ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. The aging process in men is accompanied by a progressive decrease in the level of serum testosterone (Tc). In addition to chronological aging, various factors contribute to the decline in testosterone levels. One of such factors contributing to the decrease in endogenous Tc and the development of secondary hypogonadism is the long-term use of testosterone preparations (TPs) used for non-medical purposes.
Objective. To assess the nature of lower urinary tract symptoms following discontinuation of long-term non-medical use of testosterone preparations.
Materials and methods. A clinical and statistical analysis of examination results in 31 men aged 22 – 46 years who received TPs for non-medical purposes while visiting gyms and subsequently turned to urologist with complaints of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) was carried out. The study used the International Prostatic Symptom Score (IPSS) questionnaire, laboratory and instrumental examinations: general urine examination, general blood examination, prostate secretion microscopy, evaluation of serum total Tc, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, prolactin, estradiol, prostate ultrasound and bladder ultrasound, uroflowmetry
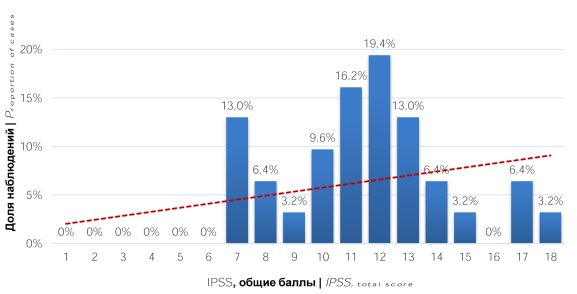
Results. When assessing LUTS, the prevalence of irritative symptoms was noted. The level of serum total Tc in 13 (41.9%) men was in the range of 8 – 11 nmol/l, in 18 (58.1%) men it was below 8 nmol/l. In addition, most patients (77.4%) had areas of reduced blood flow in the prostate, and 67.7% had prostate fibrosis.
Conclusion. Discontinuation of the use of long-term non-medical TPs can lead to the development of secondary hypogonadism and LUTS, which in most cases are irritative. In the treatment of these patients, an interdisciplinary rehabilitation program should be developed.
Introduction. It has been established in an animal model that coagulase-negative staphylococci (Staphylococcus haemolyticus) and anaerobes (Peptococcus niger) cause the development of an acute inflammatory process in the prostate when inoculated with 103 CFU/ml. At the same time, data have been published indicating the pathogenic potential of these microorganisms on a titer of 102 CFU/ml. But it was confirmed for the model of acute obstructive pyelonephritis. In addition, the characteristics of the formation of the inflammatory response at different times were determined, which require detailed verification and comparative characteristics with those during infection with a causative uropathogen (Escherichia coli).
Objective. Based on the results of the experiment, to carry out: 1) an evaluation of the relationship between the dynamics of microbial load and the degree of pathomorphological changes in prostate tissues during infection with various uropathogens in a titer of 103 CFU/ml; 2) an evaluation of the degree of microbial load and severity of histological changes in prostate tissues on follow-up day 7 with transurethral infection with various uropathogens in a subpathogenic titer of 102 CFU/ml; 3) a fundamental comparative analysis of the indicators of contamination and the severity of inflammatory changes on follow-up day 7 after the inoculation of various uropathogens in titers of 102 and 103 CFU/ml.
Materials and methods. The animal model was performed using the FELASA and ARRIVE guidelines. Lab animals: 20 New Zealand rabbits. Uropathogens: E. coli, S. haemolyticus, and P. niger. Infectious titers: 102.3 cfu/ml. Uropathogen inoculation technique: topical transurethral. Randomization: all laboratory animals were divided into 4 groups depending on the uropathogen (3 experimental, 1 control). Follow-up periods: day 1, 3, 7 and 14 for a titer of 103 CFU/ml, and day 7 for a titer of 102 CFU/ml. At the end of the follow-up, euthanasia and autopsy were performed with the extraction of the urogenital organ complex. Hereafter, biopsies were taken from various parts of the prostate. Cultural and histological studies of prostate tissues were carried out using standard methods. The results were analyzed using Statistica 10.2 (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA) and GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software Inc., Graphpad Holdings LLC, San Diego, CA, USA) programs through descriptive and nonparametric statistics.
