ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Currently, urologists are divided on which method is most effective for treating bladder neck contracture (BNC) after surgery: transurethral resection (TUR) or incision.
Objective. The study aimed to assess the balloon dilation safety and success in patients with recurrent bladder neck contracture (BNC) after endoscopic surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Materials & Methods. This study involved 110 patients with recurrent BNC after transurethral interventions for BPH. All patients underwent TUR of the bladder neck and were divided into 2 groups: group A (n = 45) included men who, after TUR, additionally underwent repeated balloon dilation, while the control group B (n = 65) included men who were treated with alpha-blockers alone.
Results. In 9 months after TUR and 3 months after the fourth balloon dilation procedure in group A, the mean international prostate symptom score (IPSS) decreased from 20.1 ± 8.4 to 17.2 ± 7.4, and the IPSS-quality of life (QoL) was 4.2 ± 1.2 (p > 0.05). In group B, they were 21.7 ± 7.7 and 4.7 ± 1.1 (p > 0.05), respectively. Additionally, the mean flow rate in group A was 13.2 ± 5.4 ml/s, while in group B, it was 8.7 ± 4.9 ml/s (p < 0.05). There was a significant decrease in the post-void residual urine volume (PVR) from 76.2 ± 96.1 ml to 37.6 ± 55.1 ml in group A, whereas, in group B, it increased from 63.0 ± 36.9 ml to 79.4 ± 71.6 ml (p > 0.05). Also, 28.0% of patients of group B, and 13.3% of patients of group A underwent repeated TUR of the bladder neck in 9 months follow-up period (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. Balloon dilation procedure is a relatively safe less invasive procedure and can reduce the BNC recurrence rate and consequently the rate of repeated transurethral interventions.
Introduction. The influence of the length of the number of CAG repeats in the androgen receptor gene (nCAG AR) on endothelial dysfunction (EnD) is currently understudied.
Objective. The study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the nCAG AR and the dynamics of biochemical and ultrasound markers of EnD in men with functional hypogonadism and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) receiving testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Materials & methods. This study included 45 hypogonadal men with T2DM, receiving TRT for 1 year. Patients were assessed for carbohydrate and lipid metabolism parameters; total and free T; sex hormone-binding globulin; biochemical markers of EnD (NO, eNOS3, endothelin) and the nCAG AR; brachial artery (BA) vasoreactivity. Patients were divided into 3 groups: group I — 9 men with nCAG AR < 19; group II — 27 men with nCAG AR > 19 – 24; and group III — 9 men with nCAG AR >24.
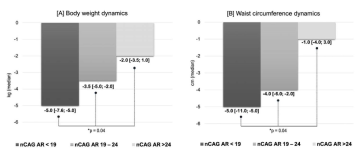
Results. Patients with nCAG AR < 19 exhibited a 2-fold greater and faster increase in BA vasoreactivity on TRT compared to patients with nCAG AR 19-24 and 3-fold greater than men with nCAG AR >24 (p < 0.05). Patients with nCAG AR < 19 also demonstrated the most pronounced rise in NO and eNOS3 on TRT compared to men with nCAG AR > 24. Patients with nCAG AR < 19 experienced the most pronounced decreases in weight, waist circumference, and HbA1c on TRT compared to other patients (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. The nCAG AR length significantly affects the response to TRT in men with hypogonadism and T2DM. The most significant improvements are seen in patients with short nCAG AR.
Introduction. Currently, the classical management of acute urinary retention creates a certain discomfort for the patient and leads to explore alternative method of management, such as intermittent catheterization, including focusing on the patient opinions.
Objective. To assess the preference of high-risk patients for acute urinary retention relative to bladder drainage in the occurrence of acute urinary retention.
Materials & methods. A survey was conducted among 200 ambulatory male patients. All the participants were tested to assess their mental status and ability to perform self-intermittent catheterization before filling out the questionnaire. The questionnaire included questions about the preferred method of bladder drainage for acute urinary retention, as well as factors influencing the patient's choice of self-intermittent catheterization in case of non-recovery. After completing the questionnaire, all the patients were shown a video on self-catheterization and asked to re-take the questionnaire after watching it. This allowed evaluating the impact of the training video on patients' preferences and their confidence in performing self-catheterization.
