ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. The most frequent complications after fine-needle biopsy of the prostate gland are infections and inflammations, which can occur in up to 17 % of cases. Currently, there is no standardised protocol for preventing infectious complications, including the choice of medication, duration, and timing of administration.
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness of Prostatex Plus in combination therapy after prostate biopsy compared with the generally accepted approach to patient management.
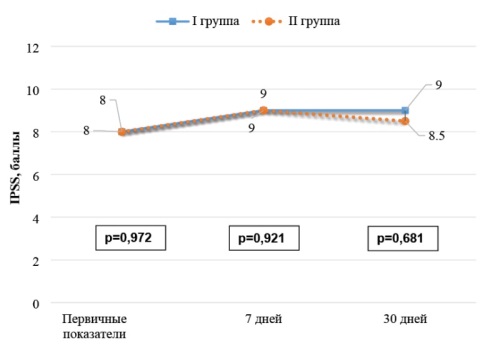
Materials and methods. A prospective study involved 62 men undergoing examination and treatment at the Regional Clinical and Diagnostic Centre «Zdorovie». Transrectal biopsy was performed using a Philips HD 11 ultrasound scanner with an endfire transrectal probe. All patients were divided into two groups: Group 1 — 30 people who received antibacterial therapy plus Prostatex Plus for 20 days. Patients completed standard urological questionnaires IPSS and NIH-CPSI preoperatively, on day 7 and 30.
Results. Group 1 patients showed worsening of symptoms at 7 and 30 days after biopsy compared to preoperative values according to IPSS. Aggravation of symptoms severity according to the NIH-CPSI questionnaire was observed on the day 7, by the day 30 the worsening of symptoms levelled out. Similar results were obtained when analysing the indicators of group 2: both IPSS and NIH-CPSI questionnaire showed worsening of the patients' condition by the post-op day 7, and on the post-op day 30 it was statistically significantly higher in comparison with the primary indicators (p = 0,001). Patients with a history of abacterial prostatitis showed a difference in IPSS scores 30 days after biopsy (p = 0.020). A similar situation was observed regarding pain syndrome according to the NIH-CPSI.
Conclusion. Patients with abacterial prostatitis who received Prostatex Plus showed statistically significant improvement in the symptomatology of urinary disorders and pain syndrome than patients who received antimicrobial therapy alone.
Introduction. Varicocele is one of the main causes of subfertility in men with primary and secondary infertility.
Objective. In this study, we compared the initial semen parameters and the effectiveness of varicocelectomy in men with primary and secondary infertility.
Materials & methods. 100 men suffering from primary infertility (PI) and secondary infertility (SI) and having varicocelectomy were recruited. Patients were divided into 2 groups. Group 1 included 58 men with PI and the group 2 42 men with SI. Preoperative clinical characteristics and semen parameters before and after varicocelectomy were analyzed and compared between groups.
Results. Analysis revealed that the mean age of patients of the group 1 was significantly lower (p < 0,001) and duration of infertility was accurately shorter (p < 0,01) than those of group 2. Main semen parameters increased significantly in group I (e. g., sperm concentration increased by 50 %, from 62,2 ± 8,7 to 93,5 ± 10,0 M/ml and total motile sperm count increased by 113 %, from 76,7 ± 17,1 to 163,4 ± 27,8 M p < 0,05), while in group 2 only % of progressive motile sperm increased significantly (by 107 %, from 13,5 ± 2,6 to 28,0 ± 5,2 % p < 0,05). We identified significant difference in varicocelectomy efficacy between group 1 and group 2 in change of total motile sperm count (by 113 % vs. 74 % respectively, p < 0,01). We also revealed discrepancy between groups in correlation ratio (r) between initial and post-surgical percentage of progressive motile sperm.
Conclusions. Patients with SI were older and had longer infertility period. Varicocelectomy resulted in significant semen parameters improvement in patients with PI. In patients with SI only a percent of progressively motile sperm improved significantly. It shows that male age and infertility duration may negatively affect varicocelectomy outcomes in male subfertility treatment.