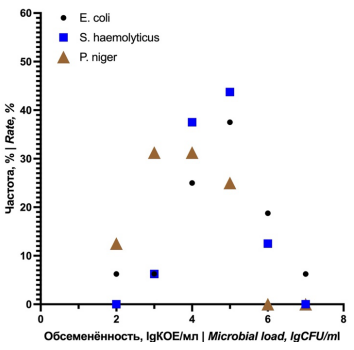
Results. Bacterial contamination of prostate tissue was determined in all cases of infection with differences (p < 0.05) in some indicators between the E. coli and P. niger groups at different observation periods, but only in the case of inoculation of the test titer of 103 CFU/ml. Histological evaluation of prostate tissues after inoculation with 103 CFU/ml verified the presence of acute destructive changes in the prostate from the follow-up day 1, which were more pronounced in the S. haemolyticus and E. coli groups. However, similar characteristics of the development of the inflammatory process in the form of hyper-eosinophilic infiltration in the early stages and pronounced congestion of the prostatic glands were identified in the S. haemolyticus and P. niger groups. Comparison of trends in dynamic changes of microbial load (rise / decline) and severity of pathological changes (increase / resolution) in prostate tissues in established follow-up periods showed the presence of relative synchronization of trends (from days 1 to 7) in the S. haemolyticus and P. niger groups, and complete synchronization in the E. coli group. When comparing the median microbial load of the prostate on the follow-up day 7, no intergroup (p > 0.05) differences were found both in cases of infection with a titer of 103 CFU/ml, and when compared with the data on contamination for a test titer of 102 CFU/ml, at the same time observations. At once, when E. coli and S. haemolyticus were infected at a subpathogenic titer of 102 CFU/ml, inflammatory changes were recorded that had a mild diffuse character, in relation to those after inoculation of these pathogens in a titer of 103 CFU/ml. In turn, P. niger induced the development of low-intensity focal alteration in isolated areas of prostate tissues.
Conclusions. Detailed analysis of culture and histological data showed that E. coli, S. haemolyticus and P. niger have significant pathogenic potential at titer of 103 CFU/ml. In turn, when the titer decreases to 102 CFU/ml, E. coli and S. haemolyticus retain their pathogenic potential, but the severity of the inflammatory reaction is significantly reduced. It was also found that a change in bacterial contamination affects the severity of the inflammatory process in all groups during seven follow-up days at a given test titer.
Introduction. Chronic prostatitis / Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP / CPPS) is an extremely common condition for which no effective treatment has been found yet. Focused shockwave therapy (fSWT) is a safe method of physical intervention that could potentially be effective in CP / CPPS treating.
Objective. To evaluate the efficacy and quality of life of patients after treatment of CP / CPPS with fSWT.
Materials and methods. A prospective cohort study included 48 patients diagnosed with CP / CPPS. The patients attended the clinic three times a week for 4 weeks (12 sessions). Each time, patients received fSWT therapy sessions by “Chronic pelvic pain” protocol. One month after the last therapy session, the men completed the validated NIH-CPSI, IPSS, and QoL questionnaires.
Results. The mean age of the patients was 40 ± 9 years. After the course of therapy, the score of Domain I “Pain” from 10.0 ± 4.7 to 6.3 ± 1.9 (p < 0.001). At the same time, no statistically significant decrease was obtained in Domain II 'Urination' scores ((5,88 ± 2,40 vs 5,42 ± 1,64; p = 0,11). By the end of therapy for Domains III and IV, the scores had changed from 4.42 ± 0.90 and 4.04 ± 1.27 to 4.48 ± 1.01 and 3.08 ± 1.22, respectively (p < 0,001). It is noted that the mean IPSS questionnaire score showed no statistically significant change over the treatment period (17,2 ± 4,8 vs 17,8 ± 4,8; p = 0,074)). QoL changed from 4.48 ± 0.99 to 2.46 ± 1.03 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion. The study demonstrated the efficacy of fSWT as a standalone method in the treatment of CP / CPPS.