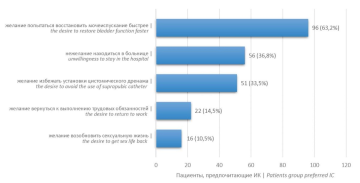
Results. Among the 200 patients, 151 (75.5 %) preferred intermittent catheterization, while 40 (25.5 %) chose an indwelling urinary catheter. Additionally, 152 (76 %) patients opted for intermittent catheterization until the planned surgery, and 48 (24 %) selected a suprapubic catheter. The main factors influencing the patient choice of intermittent catheterization were: the desire to restore bladder function faster (on the first or second day) in 96 (63.2 %) patients; unwillingness to stay in the hospital in 56 (36.8 %); the desire to return to work in 22 (14.5 %); avoiding the use of a suprapubic catheter in 51 (33.5 %). After watching the video, there was a statistically significant change in patients' assessments of their ability to perform self-intermittent catheterization (p < 0.001).
Conclusion. The patient's choice of the intermittent catheterization is significantly influenced by the patient self-confidence in the ability to practice self-intermittent catheterization and the demonstration of the video tutorial. Due to the high efficiency and safety of intermittent catheterization, this method should be introduced into clinical practice based on the proposed algorithm.
Introduction. Infertility affects tens of millions of men and women across the globe. In approximately half of cases, male factors are the cause of infertility. In recent decades, there has been a significant decline in the quality of male ejaculate, which is characterized by reduced sperm concentration and motility. The insufficient diagnostic and prognostic value of routine semen analysis results highlights the challenge of developing effective diagnostic tools and searching for reliable biomarkers of male infertility. One of the most promising approaches may be assessing sperm microRNA expression.
Objective. To study the role of sperm exosomal microRNAs miR-34a and miR-210 in the development of male infertility.
Materials & methods. The retrospective study included 150 men aged 25 – 49 years; of these, 96 patients were diagnosed with idiopathic infertility. The comparison group consisted of 54 fertile men. To assess the structure and motility of sperm, the results of a standard ejaculate study (WHO, 2021) and computer data analysis using MMC Sperm (MMCSoft, St. Petersburg, Russia) software were used. The degree of DNA fragmentation was assessed using the TUNEL method. To analyze the expression of miR-34a and miR-210, quantitative real-time PCR was performed using the miRCURY LNA SYBR Green PCR Kit («Qiagen» GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and the Rotor-Gene Q PCR product detection system («Qiagen» GmbH, Hilden, Germany).
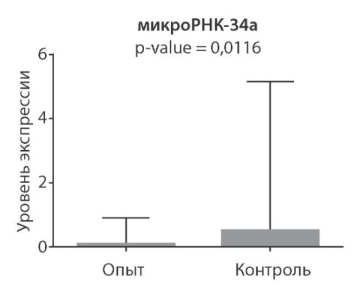
Results. The study of ejaculate using the Computer Assisted Sperm Analysis System (CASA) method revealed a statistically significant relationship between the level of DNA fragmentation of sperm and indicators of the speed of their movement: rectilinear (VSL) (r = -0.522726; p < 0.01), curvilinear (VCL) (r = -0.499096; p < 0.01), along the middle path (VAP) (r = -0.429533; p < 0.01), as well as with the amplitude of lateral head displacement (ALH) (r = -0.294779, p < 0.01), the linearity of their curvilinear path (LIN) (r = -0.385796; p < 0.01), the degree of straight-line movements (STR) (r = -0.268248; p < 0.05) and their progressive mobility (r = -0.411547; p < 0.01). A study of the level of microRNA expression in sperm exosomes revealed a statistically significant decrease in its miRNA-34a pool (p = 0.0116). According to the Chaddock scale, the strength of the correlation between miR-210 expression and the effectiveness of ART programs was moderate (0.437993). The inverse relationship between miR-34a expression and IVF and ICSI results was weak (0.135314).
Conclusion. The analysis of exosomal microRNA-34a and microRNA-210, which are involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis, reveals a direct correlation between their variations and changes in the kinetic and morphological parameters of gametes. It also indicates a relationship with the state of DNA fragmentation. These findings suggest varying levels of gene expression among infertile patients, men with proven fertility, and those undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatments, both with successful and repeated unsuccessful outcomes.
