remain unstable. This is not allowed to give patients a guarantee in maintaining this component in their sexual life.
Objective. To evaluate the frequency of ejaculation maintenance after laser ejaculatory-sparing prostate enucleation.
Materials & methods. Since 2017 ejaculation-sparing laser enucleations have been performed in prostate volume (V pr > 80 cc) in 84 patients. Fifty-four patients (64%) had three lobes benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and two lobes — 30 patients (36%). Preoperative voiding parameters were IPSS score — 21.0 ± 2.7, QoL — 4.8 ± 0.6, residual urine volume (V res) — 139 ± 43 mL, Q max — 8.1 ± 2.0 mL. We estimate the result as positive if antegrade ejaculation remained after intervention. If ejaculation volume decreased, then as partially positive and negative — ejaculation was absent postoperatively. We conducted questionnaire and follow-up examination 3 – 6 months after intervention.
Results. Thulium-fiber laser enucleations have been performed in all cases without any serious complications. Followup 3 – 6 months after operation showed V pr — 29 ± 4 cc, V res — 19 ± 17 mL, Q max — 19.1 ± 3.1 mL/sec. IPSS score — 8.1 ± 1.9 and QoL — 2.6 ± 0.7. There are the following technical remarks: 1) tissue-sparing in the verumontanum; 2) no or minor mechanical tissue tension during enucleation; 3) avoid additional resection in the bladder neck; 4) refuse total coagulation; 5) no urethral catheter tension after operation; 6) catheter balloon inflow only in the bladder, not in the fossa. Antegrade ejaculation has stored at 17 (20%) patients, partial ejaculation — at 34 (40%) patients, so overall efficacy is 60%. The presence of a median lobe is shown to be negative prognostic factor due to the absence of full antegrade ejaculation in all cases. A partial ejaculation was achieved at 21 patients. Based on the obtained results we have optimized the three-lobe prostate enucleation technique. Four from our initial 7 patients had full storage of ejaculation and 3 — partial.
Conclusion. The possibility of BPH laser surgery to store ejaculation function at the request of the patients is modest. The presence of the median lobe makes the full ejaculation-sparing impossible. In cases of two lobes BPH full storage of the ejaculation was at 57% and partial at 43%, respectively. The following evaluation of the described technique is mandatory.
Introduction. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in aging men that is often associated with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
Objective. To determine the clinical portrait of an "ordinary" patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia and develop an algorithm for improving the efficacy of treating lower urinary tract symptoms in benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Materials & methods. The study included 112 BPH-patients who received tamsulosin therapy or a combination of tamsulosin + solifenacin for three months. After three months of therapy, the patients were divided into two groups depending on the effectiveness of therapy: group 1 — a positive result (n = 77); group 2 — no positive effect (n = 35). Due to the lack of efficacy in patients of group 2, a multichannel urodynamics was performed, according to the results of which the patients were prescribed treatment with a subsequent assessment of the result after 3 months.
Results. After 3 months of therapy in patients of group 1, a decrease in pollakiuria was noted. Regression of obstructive and irritative symptoms was also observed, and the urination-associated quality of life (QoL) improved. The maximum urine flow rate (Q max) remained unchanged mainly. By the sixth month, the frequency of urination continued to decrease (11.05 vs 9.32 episodes; p = 0.022), as well as the improvement of other parameters (IPSS, QoL, Q max and post-void residual urine volume (PVR) (80.87 vs 56.17 ml; p = 0.012). The indicators of patients of group 2 following three months of therapy remained without significant changes. Sixteen patients underwent transurethral prostate resection, 19 patients underwent therapy correction, which allowed reducing the number of episodes of daily pollakiuria. The total IPSS score decreased by 4.37 compared to baseline (IPSS (obstructive) — 13.79 vs 7.26 pts; p = 0.032). The QoL value was 2.84 pts, Q max — 14.90 mL/s, PVR — 10.58 mL.