Introduction. In recent years, there has been a shift in the perspective on the pathogenic basis of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the lower urinary tract. This change is due to the paradigm of non-sterility of urine and the urinary tract. As a result, the long-held view of the etiological structure, pathogenesis, and methods of diagnosis and treatment is being revised.
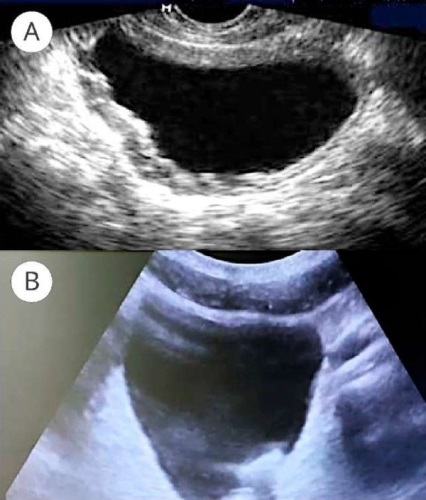
Objective. To study ultrasound changes in the bladder wall of patients with chronic recurrent cystitis (CRC) depending on the etiologic factor.
Materials & Methods. The prospective study involved 177 sexually active women aged 20 – 45 years who had previously been diagnosed with CRC during an exacerbation. Depending on the etiologic factor, they were divided into three groups: Group 1 (n = 96) — papillomavirus CRC (PV-CRC), Group 2 (n = 70) — bacterial CRC (B-CRC), and Group 3 (n = 11) — candidal CRC (C-CRC). To perform a bladder ultrasound, scanner «Philips En Visor» CHD was used using in the B-mode.
Results. The study data analysis on the bladder volume in patients of groups 1 and 2 showed significant differences from the results of group 3. When assessing the ultrasound data for residual urine, no clinically significant deviations were found in any of the groups. Regarding the bladder wall thickening, there are reliable differences between the studied groups: in most patients from group 1 and almost all patients in group 3, the bladder wall thickness exceeded standard values.
Conclusion. CRC is a multi-causal disease, and the etiological factor determines its pathogenetic basis. Ultrasound examination of the bladder can serve as a screening method for CRC, providing clues about the nature of infectious and inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Introduction. Injury to the testicular artery during microsurgical subinguinal varicocelectomy (MSV) results in testicular atrophy in 20 – 40% of cases. The use of techniques that improve visualization of the testicular artery could increase the efficacy and safety of MSV.
Objective. To evaluate the effect of intraoperative Doppler control (IDC) on the outcomes of microsurgical subinguinal varicocelectomy.
Materials & methods. Retrospective cohort study. The study included 101 patients with clinical left-sided varicocele who underwent surgical treatment at the «Mother and Child Yaroslavl» clinic between January 2022 and November 2023. Fifty-two patients underwent standard microsurgical subinguinal varicocelectomy (MSV group), while 49 patients had MSV with intraoperative Doppler control (MSV + IDC group). The intraoperative Doppler control was performed using the Minimax-Doppler-K 20 MHz («SP Minimax», St. Petersburg, Russia). Intraoperatively, the number of preserved arterial and ligated venous stems was counted. Three months after the surgery, the presence of postoperative complications and changes in pain syndrome were assessed.
Results. The average surgery time was 79.5 ± 11.3 minutes in the MSV group and 75.4 ± 12.1 minutes in the MSV + IDC group (p = 0.083). Multiple branches of the testicular artery were observed in 77.6 % of patients in the MSV + IDC group compared to 36.5 % in the MSV group (p < 0.001). The mean number of ligated veins was 16.7 ± 2.9 in the MSV + IDC group versus 15.0 ± 3.8 in the MSV group (p = 0.014). No differences were found in the number of preserved lymphatic vessels between the groups. Three months after surgery, no complications such as varicocele recurrence, hydrocele, or testicular atrophy were reported. Pain relief three months post-surgery was noted in 66.7% and 91.7 % of patients with preoperative pain syndrome in the MSV and MSV + IDC groups, respectively (p = 0.047).
Conclusion. The utilisation of intraoperative Doppler control during microsurgical subinguinal varicocelectomy permits the preservation of a greater number of branches of the internal testicular artery, the ligation of a larger number of veins, and the attainment of superior outcomes with respect of post-operative pain relief.