Introduction. The use of oral mucosa in augmentation and replacement urethroplasty is the gold standard for several reasons. Most commonly, the mucous membrane of the cheek, the underside of the tongue or lip is employed. Assessing postoperative complications in the donor area is crucial as it impacts patients' quality of life.
Objective. To evaluate early and late postoperative changes in the donor area after oral graft extraction for urethroplasty
Materials & methods. A retrospective analysis of the results of surgical treatment using oral mucosa from 2017 to 2022 was carried out. The study included 65 patients. The intensity of pain syndrome in the graft sampling area was assessed by patients on a visual analog scale (VAS). The donor area was sutured only in the case of tongue and lip mucosa sampling.
Results. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity was harvested from different sites in 65 patients. Specifically, it was taken from the inside of the cheek in 49 patients (75.38%), from both inner sides of the cheeks in 13 (20.0%), the lower lip in two (3.07%) and the lower surface of the tongue in one (1.54%) patient, respectively. On the first day after surgery, the median pain level according to VAS was 4 points (range: 2 – 7), at the time of discharge — 3 points (1 – 6). After 120 days, a follow-up examination showed a regression of pain symptoms: the median was 0 points (0–1). In the late postoperative period, incomplete opening of the mouth was recorded in two patients (3.07%), cosmetic defect in the donor area in two (3.07%), discomfort during meals in six (9.23%), impaired sensitivity in the donor area in two (3.07%), exacerbation of chronic stomatitis and hypersalivation in two (3.07%) patients, respectively.
Conclusion. The incidence of complications in the donor area is low, but for some patients this can result in a reduced quality of life. Using proper technique when extracting oral mucosa grafts reduces pain and the likelihood of early- and late-stage postoperative complications in this area.
Introduction. Overactive bladder (OAB) remains one of the most difficult-to-treat conditions in neurourology. The number of patients seeking help for OAB symptoms does not decrease each year, while a pathogenetic treatment has not yet been developed. This motivates the search for new approaches.
Objective. To assess the efficacy of the peptide regulator Vezusten for women with idiopathic OAB based on their health condition and urodynamic assessment of bacterial detrusor overactivity (DO).
Materials & methods. A prospective cohort study included 20 patients diagnosed with OAB, which was confirmed by a comprehensive urodynamic study of DO. The patients visited the clinic three times a week. Each patient received ten intramuscular injections of the peptide regulator Vezusten. Within one month after the last injection, the women were given a monitoring voiding diary, a validated Continental Society OAB Symptom Questionnaire, the Overactive Bladder Questionnaire (OAB-q), and a follow-up urodynamic study (UDS).
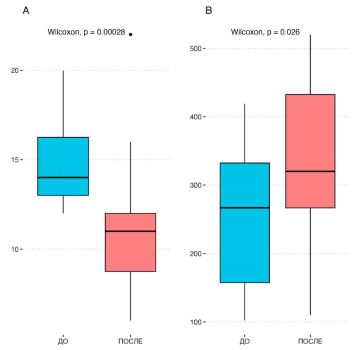
Results. We obtained statistically significant differences in the following indicators: the number of daily urinations according to the urination diary decreased from 14.0 [13.0; 16.3] to 11.0 [8.8; 12.0] (p < 0,001), patient’s episodes of urge incontinence began to be noted for the first time (p = 0.004). At the same time, the urodynamic maximum cystometric capacity (MCC) increased from 267 [158; 332] to 320 [267; 433] ml. Subjectively, participants noted an improvement in the scores of the OAB questionnaire (OAB-q) — the score decreased from 28 [22; 30] to 19 [14; 24] (p = 0.001), and the number of episodes of nocturia decreased from 4 to 2 (p < 0.001). No side effects from therapy were observed in any of the patients.
Conclusion. This study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in subjective symptoms of OAB in DO-women treated with the peptide regulator Vezusten, but further large placebo-controlled studies are required for confirmation.
Introduction. Gleason grading is one of the key parameters for determining the prostate cancer (risk group after receiving the results of a prostate biopsy in addition to the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA). However, an important clinical issue arises from changes in this grading following radical surgery. In some cases, such discrepancies in data can lead to a shift in patient management tactics from radical surgery to active follow-up recommended for patients with low cancer risk.