Introduction. The widespread use of modern immunosuppressive therapy schemes has increased the duration of transplanted organ function. However, along with an increase in life expectancy, there is an elevation in malignant neoplasms in patients with a transplanted organ.
Objective. To present own clinical experience in the treatment of patients with malignant skin neoplasms after kidney transplantation.
Materials and methods. Four patients with malignant skin neoplasms were observed in our clinic from 2010 to 2017. Three of them developed Kaposi's sarcoma between 6 months and 6 years after kidney transplantation, and one was diagnosed with squamous-cell skin cancer 10 years after the operation.
Results. After histological verification of Kaposi's sarcoma, excision of neoplasms was performed in two cases, followed by a decrease in the dosage of immunosuppressive drugs. In one case, a complete conversion of immunosuppressive therapy was performed. Stabilization of the oncological process was noted during therapy. However, subsequent deterioration in the function of the transplanted organ was recorded up to a complete loss of function in all patients, which led to the removal of the kidney. A patient with squamous-cell skin cancer underwent surgical treatment with a course of close-focus radiotherapy, but further progression led to a lethal outcome.
Conclusion. Kidney transplant recipients receive lifelong immunosuppressive therapy and represent a high-risk group for developing skin malignancies and an increased risk of cancer mortality. Withdrawal of immunosuppressive drugs, i.e. calcineurin inhibitors, is still the main condition for the complete cure of patients with Kaposi's sarcoma but is accompanied by an extremely high probability of loss of function of the transplanted organ.
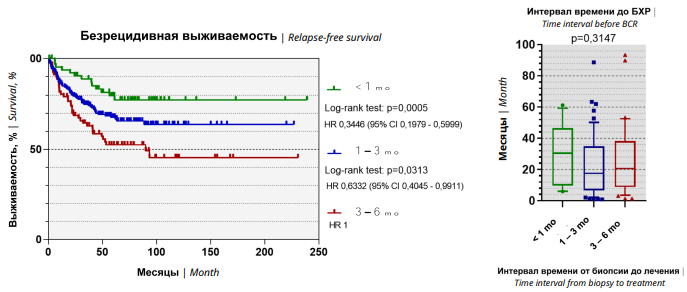
Introduction. To date, the impact of the time interval from diagnostic prostate biopsy to radical prostatectomy on treatment outcomes remains a topical issue.
Objective. To evaluate the effect of the timespan from diagnosis to radical treatment of prostate cancer (PCa) patients on tumor morphology and long-term oncological outcomes.
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis of the results of treatment of patients with high-risk PCa who underwent radical prostatectomy with extended lymphadenectomy from 2001 to 2019 in three St. Petersburg clinics was performed. The influence of the time interval from prostate biopsy to radical treatment on long-term outcomes was assessed.
Results. An increase in the time interval before surgical treatment over three months did not affect the tumor morphology. Five-year biochemical relapse-free survival was 79.7%, 67.8% and 52.5% among patients with time interval from biopsy to surgical treatment less than 30 days, 30 – 90 days and more than 90 days, respectively. The time interval prior to radical treatment did not have any effect on overall and cancer-specific survival.
Conclusion. The time interval from prostate biopsy to surgical intervention, not exceeding 3 months, is the most favorable with respect to long-term outcomes.