Introduction. Percutaneous nephrolithotripsy is an important minimally invasive method for treating kidney stones. It is appreciated for its low injury rate and quick recovery. However, one of the most serious complications that can occur after this procedure is calculous pyelonephritis. The timing and safe removal of nephrostomy drainage in the postoperative period remain a significant concern for urologists.
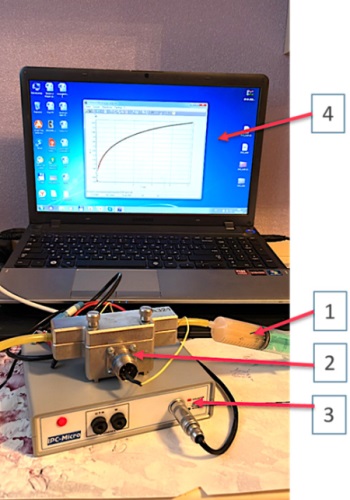
Objective. To determine the possibility of using joulemetry and monitoring urinary IL-8 levels to diagnose stone-related pyelonephritis activity following percutaneous nephrolithotripsy.
Materials & methods. The study involved 220 patients with kidney stones who had percutaneous nephrolithotripsy at the SSMU Urology Clinic in 2022 – 2023. The patients were aged between 25 and 65 years, including 135 women (61.3 %) and 85 men (38.7 %). The control group consisted of 30 healthy people aged 24 to 67 years: 18 women (60 %) and 12 men (40 %). After surgery, electrochemical urine examination using the joulemetric method according to a patented technique was performed for patients with stone-related pyelonephritis and for those in the control group.
Results. When analysing the urine IL-8 level, leukocyturia in the urine test, and the current operation based on joulemetry data, we observe a significant increase in all studied parameters on day 1 compared to the control group (p > 0.05). The values of the studied indicators reach their peak range by day 3 and return to those of the control group by day 5. At the same time, even if there is no leukocyturia on day three, the values of the current parameter and the urine IL-8 level remain elevated in most patients.
Conclusion. Joulemetry helps to diagnose the activity of stone-related pyelonephritis in the postoperative period. This is confirmed by general clinical examinations and the determination of urine IL-8 as a marker of inflammation. Using this method allows optimising the timing of drainage removal after surgery.
REVIEWS ARTICLE
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most prevalent forms of male malignancies globally, ranking second in terms of incidence and sixth in terms of mortality. Low-dose-rate brachytherapy (LDRT) represents a treatment modality for PCa, involving the implantation of permanent radioactive sources into the prostate tissue. The isotopes predominantly utilised are I–125 and Pd–103. LDRT demonstrates high rates of biochemical and clinical relapse-free survival, with cancer-specific and overall survival rates comparable to those achieved through radical prostatectomy. Despite the advantages associated with LDRT, evidence has accumulated regarding the potential complications accompanying this treatment approach, including sexual dysfunction and erectile dysfunction. Sexual satisfaction constitutes a critical concern for men undergoing PCa treatment. It is essential that both the patient and the healthcare provider prioritise not only erectile function but also the preservation of sexuality in its entirety.
The present study endeavours to evaluate the accumulated material on the topic of diagnosing and treating sexual dysfunctions following low-dose-rate brachytherapy (LDRT).
The analysis encompassed articles by foreign and domestic authors published between 2014 and 2024, as well as fundamental articles and literature dating back earlier. These works were devoted to sexual dysfunction, assessment, and rehabilitation of sexual function in patients with PCa who underwent LDRT. Our review confirmed the existing necessity for a detailed study of rational methods for diagnosing sexual dysfunctions prior to selecting a treatment method, as well as the possible prevention of disorders after LDRT. It is also essential to develop sexual and penile rehabilitation strategies following LDRT for PCa, which is currently widely employed.