Objective. To assess the consistency of the results of prostate biopsy and radical prostatectomy with an assessment of possible predictors of increased tumor Gleason grading.
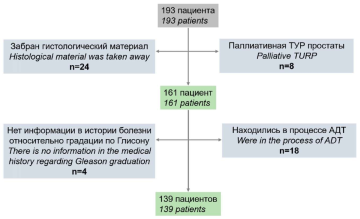
Materials & methods. Between 2019 and 2021, 193 patients with prostate cancer were selected for treatment at the Medical Centre of Moscow State University. Of these, 139 patients were chosen for the final analysis of Gleason tumour grading consistency after biopsy and radical prostatectomy.
Results. The results of prostate biopsy and radical prostatectomy were comparable in 54.7% of patients (n = 76), while the remaining 45.3% (n = 63) showed a change in Gleason gradaing after radical prostatectomy: 29.5% (n = 41) patients showed an increased gradation, and 15.8% (n = 22) — decrease. Most often, the data were consistent for patients with a Gleason score 7: 63.6% for 3 + 4 = 7 and 57.9% for 4 + 3 = 7. The highest percentage of graduation increase was observed for patients from the group 3 + 3 = 6 and amounted to 48%. Cohen's kappa value was 0.351 (p < 0.001), indicating poor consistency between the results of the two studies. The total number of biopsies was associated with an increase in Gleason score after radical prostatectomy (OR = 0.816; 95% CI = 0.680 – 0.978). For example, the odds of Gleason tumour grading decreases by 18.4% when the number of biopsy specimens per unit increases
Conclusion. The concordance of Gleason grading of prostate cancer after prostate biopsy and radical prostatectomy remains poor. The only predictor of improved concordance is the biopsy count, thereby reflecting biopsy quality and encouraging clinicians to move away from sextant biopsies to systematic and targeted biopsies. Increasing the consistency of results can provide more accurate staging and classification of patients according to cancer risk, thereby influencing future management.
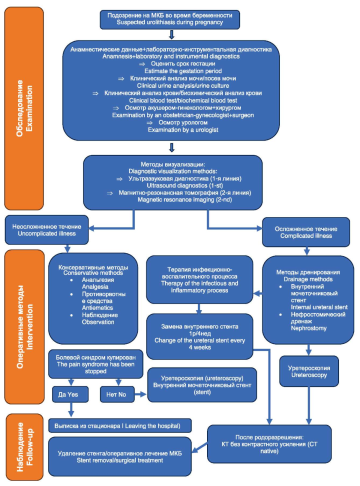
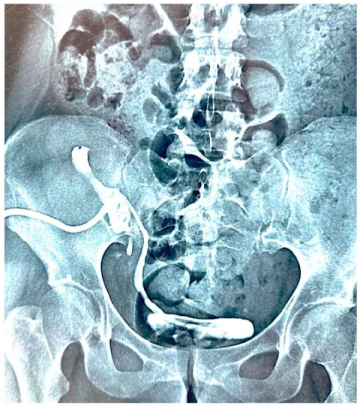
Introduction. Renal colic during pregnancy is a common cause of pain in the lower back. Currently, with a diagnosed kidney or ureter stone, the standard treatment is serial drainage of the urine tract using an internal ureter stent, with replacement of the drainage before delivery, followed by surgery to remove the stone after delivery.
Objective. To study the effectiveness and safety of ureteroscopic interventions in the treatment of urolithiasis in pregnant women in comparison with the method of serial drainage of the upper urinary tract during gestation followed by surgical treatment of urolithiasis 4 weeks after delivery.
Materials & methods. The study group consisted of 119 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of urolothiasis using instrumental diagnostic methods and a gestational age up to and including the 27th week. Two groups were formed based on treatment approaches for urolithiasis: group 1 included 59 patients (49.6%) who underwent surgical removal of the stone; group 2 included 60 patients (50.4%) who underwent internal ureteral stent replacement every 4 – 6 weeks prior to delivery and subsequent ureteroscopy There were no significant differences in age, body mass index, or number of pregnancies between the two groups.