Conclusion. 19.8% of BPH-patients are resistant to drug therapy. The ineffectiveness of therapy may be due to the severe BOO. In the absence of the effect of the therapy within 3 months, it is recommended to perform multichannel urodynamics. Correction of therapy according to the multichannel urodynamics data improves its effectiveness by the sixth month of treatment. Indicators of IPSS, Q max and PVR after 3 months of therapy allow predicting the effectiveness of therapy, or suspect the need for surgical treatment.
Introduction. The adverse effects of urine on unadapted tissues are known. This is also entirely relevant for buccal grafts used in augmentation urethroplasty, where these effects have not been thoroughly studied so far.
Objective. To assess the ongoing pathomorphosis in buccal grafts used for urethral augmentation of extensive strictures in the bulbous region and to evaluate how much urine influences their histological transformation following surgery.
Materials & methods. The study included 15 patients with extensive strictures of the bulbous urethra, who underwent a two-stage augmentation urethroplasty with buccal grafts. The grafts pathomorphosis was studied 6 months after the first surgery stage where urethrotomy had been performed with graft augmentation of the dorsal semicircle and the formation of distal and proximal neomeatuses. Natural urination through the latter was restored on days 14 – 20 following the surgery. During the second stage, six months later, urethral tubularisation was performed with two preliminary biopsies of the proximal and distal segments of the grafts implanted in the areas of the neomeatuses formed earlier. The distal area of the graft had no contact with urine, while this contact has occurred in the proximal segment since restoration of natural urination. In biopsy specimens, pathomorphosis of the grafts was studied using immunohistochemical markers: vimentin, clone SRL33; CD34, clone QBEnd/10; MSA HHF-35; СD3, clone LN10; Bcl-2, clone bcl-2\100\D5; CK-HMW 34BE-12.
Results. It was found that inflammation was minimal in areas of grafts implanted that had no contact with urine, while in areas where such contact occurred it was verified to be pronounced even 6 months after the operation. On the submucosal level, this was manifested by an uneven arrangement of collagen fibers, a dysplastically developed vascular network, uneven proliferation of the endothelium with swelling and loss of cellular connectivity, in contrast to areas where there was no contact with urine. In such areas, the graft submucosa had a dense collagen framework with organized microvasculature and uniform epithelial surface.
Conclusion. The impact of urine on buccal grafts used in augmentation urethroplasty is characterised by the disorganisation of its collagen framework, with a pronounced inflammatory component and the “reactivity” of the epithelial lining to the “toxic agent” that persists even 6 months after surgery. This may underlie the risk of a stenosis relapse in the proximal anastomosis area.
Introduction. Patients with bilateral nephrolithiasis are a challenge for the treating physician. Therefore, such patients traditionally are subject to phased surgery to reduce the rate of complications. At the same time, the enhancement of endoscopic technologies and anesthesia makes it possible to perform surgical treatment of bilateral nephrolithiasis simultaneously.
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of performing simultaneous bilateral percutaneous nephrolithotripsy (PCNL).
Materials & methods. The main group comprises 19 patients (avg age 45.0 ± 2.25 years) suffering from bilateral nephrolithiasis (13 men and 6 women). The control group include 20 patients (avg age 45.80 ± 2.29 years) suffering from bilateral nephrolithiasis. Main group patients underwent simultaneous bilateral mini-PCNL, control group patients — staged PCNL within two hospitalisations. The visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to assess the pain severity. Patients noted subjective pain sensations on post-op days 1 and 3. QoL indicators were assessed using the SF-36 general questionnaire, as well as the Russian-language validated version of the WISQoL questionnaire.