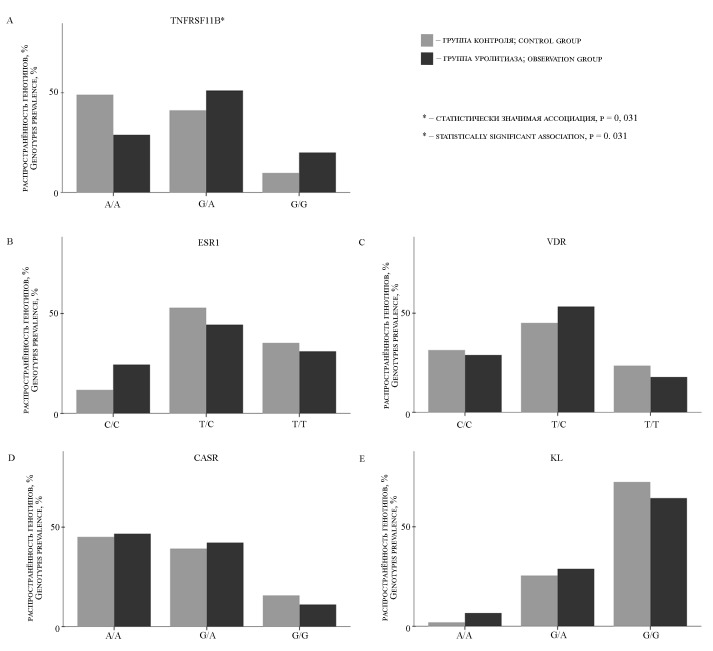
Introduction. Urolithiasis is a polyethylological disease of the urinary system. Epidemiological data on urolithiasis is disappointing: over the past 30 years, the number of patients with urolithiasis has increased by 48.57%, and the mortality rate has increased by 17.12%. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in various genes can influence the risk of development and recurrence of this disease. Early diagnosis of a patient's genetic predisposition to primary or recurrent urolithiasis is important for the effective prevention of urolithiasis.
Objective. To explore the association of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) rs3134057 (TNFRS11B), rs851982 (ESR1), rs1540339 (VDR), rs2202127 (CASR), rs526906 (KL) with the development of recurrent urolithiasis.
Materials and methods. The observed group consisted of 96 patients with a single-sided ureteral stone, of whom 45 had recurrent urolithiasis; the control group consisted of 51 volunteers. Venous blood samples were collected from all participants, DNA was extracted from the blood and analyzed for each SNP studied by real-time polymerase chain reaction. We analyze the data obtained on genotype and presence or absence of urolithiasis in the participants using a binomial logistic regression model.
Results. An association was found between the presence of SNP rs3134057 in the TNFRS11B gene (odds ratio (OR), 1.92; confidence interval (CI): 1.05-3.52; p = 0.031) and the development of recurrent urolithiasis.
Conclusion. The association of rs3134057 with urolithiasis relapse leads us to investigating the effect of this SNP on serum osteoprotegerin levels, a product of the TNFRS11B gene.
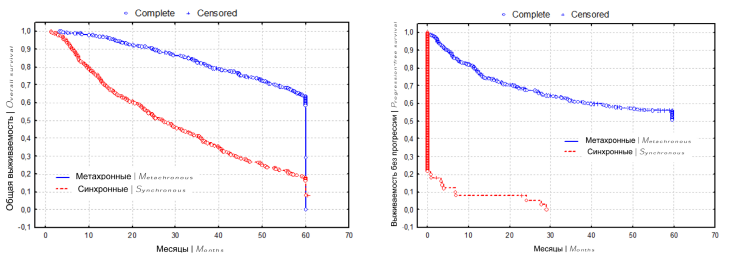
Introduction. The differences in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) depending on the line of systemic therapy, the timing of the onset of metastases, and Heng prognostic groups in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) remain unclear. This leads to the search for new prognostic factors or their combinations, depending on the characteristics of the metastatic disease.
Objective. To identify prognostic factors affecting survival rates in patients with synchronous and metachronous renal cell carcinoma metastases.