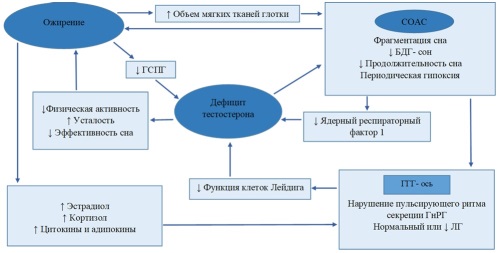
Healthy sleep is essential for human health. It performs important biological functions and positively affects health and longevity through the metabolic and endocrine systems. Sleep disorders are serious clinical conditions that can reduce life expectancy and quality of life. Sleep deprivation, circadian rhythm disruption, and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome are widespread in modern society and can accumulate over time. The adverse cardiometabolic and reproductive consequences of insufficient sleep are becoming increasingly evident. In men, persistent sleep deprivation and sleep disorders can lead to several health problems, including hypogonadism. This is because testosterone levels increase during sleep and peak during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Consequently, persistent disruptions in sleep architecture and loss of sleep can lead to a decrease in male sex hormone levels. On the other hand, low testosterone levels can worsen sleep quality and efficiency and lead to nighttime awakenings. This article reviews and discusses the relationship between sleep disturbances and testosterone deficiency, as well as methods for correcting these conditions.
CLINICAL CASES
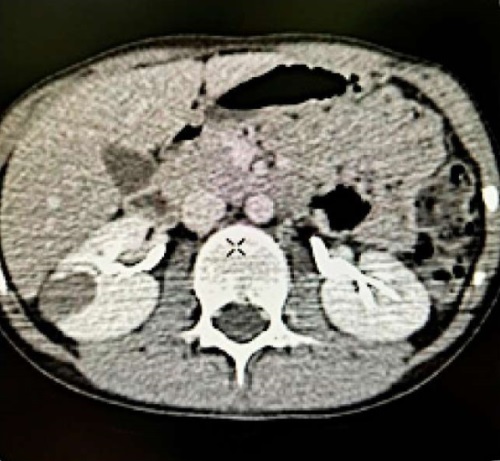
Kidney tumours are among the most common solid malignant pathologies in children, accounting for 6 % of all childhood malignancies. About 89 % of these tumors are nephroblastomas (Wilms' tumors). Renal cell carcinoma in children is extremely rare, representing less than 1 % of all renal tumor pathologies in childhood and adolescence. Given the rarity of this pathology in children and the small size of neoplasms in the renal parenchyma, differential diagnosis between renal cancer and cystic renal lesions can be challenging. This clinical case describes a successful treatment case of a 14-year-old patient with a detected renal parenchymal mass, subsequently diagnosed as renal cell carcinoma.
Introduction. R Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common type of sarcoma in children, which can affect the genitourinary system. Treatment protocols for patients with rhabdomyosarcomas of the prostate and bladder differ, particularly regarding the need, extent, and timing of surgical treatment. Currently, there are two main treatment protocols for rhabdomyosarcomas of the bladder and prostate: the European (SIOP), approved by the International Society of Pediatric Urology, and the North American one, supported by the Children's Oncology Group (COG). Both protocols share the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy after biopsy of the lesion to clarify the diagnosis. However, the North American protocol recommends further radiotherapy to prevent dysfunction of pelvic organs after surgery, while the European protocol advocates for surgical correction after chemotherapy. Moreover, there is no unified approach to selecting the surgical treatment method. Specialists use both organ-preserving and organ-sparing operations.
Objective. To describe a clinical case of using robotic cystoprostatectomy as a radical treatment method for a patient with prostate rhabdomyosarcoma.
Clinical case. The paper describes a clinical case of a 13-year-old boy with prostate rhabdomyosarcoma who received staged chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Since residual tumor tissue remained, the child underwent radical surgery, including robotic cystoprostatectomy with the creation of bilateral ureterostomy.
Conclusion. In this case, it was decided to opt for a radical surgical treatment method — cystoprostatectomy with removal of the bilateral ureterostomy. This decision was based on the presence of residual tumor tissue according to MRI data, as well as after numerous blocks of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This approach allowed the patient to undergo an adjuvant course of chemotherapy without the risk of postoperative complications, such as infection of the intestinal reservoir in cases where it is created simultaneously with cystoprostatectomy.