Results. The frequency of complete stone removal in groups 1 and 2 was 96.6 and 96.7%, respectively. The median amount of time spent on urolithiasis treatment in groups 1 and 2 was 60 [45; 72] and 97 [54; 105] minutes, respectively (p = 0.002). Migration of the ureteral stent in group 2 was observed in 13.3% of cases (p = 0.05). Among group 1 patients who underwent ureteroscopic intervention aimed at stone removal, the incidence of internal drainage dislocation was 3.4%. Encrustation of the ureteral stent in groups 1 and 2 was observed among 2 (3.4%) and 17 (28.3%) patients, respectively (p < 0.001). The bed-day (median time in days spent in hospital for drainage replacement and time of surgical treatment of urolithiasis) in groups 1 and 2 was four and eight days, respectively (p < 0.05). The frequency of natural childbirth in groups 1 and 2 was 81.35% and 55.0%, respectively (p = 0.002).
Conclusion. Urolithiasis among pregnant women is a complex multifactorial disease that affects not only the health of the mother, but also the condition of the developing foetus. It is possible to perform surgical treatment with high efficiency and low complication rate, which improves the quality of life.
Introduction. This study is relevant due to the high prevalence of organic brain pathology and the negative influence of urination disorders on the quality of life.
Objective. To analyse the impaired function of lower urinary tracts in patients with organic brain pathology.
Materials & methods. We analysed 607 patients with severe organic brain pathology (105 had traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) and 457 had consequences of acute stroke (AS)). We performed clinical urological examinations. During the survey, attention was paid to the presence of urinary tract pathology at the examining time and anamnesis. Structural changes in the urinary tract were objectively assessed. We objectively assessed structural changes in urinary tracts including prostate adenoma in men, insufficiency of pelvic floor muscles in women and strictures of the urethra or ureters. The degree of the spastic syndrome was assessed with the Ashworth Scale. The neurourological examination included cystometry with the measurement of bladder volume and post-void residual urine. The cognitive status of the patients was assessed with the MMSE (Mini-Mental State Examination) questionnaire. The correlation analysis between the degree of spastic syndrome measured with the Ashworth Scale and urination disorders was performed with Spearman rank correlation.
Results. All patients had neurogenic dysfunction of the lower urinary tract. A combination of bladder retention and emptying disorders was found in 62 men older than 45yo with benign prostate hyperplasia (10,2% of all cases). An impaired accumulation function in history was found in 45 women older than 45yo (7,4% of all observations). The level of spasticity was 3 or 4 points on the Ashworth Scale in patients with TSCI and 2 to 4 points in those with AS. The analysis of correlations between the degree of spasticity and urination disorders showed a moderate relationship (r = 0,4) in patients with TSCI and a medium relationship (r = 0.65) in patients with AS.
Conclusion. Neurogenic dysfunction of the lower urinary tract accompanies patients with severe organic brain pathology throughout their life and requires adequate correction.
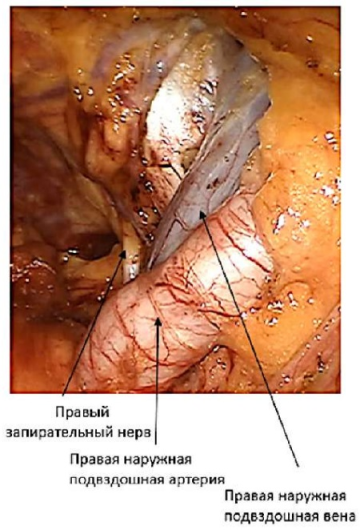
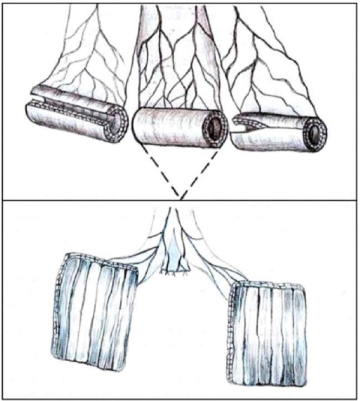
Introduction. The clinical guidelines recommend performing extended pelvic lymph node dissection for patients with intermediateor high-risk cancer prostate. The incidence of lymphocele development reaches 10.3%.
Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficiency of the drug Lymphoblock after radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy.
Materials & methods. The study involved 79 patients with prostate cancer who underwent robot-assisted radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy, that were randomized into three treatment groups: 1. Patients with free peritoneal flap fixed to the pubic bone (n = 26); 2. Patients who received Lymphoblock: during the surgery (n = 26); 3. Control group (n = 27). The median follow-up was 180 d.