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis of 934 patients with mPCC treated in the period 2006 to 2020 was performed, of which 319 (34.2%) patients were assigned to the intermediate prognosis group, and 388 (41.5%) to the unfavorable prognosis group. Synchronous metastases (Smts) and metachronous metastases (Mmts) were detected in 380 (40.7%) and 554 (59.3%) patients, respectively. The clinical and morphological characteristics of the tumor were analyzed, as well as laboratory parameters. Statistical analysis was carried out using Statistica 10.0 software («StatSoft Inc.», Tulsa, OK, USA ) by constructing Kaplan-Meyer curves and survival tables, building a mathematical survival model.
Results. The 3-year and 5-year OS of Smts-patients and Mmts-patients were 40.3% and 82.5%, 18.8% and 64.3% respectively. The median OS was 25 and 88 months, respectively (p < 0.001). The 3-year and 5-year PFS rates in Mmts-patients were 60.5% and 55.7%, respectively. In Smts-patients, PFS was only 9 months, compared with a median PFS of 60 months in Mmts-patients (p < 0.001). Anemia and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate were observed more frequently in Smts-patients. Mmts-patients were more likely to have normal platelet and alkaline phosphatase counts. Smts-patients more often had an unfavorable prognosis according to Heng and ECOG status, a higher T stage, a low tumor differentiation, and histologically, non-clear cell carcinoma variants, the presence of lymphogenous metastases, and an increased number of organs with metastatic lesions (p < 0.001). In univariate and multivariate analyses, OS in Smts- and Mmts-patients, anemia, and poor Heng prognosis were the only statistically significant prognostic factors. In a univariate analysis of OS of Smts-patients, increases in elevated erythrocyte sedimentation platelets, and alkaline phosphatase were significant adverse prognostic factors (p < 0.001).
Conclusion. Research into new prognostic factors and their combinations, focusing on the specifics of the metastatic disease itself, will improve prediction outcomes and optimize systemic treatment outcomes.
Introduction. Partial nephrectomy occupies a rightful priority position in the treatment of localized renal cell carcinoma. It not only provides high oncological results but also allows you to save the renal parenchyma. This reduces the risk of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular accidents, which is especially important in young patients. The main technical problem is the closure of the renal wound with reliable hemostasis and low risk of urine leakage, especially in patients with large endophytic lesions.
Objective. To study the mechanical properties of the renal parenchyma and to establish ways to prevent suture eruption under an experimental model.
Materials and methods. The studies were carried out using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use "Technologies and Materials of the Belgorod State National Research University". Mechanical tests of the strength characteristics of the layers of the renal parenchyma were performed on 60 cadaveric kidneys. The tensile strength and tension of tissues during the application of various surgical sutures, as well as variants of the latter with the use of spacers made of materials that prevent thread eruption, were studied using a tensile machine.
Results. During mechanical tests, the medulla was found to have the highest strength (23.58 ± 9.17 load (L)) between the layers of the renal parenchyma. The mechanical strength (8.40 ± 2.89 L) of the cortical substance in the absence of the capsule was minimal. When replacing the vertical suture through all layers by tied a knot along the resection line with a similar horizontal mattress suture, it significantly increased tensile strength (27.35 ± 12.04 L) to levels comparable to the tensile strength of the medulla. The use of a hemostatic mesh (SurgicelÒ) as a lining did not significantly affect the ultimate strength (23.58 ± 9.17 L) of the horizontal mattress suture. The use of a prolene mesh (LintexÒ mesh) for this purpose significantly prevented suture eruption (31.48 ± 9.98 L) compared to the native suture and the SurgicelÒ mesh. The maximum tensile strength (45.61 ± 6.1 L) of a horizontal mattress suture was obtained for a tape made of a polytetrafluoroethylene vascular prosthesis.