EXCHANGE OF PRACTICAL EXPERIENCE
Introduction. Bladder cancer ranks among the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) constituting most cases. Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy is a cornerstone in NMIBC management, reducing recurrence and progression rates. However, patient compliance remains a challenge due to adverse effects, discomfort, and the demanding treatment regimen.
Objective. To evaluate the tolerability and complications associated with intravesical BCG therapy and to assess the efficacy of strategies implemented to enhance patient compliance and mitigate dropout rates.
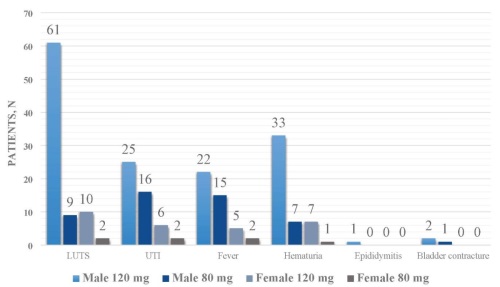
Materials & Methods. A retrospective analysis was conducted on 163 patients diagnosed with NMIBC who underwent intravesical BCG therapy at our institution from August 2018 to December 2022. Data included patient demographics, tumour stage, BCG dosage, therapy duration, and adverse effects. Compliance strategies involved dedicated outpatient clinics, exclusive resident and nursing staff, and proactive toxicity management. Dosage modulation to 80 mg was employed for patients unable to tolerate the standard 120 mg BCG dose.
Results. Among the cohort, 86 % were male, with 63 % being chronic smokers. Recurrence occurred in 16 % of patients, with 4 progressing to muscle-invasive disease (T2). BCG-related toxicity (Grade 1) was observed in 50 % of patients, with conservative management proving effective. A dose reduction to 80 mg was necessary in 17 % of patients, improving tolerance in the majority. Key compliance strategies significantly reduced dropout rates, with 80 % of patients completing the full course of therapy.
Conclusion. Strategic interventions such as dosage modulation, dedicated clinic days, and comprehensive patient counselling markedly improved adherence to intravesical BCG therapy, reducing adverse effects and dropout rates. These findings underscore the importance of tailored strategies to enhance compliance, ultimately improving NMIBC management and patient outcomes.
CURRENT STATE-OF-THE-ART
Cystitis is a common disease worldwide, with up to 36 million cases recorded annually in Russia alone. In 10 % of patients, the condition transforms into a chronic recurrent form. Up to 30 % of visits to outpatient urologists are related to acute or recurrent cystitis. The prevalence of chronic cystitis in women is closely linked to the anatomical and topographical characteristics of the genitourinary system, the presence of gynecological diseases, and hormonal status. Effective treatment for acute or chronic cystitis involves complex therapy, with the key to success lying in the appropriate selection of antibacterial drugs. The current study aimed to analyse the literature data on the effectiveness of Furamag® in the complex treatment of patients with acute and chronic cystitis. To achieve this objective, we conducted a search for articles in scientific databases such as PubMed, Medline, minzdrav.gov.ru, and elibrary.ru using the following keywords: «urinary tract infection», «acute cystitis», «chronic cystitis», «furazidine», «potassium furazidine». Based on the results of our search, we concluded that Furamag® has been successfully used for a long time in the treatment of both acute and chronic cystitis, demonstrating high efficacy and good patient tolerance. This explains its widespread use in routine clinical practice among urologists, gynecologists, and therapists.
Transversus abdominis plane block (TAP block) is a regional anesthesia technique used as part of multimodal postoperative analgesia for a wide range of abdominal surgical procedures. However, the use and effectiveness of this technique in urological surgeries are not well documented in Russian literature. We conducted a literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Knowledge, and Cochrane Library databases to evaluate the effectiveness of using transversus abdominis plane blocks compared to other anesthesia techniques in oncourological surgery. It has been determined that transversus abdominis plane block, serving as an integral component of multimodal anesthesia in patients undergoing oncourological procedures, significantly curtails the reliance on opiates both during and following surgery. Moreover, it mitigates the intensity of pain syndrome in the postoperative phase and fosters a swifter and more comprehensive recovery process for patients.