Results. In postoperative period lymphocele was diagnosed in 8 (10.1%) patients: group 1 — 2 (7.7%) patients, group 2 — 1 (3.8%), group 3 — 5 (18.5%). Lymphocele had no clinical manifestation in group patients who received Lymphoblock.
Conclusions. Preliminary results of Lymphobloc use indicate that it can reduce the incidence of lymphogenic complications in the postoperative period in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
In recent decades, neural networks have been widely applied in many fields of science and medicine. Accurate and early diagnosis of malignancies is a key challenge in oncology. Neural networks can analyse a wide range of medical data and identify relationships between qualitative and quantitative features. This allows for more precise and timely diagnoses. Moreover, they can be used to predict tumour progression, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and optimise treatment plans for each patient
In oncourology, the use of neural networks offers new perspectives for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various cancer conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive system. This review article explores how neural networks are being used in this field and present research into the use of neural networks for diagnosing, predicting the course and treating urological oncological diseases. The advantages and limitations of using neural networks in this field are demonstrated, and possible directions for future research are suggested. The application of neural networks in oncourology opens new horizons for the development of a personalised approach to diagnosing and treating oncological diseases. Artificial intelligence has the potential to become a powerful tool for improving the accuracy of patient outcome predictions and reducing undesirable side effects of therapy. Introducing neural networks into oncourological practice creates new opportunities for enhancing the work of healthcare organisations and improving the quality of care provided to patients. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
The incidence of extended ureteral strictures has been on the rise in the past decade. This increase is attributed to the growing number of endoscopic surgeries, expanded criteria for surgical treatment of cancer patients, and complications from radiation therapy. When correcting an extended ureteral stricture, if there is a lack of urinary system tissues to replace the defect or if they are involved in the pathological process, replacement reconstruction using a segment of small or large intestine becomes necessary. Options for ureteral reconstructions using ileum and colon sections were discussed, as well as the use of the appendix as a graft. Data on the effectiveness and frequency of postoperative complications were analysed, and the pros and cons of different surgical techniques for ureteroplasty were evaluated. It is necessary to conduct further scientific and practical research and evaluation of long-term results to solve the remaining unclear problems and to inform the doctors of our country about the existence of this pathology.
Introduction. Circumcision is one of the most common surgical procedures for men. WHO programs aimed at reducing HIV transmission have led to the development of various circumcision devices designed to standardize surgical techniques, reduce operating time and the number of complications.
Objective. To examine available data on the efficacy and safety of different methods of device-based circumcision.
Materials & methods. The results of a search in scientific databases such as eLibrary and PubMed were analyzed using the keywords: "circumcision", "circumcision device", and "phimosis". The search was conducted without regard to date or language of publication. After reviewing the literature, 25 articles were selected that best reflect the topic of device-assisted circumcision for further analysis.
Results. Device-based circumcision can significantly reduce surgical time, regardless of the type of device used. Device-based circumcision is the safe treatment method; however, it may have a higher incidence of adverse events compared to the standard circumcision technique. The use of self-suturing devices is preferred over ring devices due to fewer complications, better cosmetic results, and greater patient satisfaction. The article is supplemented with a description of the surgical technique of various options for device-based circumcision.
Conclusion. Device-based circumcision is effective and safe treatment method on an outpatient basis, which successfully competes with conventional circumcision of the foreskin.
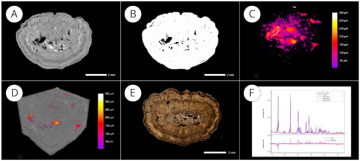
Despite advances in minimally invasive surgery, urolithiasis still recurs within the first five years after the first episode in more than 50% of patients. Researchers continue to search for new crystallisation inhibitors, metaphylaxis strategies and laser sources for stone destruction. Therefore, to achieve these goals, it is necessary to study kidney stones not only as the result of an isolated process of pathological biomineralisation in the human body, but also as a biogenic mineral or rock that obeys universal patterns and has certain properties. Consequently, kidney stones need to be studied using methods that are widely used in the geological sciences for the study of minerals, such as computed microtomography and petrological analysis. In this review, the properties of kidney stones studied using various research methods used in geosciences are discussed. These properties are also considered as new biomarkers of urolithiasis. This review discusses how new data from multimodal stone analysis can be used to develop personalised metaphylaxis and treatment strategies for all types of urolithiasis, including the most common idiopathic calcium-oxalate urolithiasis.