Conclusion. The study of the mechanical strength of the layers of the renal parenchyma showed the inexpediency of performing a cortical suture. The use of a horizontal mattress suture significantly increases the tensile strength compared to a vertical one. Maximum mechanical strength characteristics were obtained using polytetrafluoroethylene inserts.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
Introduction. The review is aimed at analyzing the worldwide experience in the use of the oral mucosa in ureteroplasty due to benign ureteral strictures.
Objective. To study the features of the use of the oral mucosa in ureteral reconstruction based on a review of the worldwide literature.
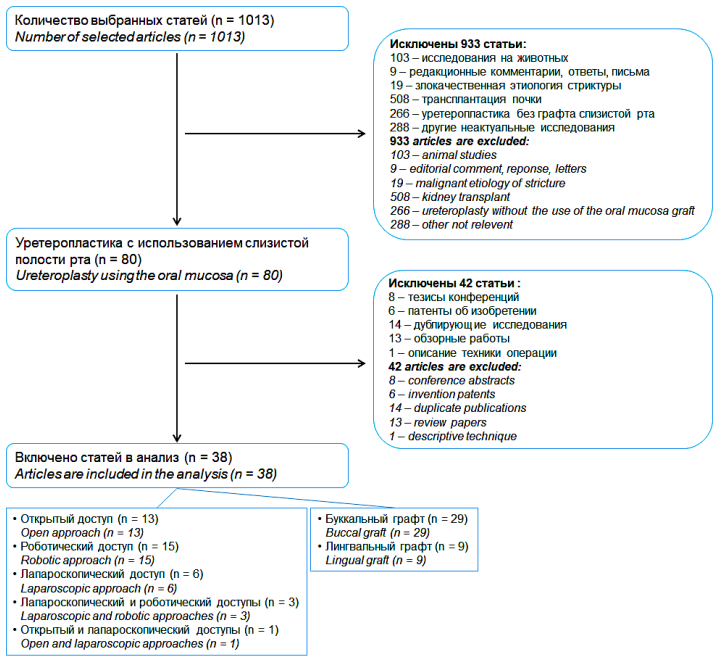
Materials and methods. The review was conducted using the PubMed, EMBASE, and the Russian Science Citation Index database. In the first stage, 1013 sources were found, of which 38 articles were selected for inclusion in the review. Of these, 13 studies used an open approach, 15 — robotic, 6 — laparoscopic, 3 — laparoscopic and robotic, 1 — open and laparoscopic. A buccal graft was used in 29 studies and a lingual graft was used in 9 studies.
Results. In total, oral mucosal ureteroplasty was performed 308 times in 306 patients: open technique — 64 times, robotic — 145 times, laparoscopic — 99 times. A buccal graft was used in 67.9% (209/308) of the cases, a lingual graft was used in 32.1% (99/308). Postoperative complications were observed in 15.9% (49/308) of the cases: 12.2% after the open technique, 10.4% after the robotic technique and 20.2% after the laparoscopic technique. With a postoperative follow-up period of 1 to 85 months (average 15.3 months), treatment success was achieved in 92.5% (285/308) of the cases: 93.8% for open technique, 88.2% for robotic, 98.0% for laparoscopic.
Conclusion. The use of the oral mucosa for ureteroplasty due to benign ureteral stricture allows high rates of efficiency and safety. The results of ureteroplasty do not depend on the choice of surgical approach, type of graft and graft transplantation technique.
According to the guidelines, percutaneous nephrolithotomy is the main treatment for patients with kidney stones larger than 2 cm. However, many studies have recently been published describing the safety and efficacy of retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) in the treatment of patients with kidney stones of similar size. This paper reviews the literature on the use of RIRS in the treatment of patients with kidney stones larger than 2 cm. The study aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of RIRS in the treatment of kidney stones larger than 2 cm. Such indicators as the duration of surgical treatment, stone-free rate, intra- and postoperative complications were evaluated. Also, the history of the development of ureteroscopy as a diagnostic and therapeutic method for diseases of the upper urinary tract is briefly reviewed. The material was searched in the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases.