Results. There were no statistically significant differences between the parameters (the difference between the hemoglobin before and after mini-PCNL was 12 g/l; between the serum creatinine was 18 µmol/l). There was a decrease in total surgery time (121.0 ± 6.1 min) for main group patients compared to (147.0 ± 7.3 min) control group patients (total surgery time during the first and second hospitalisations) and a reduction in hospital stay (4.50 ± 0.23 days) for main group patients compared to control group patients (10.0 ± 0.5 days). Complications observed by us in the two groups were comparable. The valuesobtained on the SF, RE and MH scales in main group patients were higher both on post-op day 1 (67.9 ± 3.39; 56.90 ± 2.85 and 63.80 ± 3.19, respectively) and post-op day 3 (86.80 ± 4.34; 83.70 ± 4.19 and 82.50 ± 4.13, respectively) compared to control group patients during the first and second hospitalizations. Statistically significant differences were also recorded according to the grades "Social functioning" and "Emotional influence" in main group patients (80.90 ± 0.26 and 82.6 ± 0.19, respectively).
Conclusion. Simultaneous bilateral mini-PCNL is safe and effective in well-selected patients.
Introduction. Currently, several virtual reality (VR) simulators have been described for the upper urinary tract stone surgery skill development, including retrograde or antegrade nephroscopy. However, their high cost and the lack of a detailed reconstruction of the intraluminal pelvicalyceal system (PCS) appearance limit their implementation into educational process and clinical practice.
Objectives. To develop the approach for VR-reconstruction of the intraluminal appearance of the PCS via head mounted device (HMD), as well as estimate its usefulness for novices to improve spatial orientation during retrograde flexible nephroscopy.
Materials & methods. Five residents without experience in self-performing retrograde flexible nephroscopy participated in a 7-day training course on the VR simulator developed, during which each novice studied six variants of the PCS. For the procedure simulation, a silicone kidney model was created with the stone placed in the calyx which was selected randomly in each case. Before and after VR-course, each resident assisted the experienced urologist during simulated retrograde nephroscopy to find the stone placed according to random selection. The nephroscopy time and the number of errors in stone-finding during retrograde flexible nephroscopy were analysed.
Results. There was a statistically significant decrease in nephroscopy time (on avg by 17.6 minutes, p = 0.043) and errors to find targeted calyx, which was observed once after the training one resident only.
Conclusion. The described VR simulator does not require significant time, technical and financial costs, and is available for wide implementation in the training of young specialists.
Introduction. Early diagnosis of cancer is one of the most important international strategies. Malignant and healthy tissues differ in the interaction with electromagnetic waves. Pilot studies show a potential perspective for non-invasive analysis of electromagnetic anisotropy in biological tissues.
Objective. To assess the diagnostic importance of the electromagnetic detection of prostate cancer (PCa) within the prospective study.
Materials & methods. One hundred and twenty-four patients were included to undergo a prostate biopsy, transurethral prostate resection, or radical prostatectomy. The investigators did not have information on their clinical details. Research technique: the probe was applied to the perineal region, turning it in three planes. A reduction of the 465 MHz band below a threshold was fixed and was considered suspect for PCa. The results of electromagnetic evaluation were compared with the findings of a pathomorphological study after biopsy or surgery.
Results. Fourty-seven true-positive and 21 true-negative results were detected, 20 false-negative and 46 false-positive (follow-up group as potentially true-positive group). The overall sensitivity was 82%, specificity – 31%. The positive and negative predictive values were 73% and 62%, respectively. The accuracy of the method was 54%.
Conclusion. Early PCa stage could be a reason for many false-positive results and low specificity, as a result. PCa detection is significantly reduced with lesions less than 3 mm, therefore patients with false-positive results were placed in the follow-up group. Patients’ examination with the TRIMprob TM («Galileo Avionica» SpA, Torino, Italy) could increase the early PCa detection at the screening. The research is currently ongoing.
Introduction. The amount of non-absorbable synthetic material used in the surgical treatment of pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence has been shown to directly correlate with the risks of mesh-associated complications. Previously, we developed a partially absorbable implant. Currently, there are insufficient data on the use of partially absorbable implants in female pelvic floor reconstruction, which requires comparative biomechanical and pathomorphological studies.