EXCHANGE OF PRACTICAL EXPERIENCE
Introduction. Ureteral strictures are a common urological complication of kidney transplantation. For short narrowings of the ureter, endoscopic operations are used; for extended defects the Boari operation is often performed. An alternative method may be to use a native ureter.
Purpose of the study. To study the results of such operations in four patients.
Materials & methods. We observed four patients with extended ureteral strictures of a transplanted kidney. Among them were three women and one man. Previously, all patients had undergone a cadaveric kidney transplant; the time from the operation itself to the development of stricture ranged from 3 months to 13 years. Initially, all patients underwent percutaneous drainage of the pyelocaliceal system of the transplanted kidney. After stabilization of creatinine values, the pelvis or pyeloureteral segment of the transplanted kidney was isolated using a transperitoneal approach. Further, the lower third of the ipsilateral native ureter was crossed at the level of the iliac vessels. Its upper end was clipped and anastomosis with the pelvis or ureteropelvic junction of the graft was performed.
Results. The procedures were successful in all patients. In three patients the operation was completed using a laparoscopic approach. In one patient in whom extensive ureteral obliteration developed 3 months after transplantation against the background of incompetent ureterocystoneoastomosis and urinary leakage, when the pelvis was isolated, which was covered by the external iliac vein, the latter was injured with bleeding. This required conversion to open access, suturing of the iliac vein defect, further excision of the pelvis and anastomosis with the native ureter. In the post-operative period, the patient developed thrombosis of the iliac and femoral veins below the suturing area, and successful thrombolytic therapy was performed. Nephrostomy drain was removed before discharge and the stent was removed on an outpatient visit 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. Currently the condition of all patients is stable, the graft is functioning, and their diuresis is unchanged, serum creatinine ranges from 106 to 180 μmol/l.
Conclusion. The use of a healthy native ureter is an adequate method of replacement of extended ureteral strictures of the transplanted kidney.
Introduction. The first description of ureteral appendicoplasty was provided by the Italian surgeon Giannettasio in 1901, followed by two German surgeons, Franke and Rydygier. Their work was later included in a review by Melnikoff in 1912. However, it is Melnikoff who is often erroneously credited with performing the first appendicoplasty in the literature. The first ureteral appendicoplasty operation on a 1.5-year-old child in Russia was performed by Soloviev in 1976.
Objective. To report the results of performing operations on replacement of ureteral defects by ureteral appendicoplasty in children.
Materials & Methods. Between 2009 and 2023, a total of 11 surgeries were conducted to replace extended ureteral defects using the appendix technique in four clinics in Russia and the Republic of Belarus. The follow-up included six boys and five girls with an average age of 79 months (ranging from 18 months to 16 years). Six operations were performed by laparoscopic access (mean operative time 356 minutes). Five operations were performed by open access (mean operative time 257 minutes).
Results. Long-term results were assessed between 18 and 192 months in all patients. Urinary tract patency was evaluated based on the results of micturition cystography (in one case, vesicoureteral reflux was recorded) and intravenous urography (one case of stenosis of the distal anastomosis, which was corrected by endoscopic dissection of the stricture site using a fiberoureteroscope). In patients who underwent renoscintigraphy, no progression of renal function decline was observed. In all patients, long-term follow-up showed satisfactory urine passage.
Conclusion. The results of the surgical interventions performed by us are assessed as good. In all 11 cases, the replacement of the extended ureteral stricture using an appendix allowed for the restoration of urinary flow. Furthermore, any complications that arose did not necessitate repeated reconstruction of the urinary tract. Nevertheless, it is important to note that, in our opinion, this technique cannot be considered the method of choice. Rather, it represents a last resort for patients who have undergone multiple previous operations due to severe trauma or oncological diseases. In cases involving ureteral strictures, priority should always be given to an operation involving anastomosis with sufficient ureteral length and minimal tissue tension. We firmly believe that this approach offers the best chance for a successful outcome.
CURRENT STATE-OF-THE-ART
The article discusses issues related to the treatment of patients diagnosed with locally advanced bladder cancer.