Introduction. Neuromodulation has proven itself in the treatment of patients suffering from idiopathic overactive bladder and non-obstructive urinary retention, who are resistant to conservative therapy. The possible use of the method in the population of patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD) is of undoubted clinical interest.
Objective. To analyze the current possibilities and features of neuromodulation in a cohort of patients with NLUTD.
Materials and methods. Original research materials published in the PubMed, eLibrary, SciVerse (ScienceDirect), Scopus, Medline, EMBASE databases, websites of professional associations without restrictions on the date of publication were used. Sixty sources were selected for citation, with preference given to systematic reviews, meta-analyses and RCTs .
Results. In relation to NLUTD, transcranial and peripheral magnetic stimulation, intravesical electrical stimulation, tibial, pudendal electrical stimulation, and stimulation of the dorsal pudendal nerve, as well as sacral and epidural methods of neurostimulation are considered.
Conclusion. The current literature optimistically presents the experience of using neuromodulation in the NLUTD patient population with the largest evidence base for invasive sacral and tibial stimulation. The studies are based on heterogeneous populations, limited by small sample sizes with insufficient descriptive part of the degree and severity of neurological diseases, and it should be considered when forming guidelines. However, the lack of other suitable therapies and promising initial results indicate the importance of further efforts to improve the applied methods of neuromodulation. Further studies are needed with larger sample sizes, better classification of diseases, and controlled study design
Introduction. A century and a half of experience in renal surgery has shown the clinical feasibility of preserving a functioning renal parenchyma and the pathogenetic validity of nephron-sparing surgery (NSS) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Objective. To analyze the available scientific publications on nephron-sparing sutureless kidney surgery or without so-called renorrhaphy.
Materials and methods. We have searched the eLibrary, PubMed, Сochrane Library and Scopus databases without time limits. A total of 19365 publications were found in the databases, including 71 randomized controlled clinical trials, 987 reviews of which 168 were systematic and 2 were performed based on data from the Cochrane Library. This review includes publications on the sutureless NSS technique in patients with RCC; clinical cases and abstracts were excluded from the formal analysis of publications. Thus, 132 publications were selected for the analysis, which are presented in the following independently or included in previous literature reviews. The studies available for analysis were quite heterogeneous in terms of patient groups, inclusion criteria, and control points, which did not allow for a meta-analysis of the data presented.
Results. An attempt to abandon the principle of kidney suturing after partial nephrectomy was implemented using methods of hemostasis based on the action of physical factors. At the same time, the value of any one of the methods that seemed at first glance did not show obvious unequivocal advantages in the NSS, the achievement of which would unequivocally reduce the severity of the problematic issue at the present stage. Significant prerequisites for such a state of the problem should be considered the monocentric nature of most studies and relatively little experience in the application of certain methods or their combinations. In the aspect of the foregoing, it is difficult to disagree with the statement that many different methods of hemostasis used during NSS appear not only to be the result of the tireless search for new opportunities by clinicians, but also the real lack of universal technologies.
Conclusion. An analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of the final hemostasis methods during NSS in patients with localized RCC indicates that this problem has not been solved and requires further research.