Objective. To compare the biomechanical properties of a new generation partially absorbable implants and nonabsorbable polypropylene mesh implants during animal model.
Materials & methods. Thirty-nine rabbits weighing 3200 ± 250 g were randomised into three groups depending on the implanted endoprosthesis: group 1 (n = 15) — “Axilen” implant (polydioxanone 98%, polypropylene 2%), group 2 (n = 15) — “Axilen Rapid” implant (polyglycapron 98%, polypropylene 2%), group 3 (n = 9) — “Urosling 1” implant. After implantation, rabbits of all 3 groups were divided into 3 subgroups according to the withdrawal period from the experiment: 14 days, 60 days, and 180 days. The biomaterial obtained was subjected to two studies: evaluation of the macroscopic view of the explanted mesh endoprosthesis with the formed capsule and the surrounding tissues, study of the biomechanical properties of the formed connective tissue capsule with the implant.
Results. According to macroscopic evaluation, there was a less significant tissue reaction to partially absorbed implants. A comparative analysis of biomechanical indices revealed no statistically significant difference in rupture elongation at all follow-up periods among the presented groups. Tensile strength, at 60 and 180 days, was not statistically different between the groups described. At 14 days, there was a statistically significant difference in tensile strength between groups 1 and 3 (p = 0.003).
Conclusion. During biomechanical animal experiments, the connective tissue capsule formed on the partially absorbable implant was not inferior to the similar parameter of the non-absorbable sample in its tensile strength, which explains a great potential for the use of partially absorbable implants in reconstructive surgery of pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
Male reproductive health depends on many factors, including whether infectious diseases occur in the reproductive system. Such changes may be reflected in the semen analysis. In the past three years, the number of individuals who fell ill with COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 has been growing worldwide, including in Russia. This infection causes dysfunction and a negative effect on many organs and systems, including reproductive organs, which is reflected in abnormal semen parameters. Despite the high efficacy and small number of side effects found in clinical trials, only 56% of the population in the US and 49% in the Russian Federation reported wanting the vaccine. One of the reasons for distrust of vaccines is the potential negative impact on fertility. A literature review is devoted to the study of the effect of SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination on male reproductive health. The search was carried out using Medline, PubMed, and EMBASE databases.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is one of the most common and practicable plasma-therapy techniques. The wide therapeutic range for the use of this technique in various medical fields is due to its high content of growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines. The property of PRP to induce tissue regeneration is particularly highlighted, which is used actively for the treatment of a broad range of urological diseases. The review aimed to highlight the accumulated material on the topic of the use of autologous biomaterials based on blood in urology. This article highlights the urgent need for further study of the prospects for the use of autoplasma technologies in wide multicenter studies.
Introduction. Testicular torsion (TT) is the most common pediatric emergency urological pathology. To reduce the duration of the diagnostic stage, systems for assessing the risks of testicular torsion based on anamnesis and clinical symptoms were proposed. In 2013, Barbosa et al. proposed the TWIST system (testicular examination for ischemia and suspected torsion), which became the most well-known and widespread. This system makes it possible to identify groups of patients who do not require scrotal ultrasound, which reduces the number of stages in the diagnosis of TT.
Objective. To evaluate the experience of using and diagnostic significance of the TWIST scale based on available data in scientific publications.
Materials & methods. Review and analysis of literature data on the use of the TWIST scale.
Results. We conducted an analysis of 13 publications, in which the results of using TWIST with statistical analysis were published. In all articles, the final diagnosis was established according to Doppler scrotal ultrasound or intraoperatively. Analysis of publications shows that even in large foreign medical centers there is a problem of emergency scrotal ultrasound, which increases the time of testicular ischemia with ТТ. To use the TWIST scale, only history and physical examination data are needed. Any specialist can use the scale in his practise. The low probability of TT in the low-risk group makes it possible not to perform routine scrotal revision, and, consequently, material and human resources are saved.