CLINICAL CASES
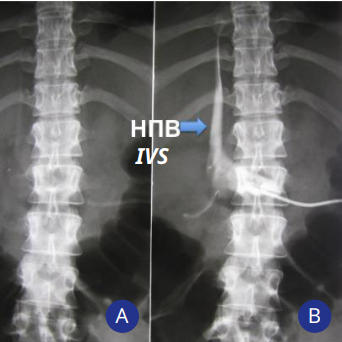
Percutaneous renal interventions are characterized by bleeding and infectious complications, as well as trauma to organs located near the kidney, renal or inferior vena cava (IVC). The article presents a clinical observation of a rare complication of percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN), i.e. migration of the distal end of the nephrostomy tube into the IVC. Its timely removal followed by re-nephrostomy made it possible to avoid bleeding and restore drainage of the pyelocalyceal system. Along with this, the article presents a literature review on this condition in the eLibrary, Springer, MedLine, Embase, UpToDate databases from 2000 to 2021. The indications for PCN, the frequency and risk factors of IVC damage during percutaneous renal interventions, as well as treatment tactics were studied. After the initial evaluation of the literature, ten articles were selected for further analysis. The main risk factors associated with IVC perforation after PCN include the surgeon's lack of experience in instrumental imaging, misjudgment of the length of the nephrostomy tube, and its insertion depth, resulting in its inadequate placement. Removal of the nephrostomy tube from the IVC under radiological and ultrasound guidance or open surgery are the main methods to correct for this complication.
Introduction. Anatomical features of the urinary tract in patients with duplicate kidneys are described using the Weigert-Meyer rule, since the orifice of the upper ureter has an ectopic location (inferomedial) and the orifice of the lower ureter has an orthotopic location (superolateral). However, there are rare cases of violation of this rule, complicated by obstructive megaureter, ectopic ureteral orifice, the presence of ureterocele.
Objective. To report the rare clinical case of a lower pole obstructive megaureter as a violation of the Meyer-Weigert rule in the patient with complete ureteral duplication and to describe the use of ureteroureterostomy as an effective and safe method of surgical correction of the presented anomaly.
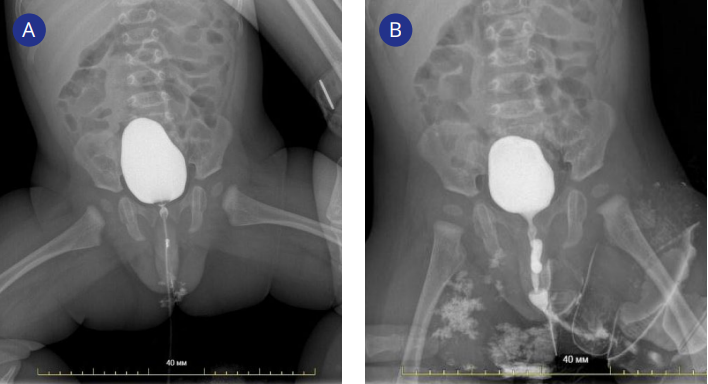
Clinical case. We present a case of the infant (5 months old) with a lower pole obstructive megaureter. This pathology was identified through intravenous urography and voiding cystourethrography. Laparoscopic proximal end-to-side ureteroureteroanastomosis was chosen as a surgical treatment. Postoperative control intravenous urography showed the effectiveness (a reduction in the lower pole collecting system of the duplex kidney was revealed) and the safety of this method of correction.
Conclusion. There are only several clinical cases about exceptions to the Weigert-Meyer rule reported in literature, and most of them are about adult patients. The main surgical method of treatment in such cases is heminephrectomy. To our knowledge, this is the only reported case of using ureteroureterostomy in the patient with a lower pole obstructive megaureter. This technique has shown its effectiveness and safety for restoring the patency of the urinary tract, confirmed during the control postoperative examination.
Primary penile melanoma is an extremely rare casuistic pathology associated with a poor prognosis. The article presents a clinical case of massive lesion of the penis with malignant melanoma, and discusses surgical methods for treating this pathology.
CURRENT STATE-OF-THE-ART
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer worldwide and the eighth leading cause of cancer mortality in men. The advent of new systemic therapies, including PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors, and advances in biomarker development have revolutionized the treatment of this disease. The current guidelines of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) support the inclusion of some new therapies in clinical practice. Over the past decade, many approvals for immuno-therapeutic agents have been obtained. Since bladder cancer is characterized by a high frequency of mutations, there has been a widespread introduction of medicines from the group of immune checkpoint inhibitors. All studies from this review were presented at a recent meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and published in reputable journals.