Conclusion. Literature analysis has shown that the use of the original TWIST scale proposed by J.A. Barbosa, in case of suspected testicular torsion, has sufficient diagnostic accuracy, high sensitivity and specificity of TT detection, which significantly reduces the need for ultrasound, reduces the diagnostic time before surgery, that increases testicular survival.
Introduction. Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common cancers among men, and the tactic to treat this disease stage-depends directly. The “gold” standard for localized PCa is radical robot-assisted prostatectomy (RARP). Patients often have excessive surgery requirements and are concerned about the development of postoperative complications. One of the most frequent functional complications after this operation is urinary incontinence (UI), whose formation mechanism is not fully understood. Clinical studies have described many UI predisposing factors, but the results obtained are often contradictory, which requires a repeated and deeper study of the issue.
Objective. To identify predisposing factors for urinary incontinence in patients undergoing radical robot-assisted prostatectomy.
Materials & methods. The search results for the scientific databases PubMed, Medline, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library and PEDro, Wang-fang Database and CNKI, Edline were analyzed for the queries "robot-assisted prostatectomy", "radical prostatectomy", "incontinence", "predictors", "urinary incontinence".
Results. The predisposing factors to UI after RARP were studied. The review discusses and illustrates in detail all known predisposing factors for UI and shows the inconsistency of the data obtained by different researchers, which once again emphasizes the need for further study of this issue.
Conclusion. Despite the long history of studying postoperative complications of RARP, reliable and consistent data on all the risks of UI after RARP have not yet been obtained. Therefore, this literature review summarizes and analyzes the results of the latest research in recent years.
CLINICAL CASES
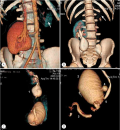
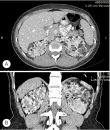
Urethral doubling is a rare congenital malformation of the lower urinary tract. A little more than 200 cases of various forms of this defect have been described in the literature worldwide. We present a rare clinical case of duplication of the urethra in combination with the megaureter of the only functioning kidney. In this patient, we encountered a previously undescribed anomaly within the generally accepted classification of the kidney collecting system in combination with a true diverticulum of the bladder and a descending orthotopic ureterocele.
Tuberous sclerosis is one of the forms of monogenic hereditary pathology related to neurocutaneous diseases (phacomatoses). Diagnostic difficulties are associated with pronounced clinical polymorphism and age-dependent onset of symptoms. The article presents current data on the prevalence and clinical manifestations of tuberous sclerosis. A clinical case of tuberous sclerosis is given in several generations of the same family.
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
Despite many shortcomings, the semen analysis remains the leading method of male fertility assessment. For several decades, the WHO has been working on standardisation of the methodology for examining human ejaculate. In 2021, the sixth edition of WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen was released, which proposed several concepts for performing and interpreting the results of a semen analysis. Many of these concepts are not new and have already been covered in previous tutorials. At the same time, the rejection of reference values and the transition to “decision limits” raises several questions that have not yet been answered.
CURRENT STATE-OF-THE-ART
The analysis of domestic and foreign literature on the epidemiology, etiology, and possible sexual transmission of urinary tract infections (UTI) was carried out. It has been established that more than 30 pathogens are currently classified as sexually transmitted infections (STI). The molecular genetic method has shown the identity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in familial cases of UTI, which confirms the sexual route of infection transmission, which was not previously classified as a classic STI. Several works are cited that undoubtedly testify to the possible sexual transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Up to date, few reports of sexual transmission of UTI have been published, although tuberculosis is one of the most common infectious diseases worldwide. Perhaps because the partner of a patient with genital tuberculosis or other UTI is not actively evaluated. Thus, the possibility of sexual transmission may be underestimated. Sexual transmission of M. tuberculosis as well as uropathogenic E. coli is unlikely, but possible.